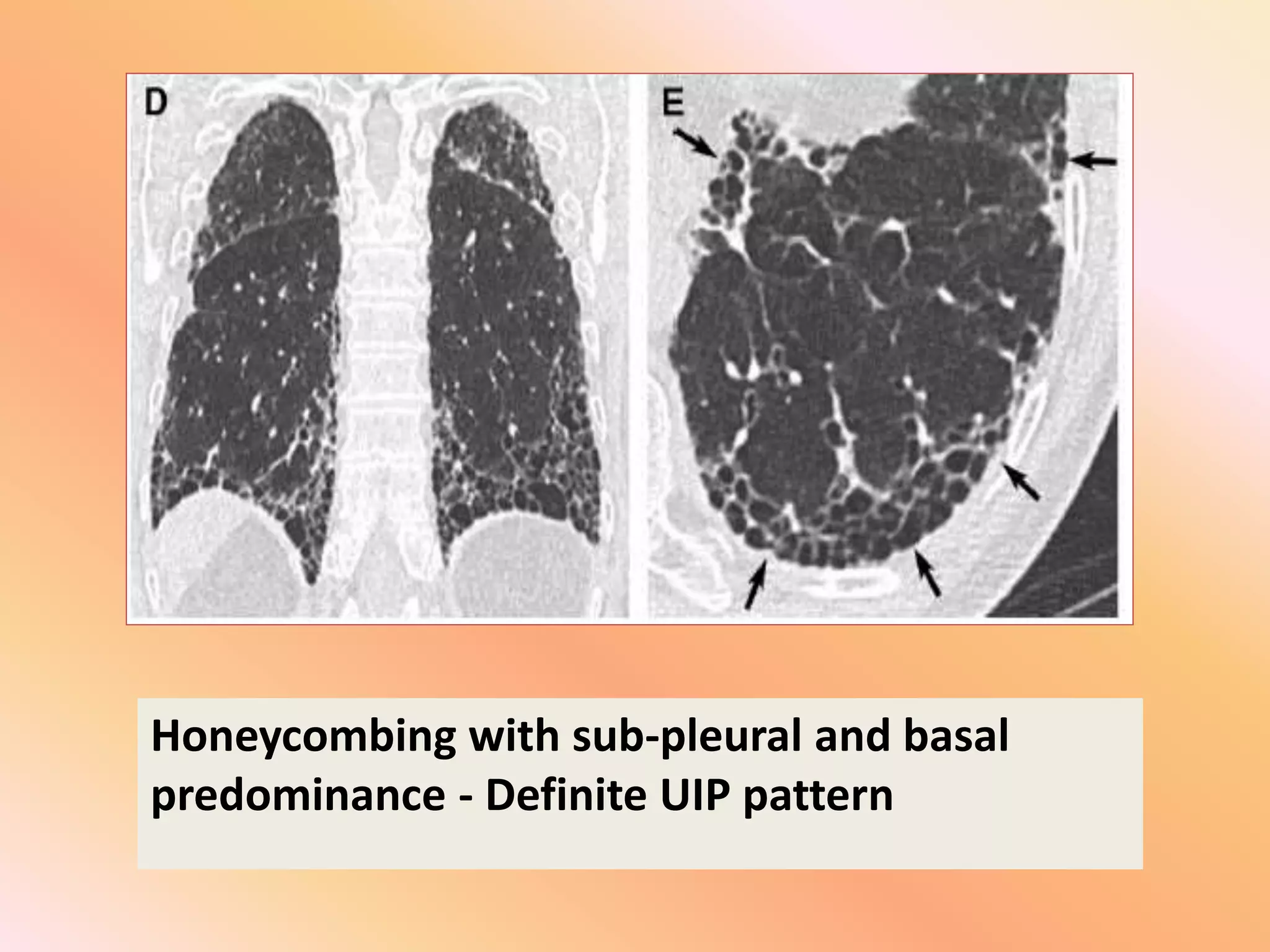
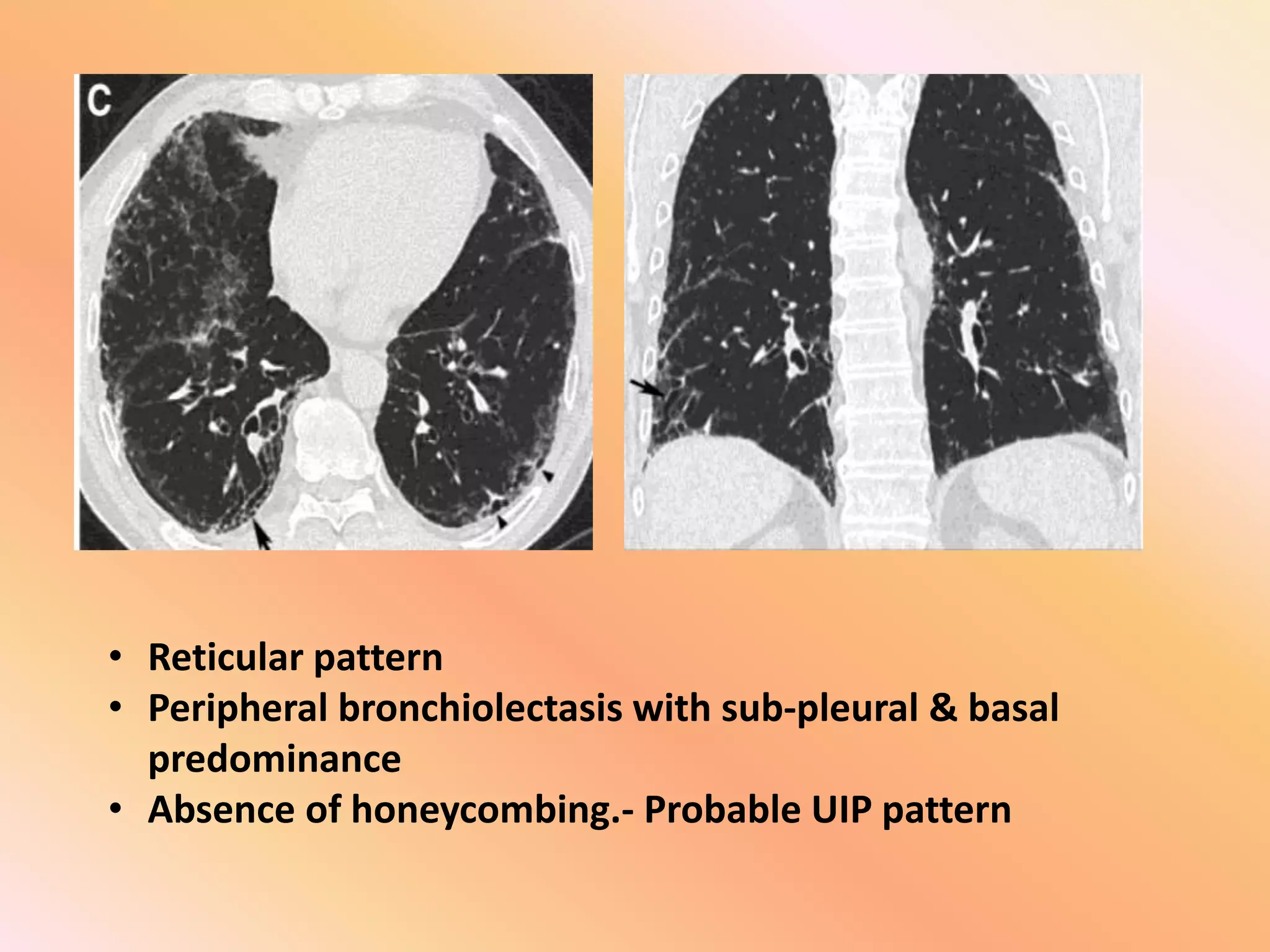
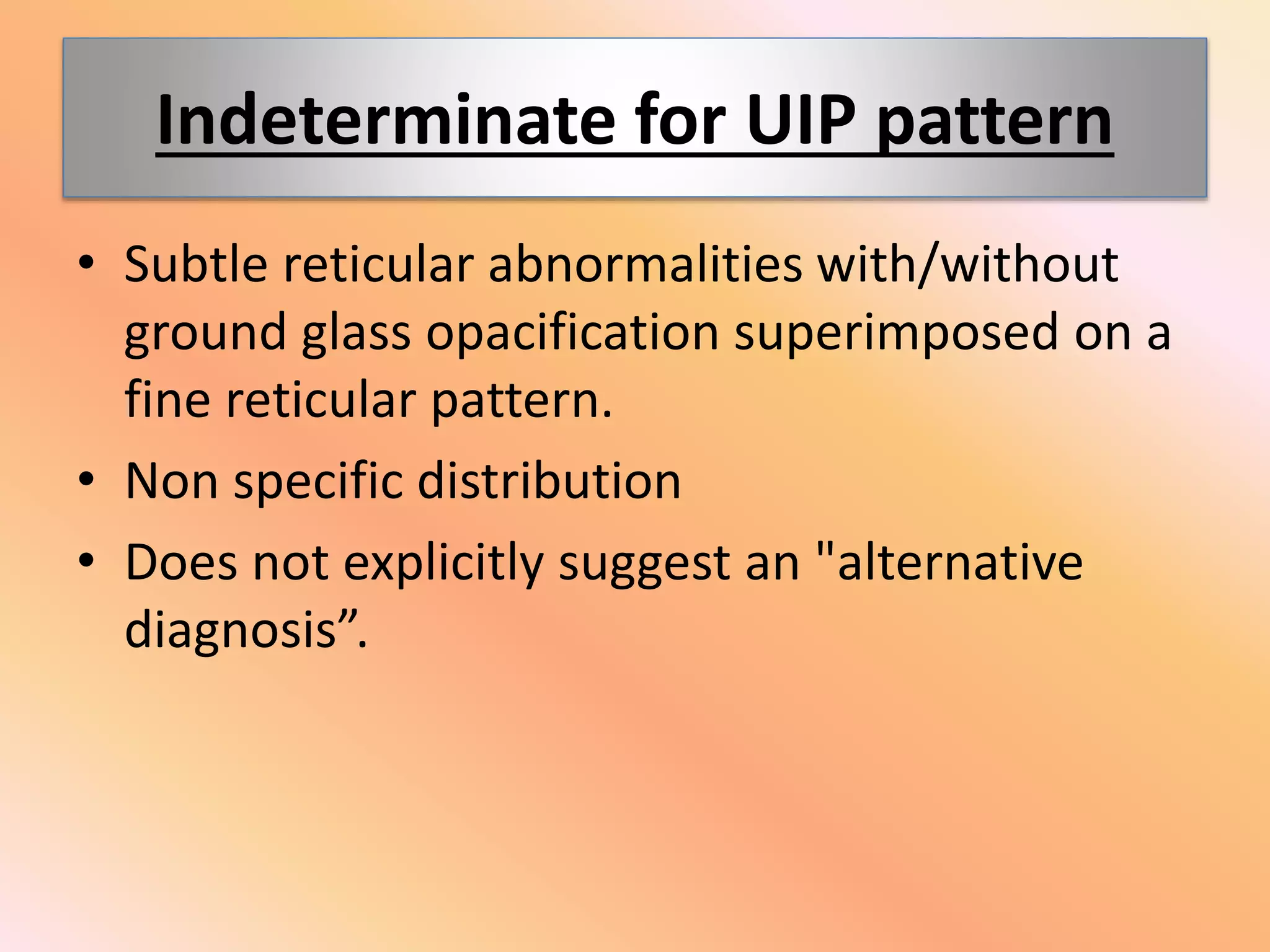
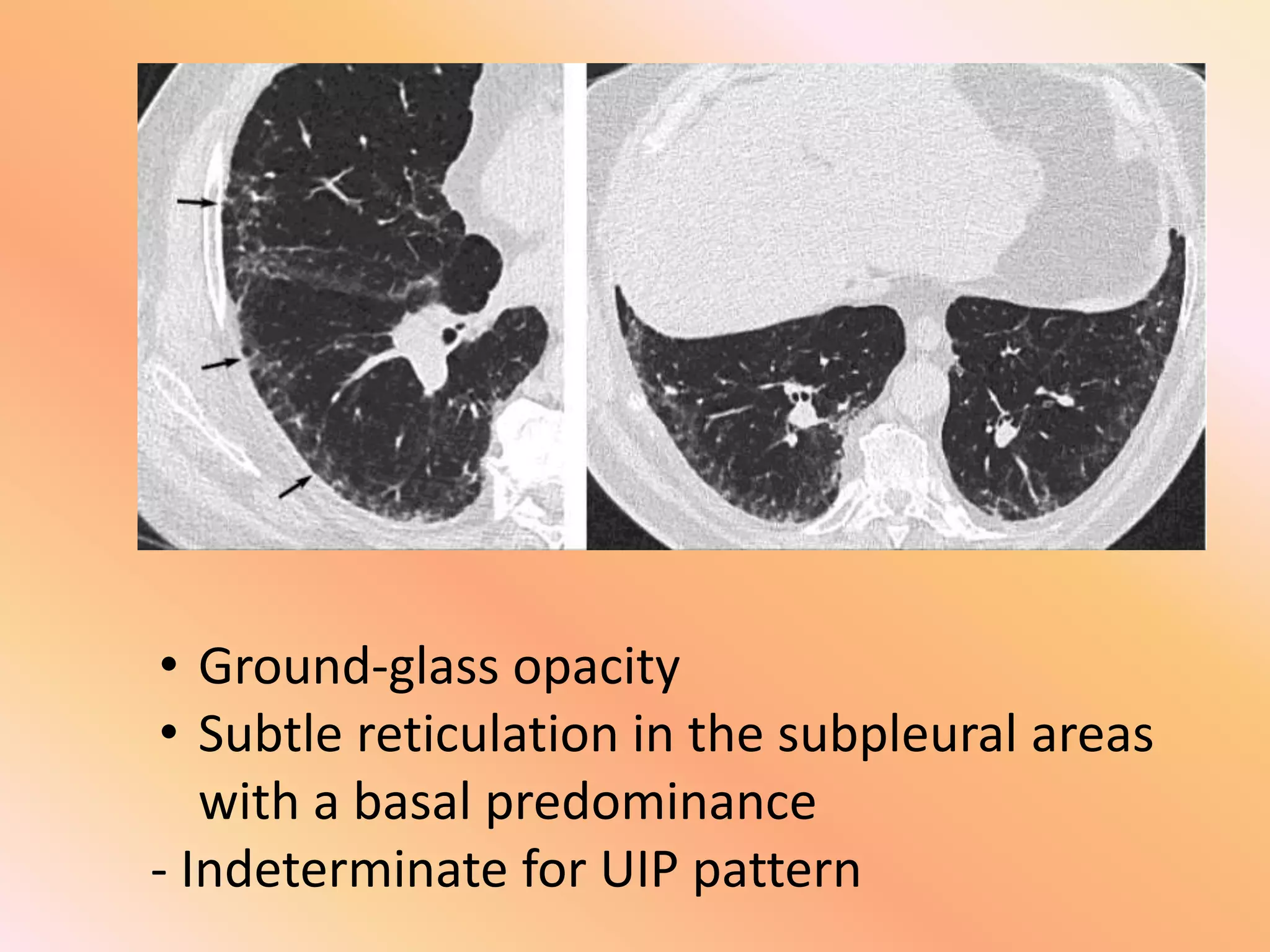
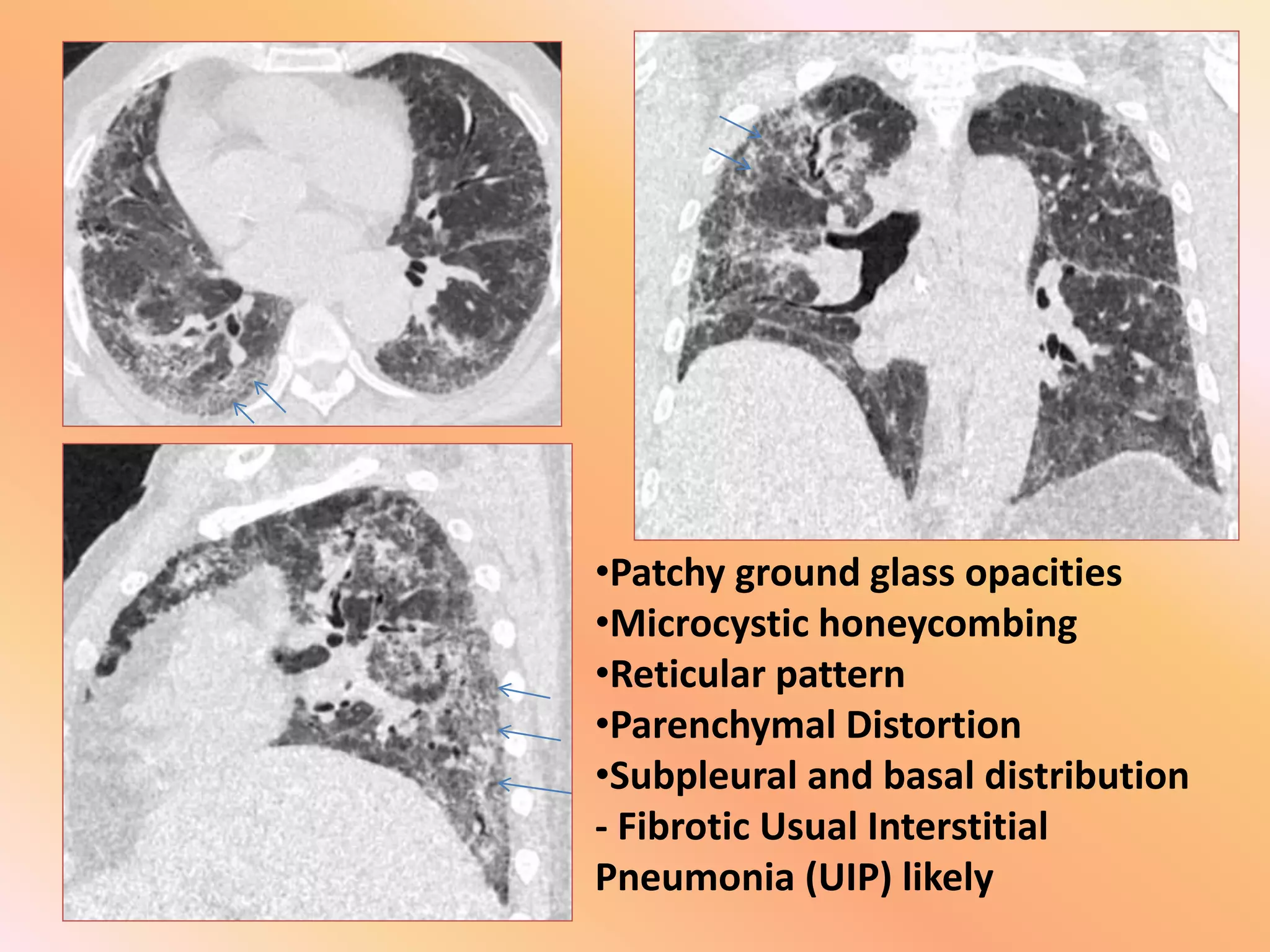
This document summarizes the key radiological patterns seen in usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) on HRCT scans. It outlines the definitive, probable, and indeterminate patterns for UIP as defined in the 2018 ATS/ERS classification. The definitive UIP pattern shows honeycombing with subpleural and basal predominance. The probable pattern shows reticular abnormalities and traction bronchiectasis or bronchiolectasis in the typical distribution without honeycombing. An indeterminate pattern shows subtle reticulation that does not suggest an alternative diagnosis. Examples of alternative diagnoses are also provided. A case presentation is given of a 64-year-old male smoker showing imaging findings consistent with fibrotic UIP.