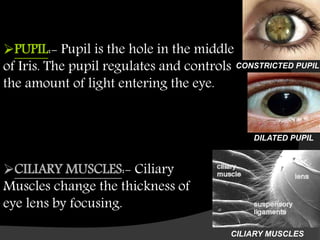
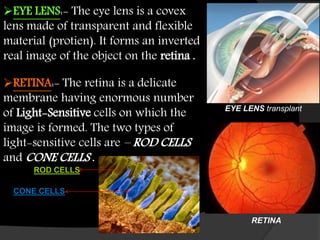
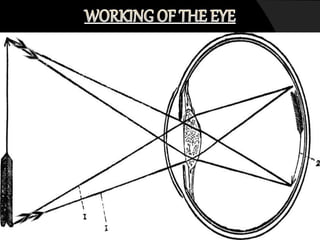
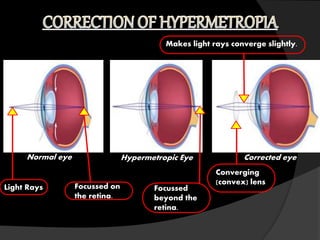
The human eye allows us to see the world through refraction of light. It contains structures like the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina and optic nerve. Light enters through the cornea and passes through the pupil, where it is focused by the lens onto the retina. The retina contains light-sensitive cells that generate signals sent to the brain via the optic nerve, allowing us to see. The lens adjusts its curvature for accommodation to focus on near or far objects. Defects in refraction can cause issues like myopia, hyperopia or presbyopia later in life.