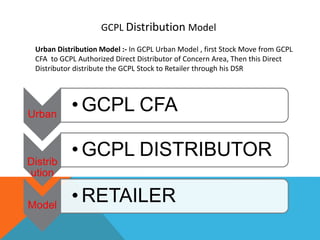
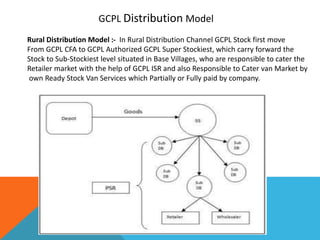
This document presents a hub and spoke distribution model used by GCPL in rural areas. In this model, GCPL sends products from central filling agents to authorized super stockists, who then send the products to sub-stockists located in villages. The sub-stockists are responsible for supplying retailers. The super stockists act as hubs, receiving products and dispatching them to the sub-stockists, which act as spokes. Rural sales representatives help the sub-stockists with retailing and ensuring regular supplies from the super stockists. The document defines billing efficiency as the percentage of sub-stockists receiving products from a super stockist, and distribution efficiency as the percentage of brands billed to a sub-stockist