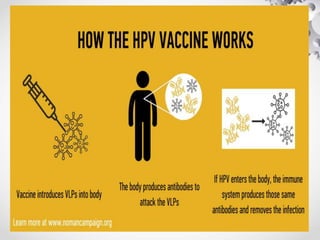
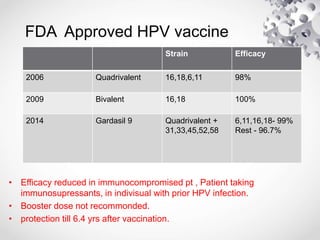
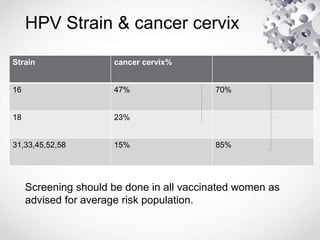
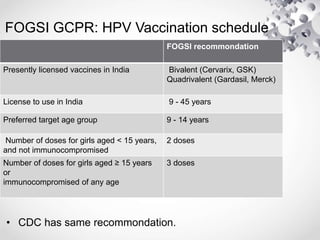
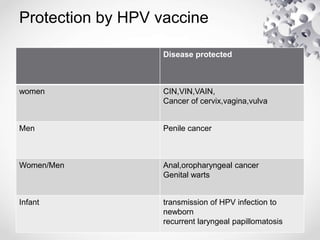
HPV vaccination provides protection against HPV strains that cause cervical cancer and genital warts. The FDA has approved several HPV vaccines, including a quadrivalent vaccine protecting against strains 16, 18, 6, and 11, and a bivalent vaccine protecting against 16 and 18. Vaccination is recommended between ages 9-14 with a two dose schedule, or ages 15 and older with a three dose schedule. HPV vaccination has been shown to be safe and effective with common side effects being mild local reactions. Screening is still recommended for vaccinated individuals as the vaccines do not protect against all cancer-causing HPV strains.