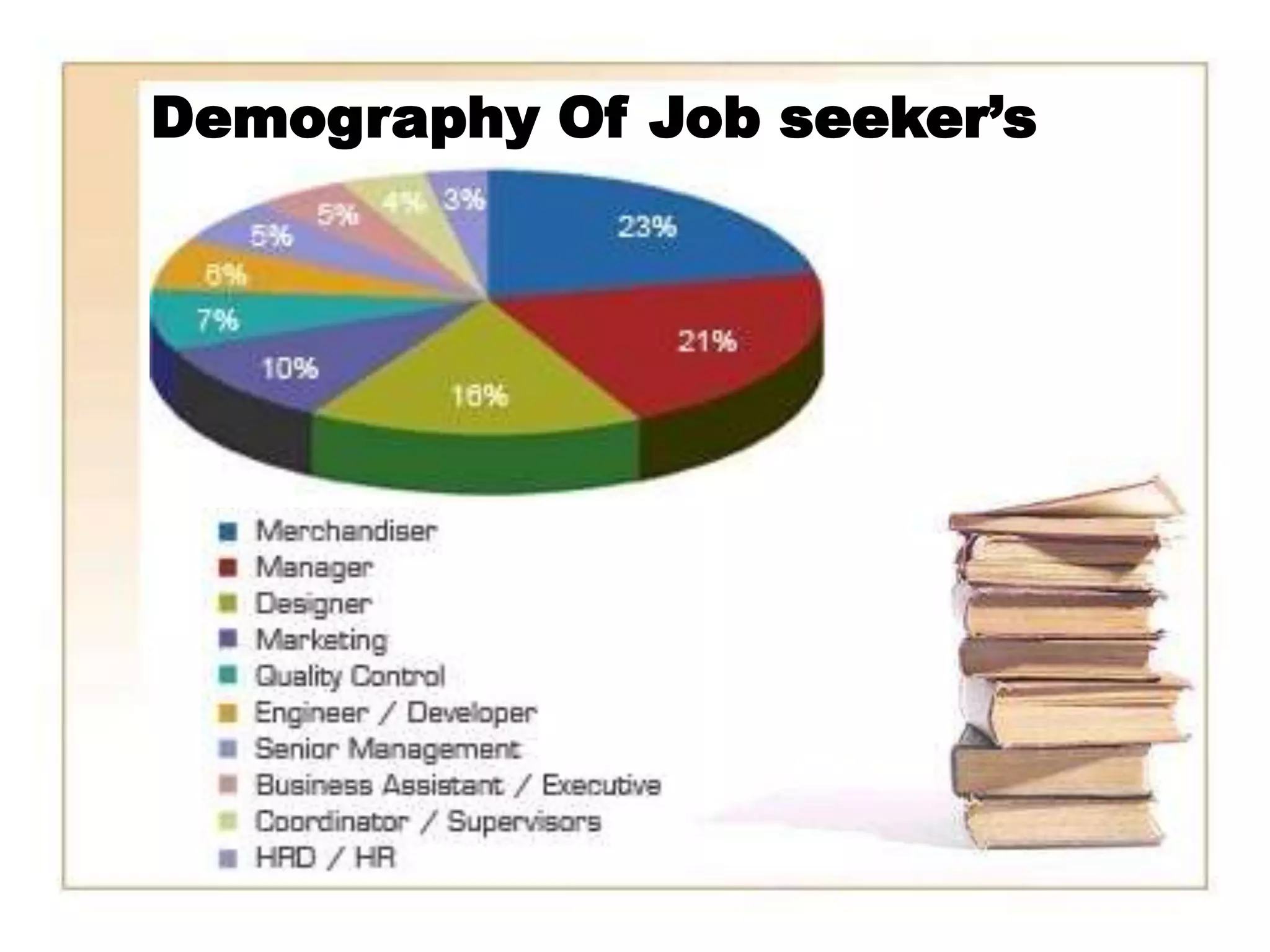
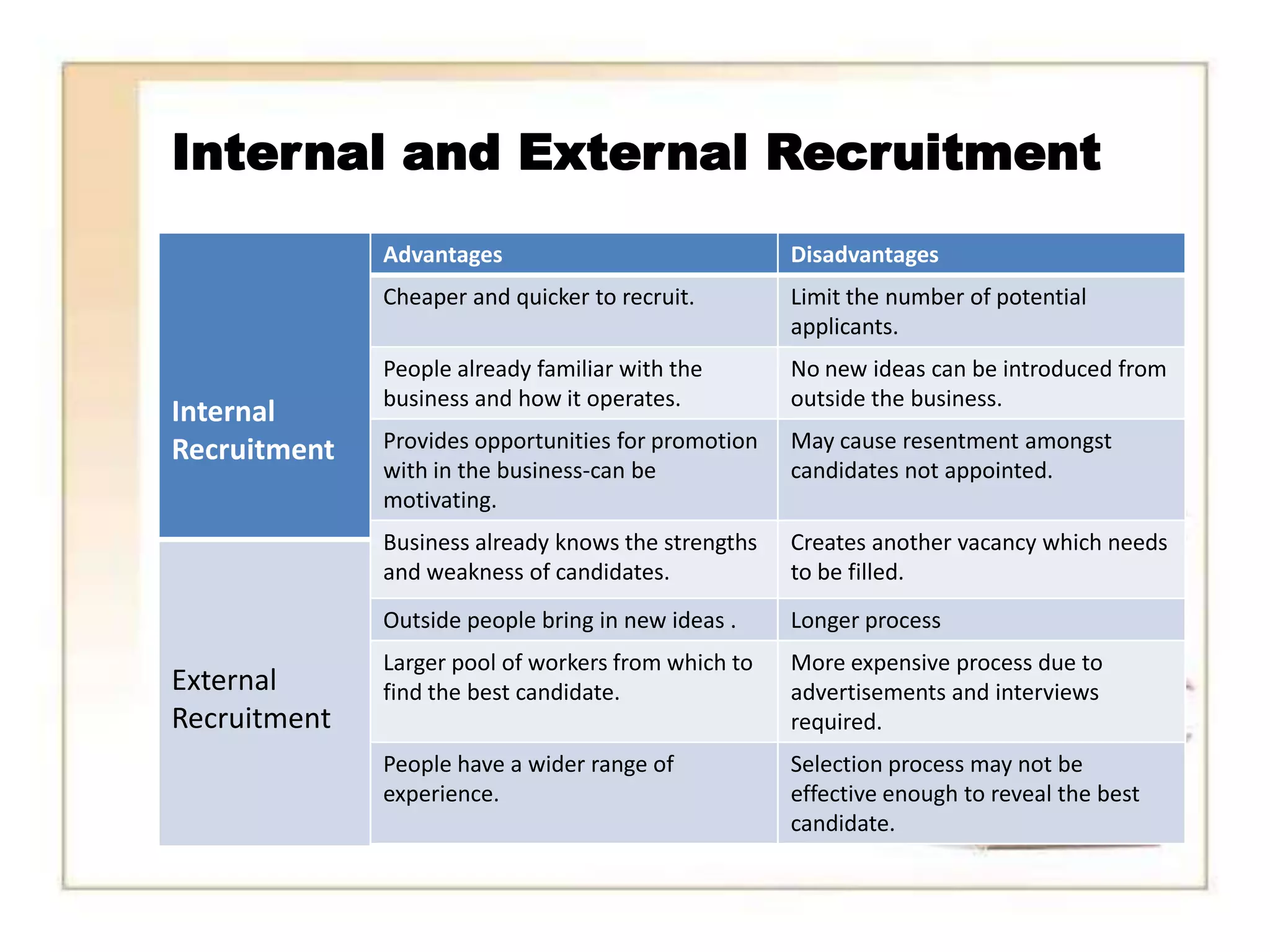
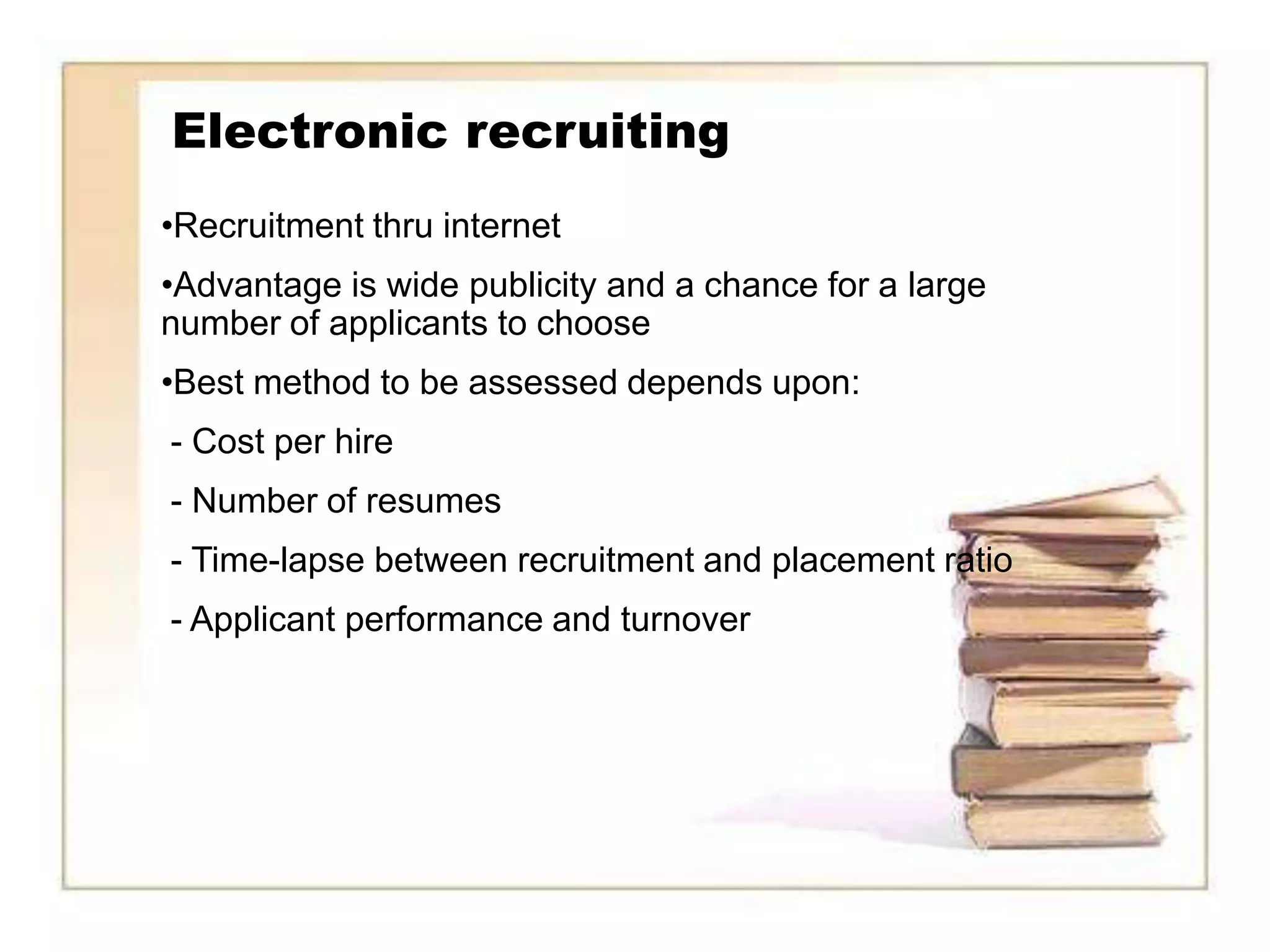
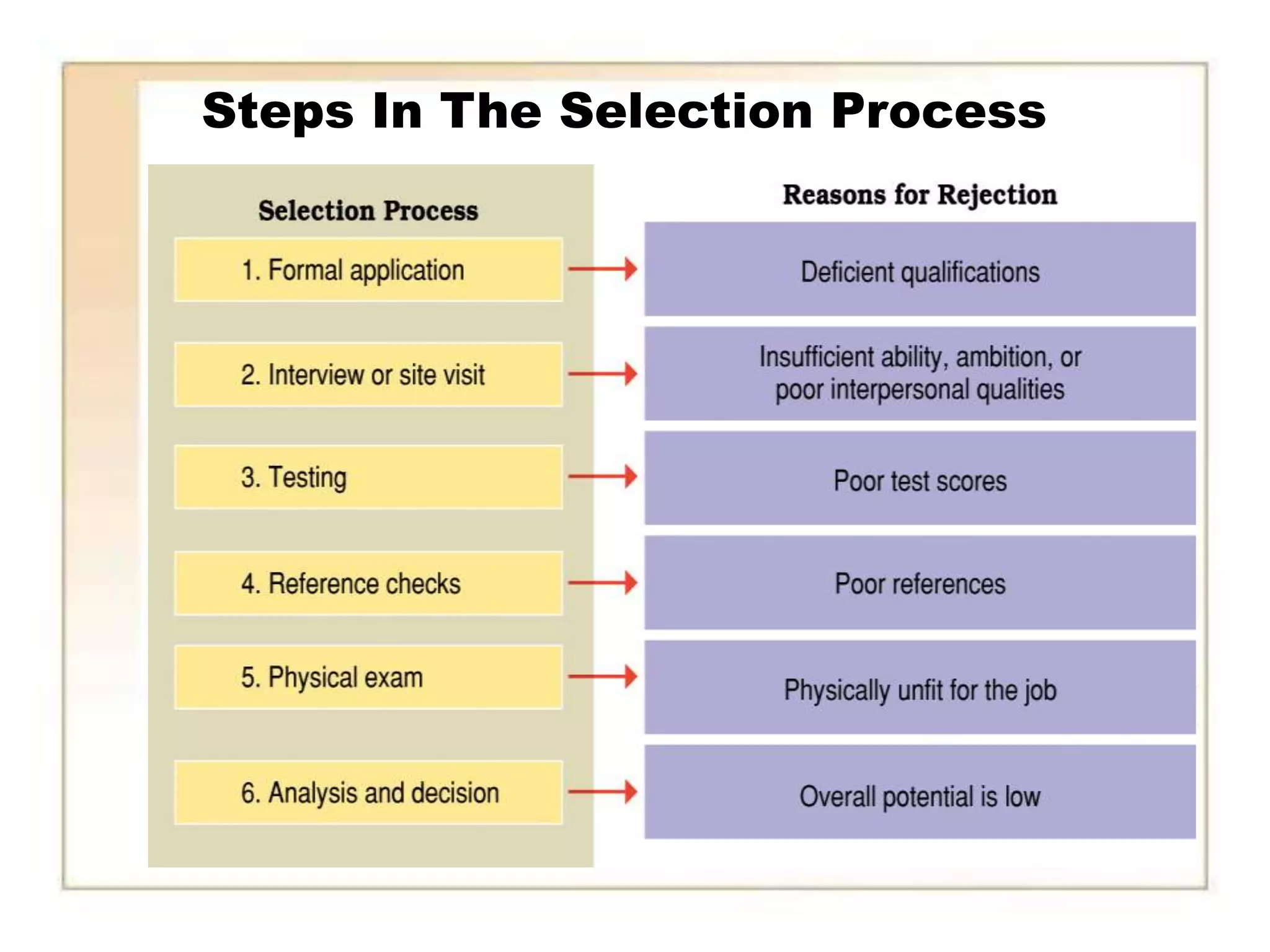
The document discusses recruitment methods in the fashion industry. It describes various recruitment channels like internal recruitment, external recruitment through advertising, agencies, and campus recruitment. Electronic recruitment through internet is also mentioned. The advantages and disadvantages of internal and external recruitment are provided. The selection process includes application, interview, testing, reference and background checks, physical examination and final decision. Onboarding of new employees involves introducing them to the organization, employee benefits and training opportunities.