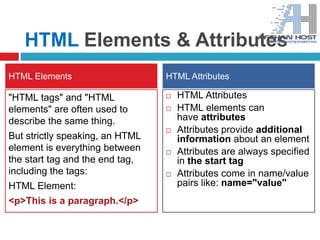
The document provides an introductory overview of HTML, explaining its purpose as a markup language for web pages and detailing its components such as tags, elements, and attributes. It describes the function of web browsers in rendering HTML documents and how to use tags for headings, paragraphs, and text formatting. Additionally, it covers the syntax and structure of HTML tags, including the importance of start and end tags.