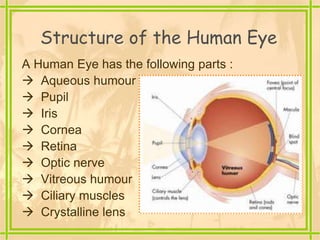
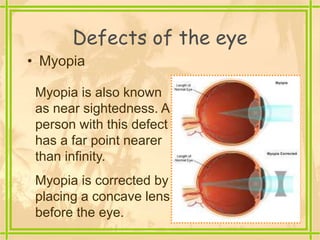
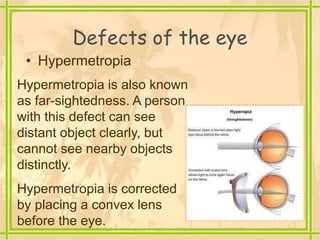
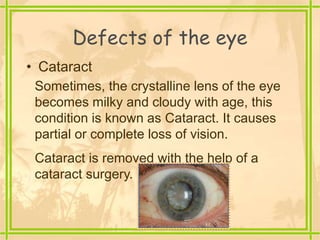
The document discusses the structure and functioning of the human eye, highlighting its importance in vision. It explains the eye's anatomy, the process of image formation, the power of accommodation, and various defects such as myopia, hypermetropia, presbyopia, and cataracts, along with their corrections. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of eye donation in helping those who are visually impaired.