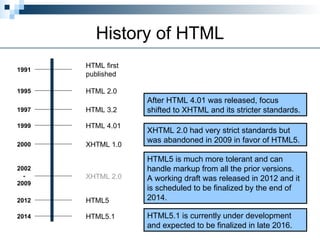
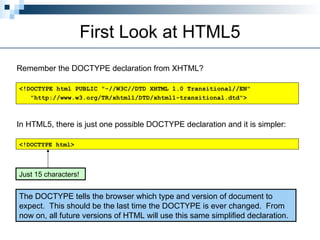
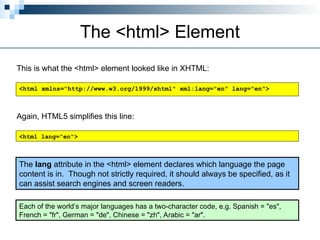
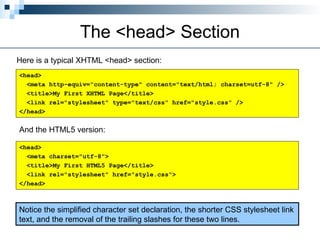
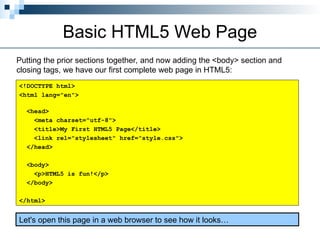
HTML5 is the latest version of HTML, released as a working draft in 2012 and aimed to be finalized by 2014, incorporating features from earlier versions and focusing on a more tolerant markup system. It aims to support existing web pages, reduce reliance on external plugins, improve semantic definitions, and facilitate universal rendering across devices while introducing new elements and features like built-in audio and video support. Despite being a work in progress, it simplifies many coding aspects, including the doctype declaration and character sets, making web development more efficient.