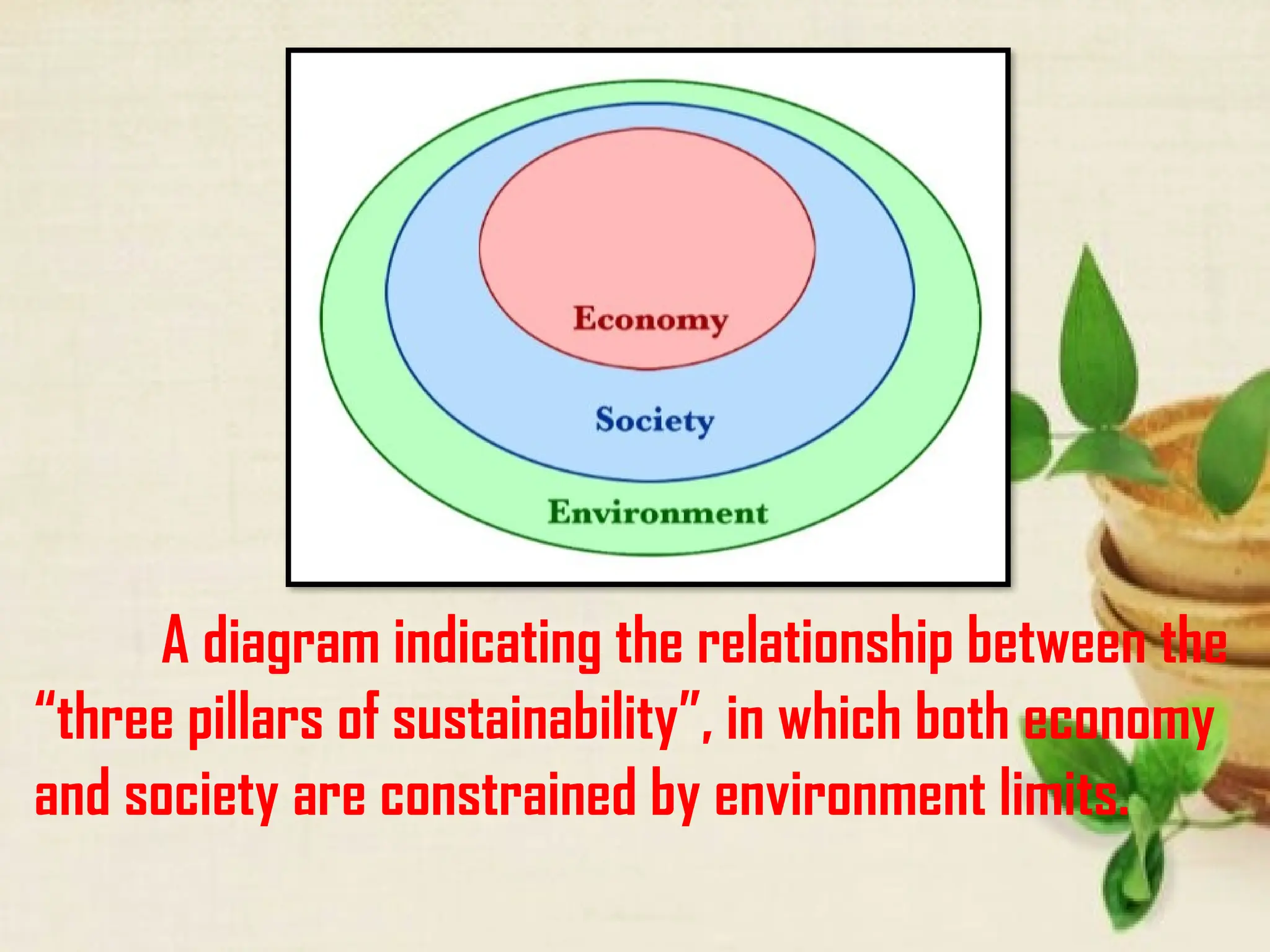
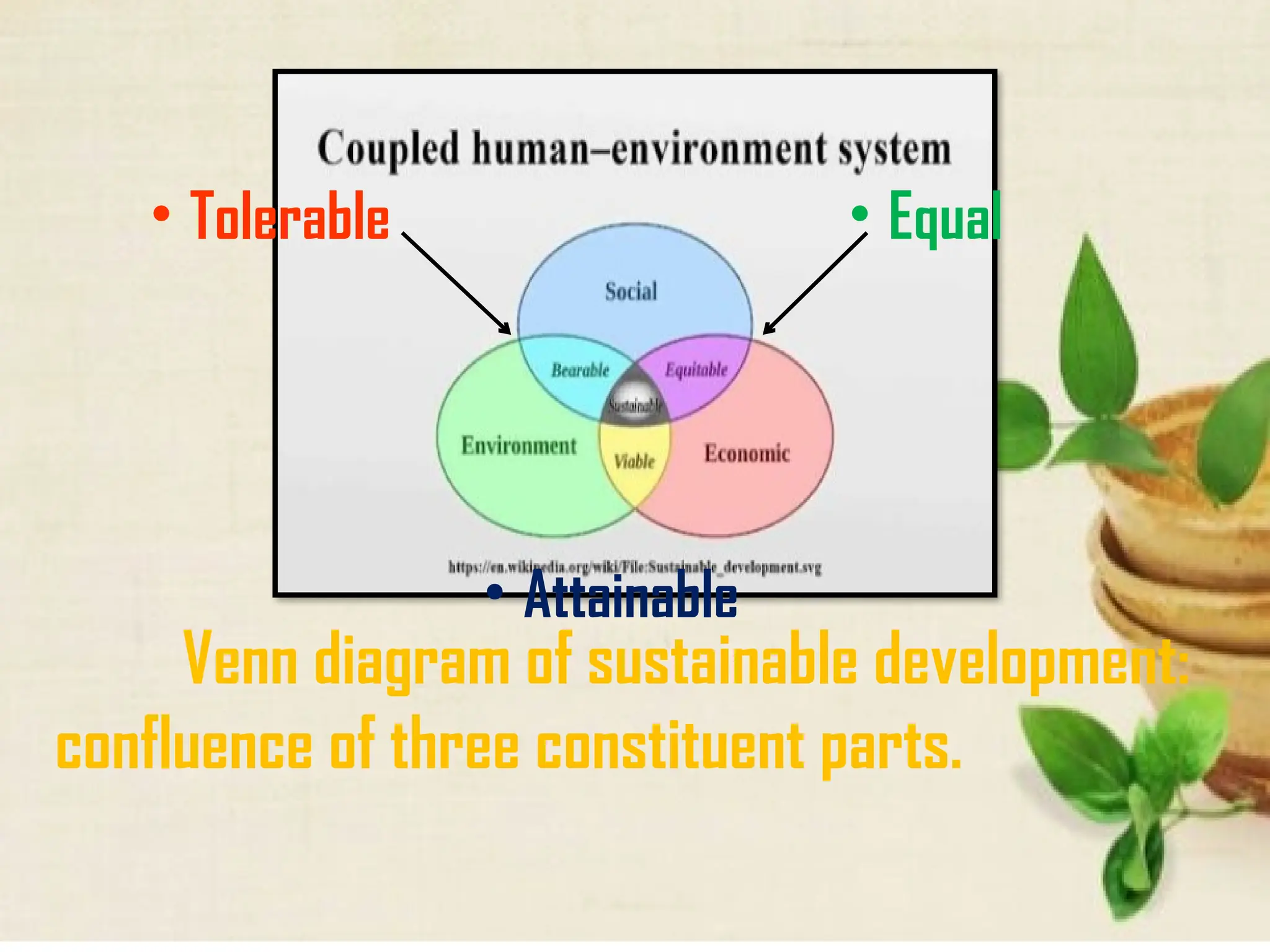
The document discusses the complex interactions between humans and their environment, emphasizing the concept of the human-environment system, which studies the reciprocal relationships linking human and natural subsystems. It outlines environmental challenges posed by human activities, such as overpopulation and intensive agriculture, and calls for sustainable practices to mitigate negative impacts. Furthermore, it highlights the strengths and weaknesses of the human-environment framework in addressing ecological issues.