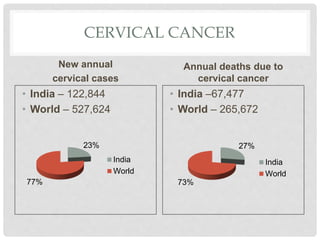
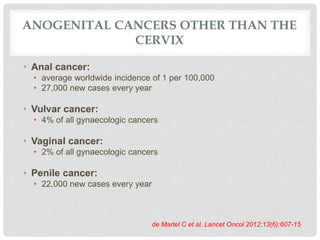
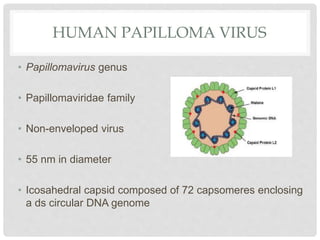
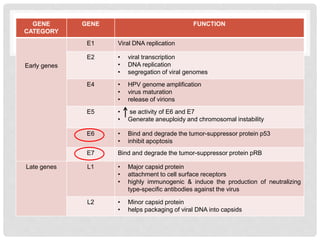
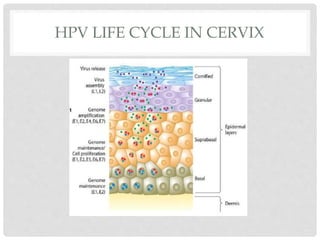
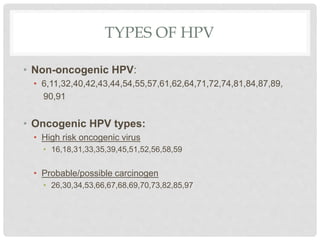
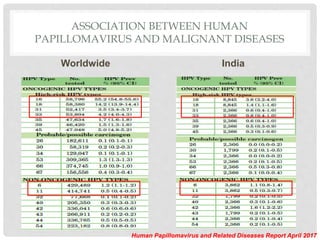
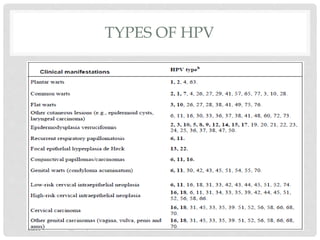
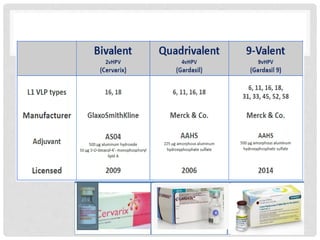
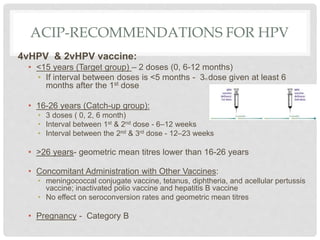
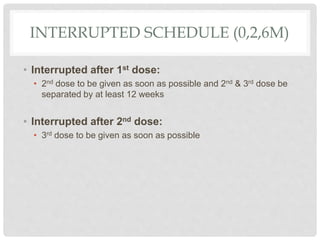
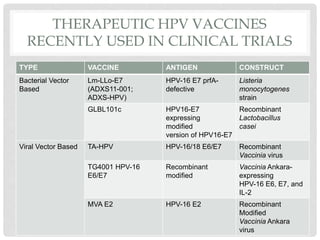
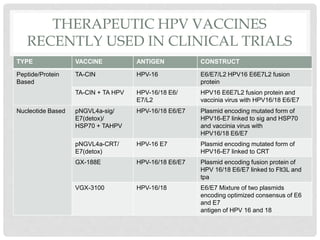
This document discusses HPV vaccines and cervical cancer prevention. It provides details on HPV types, transmission, and associated cancers. It outlines recommendations for HPV vaccination including target groups, dosing schedules, and delivery strategies. The goals of HPV vaccination are to reduce the global burden of HPV-related cancers through immunization programs.