More Related Content
PDF
Anomaly detection Workshop slides PPTX
Outlier analysis and anomaly detection PDF
Data-Screening qqwewqewqeqeqwewqewqeqweqweqwewq.pdf PPTX
Navigating-the-Noise-A-Practical-Guide-to-Outliers-in-Data.pptx PDF
Introduction to unsupervised learning: outlier detection PPTX
PDF
PDF
Multiple Linear Regression Models in Outlier Detection Similar to How to Detect Outliers in IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx
PPTX
Exploratory_Data_Analysis on data analysis using python.pptx PPTX
Variables , outlier and its detection and Missing values PPTX
Outlier-Detection-in-Higher-Dimensions in data mining PPT
PDF
Course-CO9301: Unsupervised Modelling for AIML Unit-II:Feature Engineering T... PPTX
40_P17CSC310_2020120905054844.pptxffffff PPTX
Outlier analysis,Chapter-12, Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques PDF
Dealing with outliers in Clinical Research PPT
data engineering topic on cluster analysis PDF
PPT
12Outlier.for software introductionalism PPT
Chapter 12. Outlier Detection.ppt PPTX
What is Outlier Analysis and How Can It Improve Analysis? PPTX
Data Mining: Outlier analysis PPT
Data cleaning-outlier-detection PDF
PPTX
Data Mining: Outlier analysis DOCX
Data Mining Anomaly DetectionLecture Notes for Chapt.docx PDF
PDF
SELECTED DATA PREPARATION METHODS More from Version 1 Analytics
PPTX
Aggregating Records in IBM SPSS Statistics PPTX
Auto Data Preparation in IBM SPSS Modeler.pptx PPTX
How to Create Groups from Numeric Variables with Visual Binning.pptx PPTX
Running Means Procedure in IBM SPSS Statistics PPTX
ChiSquare Procedure in IBM SPSS Statistics Version 31.pptx PPTX
Customise Your Correlation Table in IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx PPTX
Visualising Data with Scatterplots in IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx PPTX
Curated Help for T-Tests in IBM SPSS Statistics PPTX
How to Import a CSV File into IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx PPTX
Split into Files in IBM SPSS Statitistics.pptx PPTX
Replace Missing Values. in IBM SPSS Statistics PPTX
How to Import an Excel File into IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx PPTX
Change Common Properties in IBM SPSS Statistics Version 31.pptx PPTX
Finding Your License Details in IBM SPSS Statistics Version 31.pptx PPTX
Homogeneity of Variance Test Options IBM SPSS Statistics Version 31.pptx PPTX
Coefficient of Variance in IBM SPSS Statistics Version 31.pptx PPTX
Clustered Bar Charts IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx PPTX
Row Panels for Bar Charts in IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx PDF
Add Background Images to Charts in IBM SPSS Statistics Version 31.pdf PPTX
Help for Correlations in IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx Recently uploaded
PPTX
Session 2 - Solving Unstructured & Complex Documents with UiPath IXP PDF
The State of the Gen AI economy - 2025 - The Meliora Company PDF
100 Insights After the 200th Issue of NewMind AI Journal PDF
Real-Time Data Insight Using Microsoft Forms for Business PPTX
UiPath Autonomous Agents | Building and Orchestrating Agents End-to-End PPTX
From Backup to Resilience: How MSPs Are Preparing for 2026 PDF
TrustArc Webinar - Looking Ahead: The 2026 Privacy Landscape PDF
HCSP-Presales-Campus Network Planning and Design V2.0 PPTX
Conversational Agents – Building Intelligent Assistants [Virtual Hands-on Wor... PDF
Security Forum Sessions from Houston 2025 Event PDF
Day 4 - Access, Deployments, and Monitoring - 2nd Sight Lab Cloud Security Class PDF
Data Virtualization in Action: Scaling APIs and Apps with FME PDF
WHITE PAPER_ Ransomware Payment Policy and Resilience Strategy_ A Framework f... PDF
Our Digital Tribe_ Cultivating Connection and Growth in Our Slack Community 🌿... PDF
WCAG Analyzer Tools and Techniques for User-Friendly Websites DOCX
iRobot Post‑Mortem and Alternative Paths - Discussion Document for Boards and... PDF
Day 5 - Red Team + Blue Team in the Cloud - 2nd Sight Lab Cloud Security Class PPTX
wob-report.pptxwob-report.pptxwob-report.pptx PPTX
MGw_MRS Benfits seu beficios de redes 4g PDF
Is It Possible to Have Wi-Fi Without an Internet Provider How to Detect Outliers in IBM SPSS Statistics.pptx
- 1.
- 2.
Classification: Controlled. Copyright©2025 Version 1. All rights reserved.
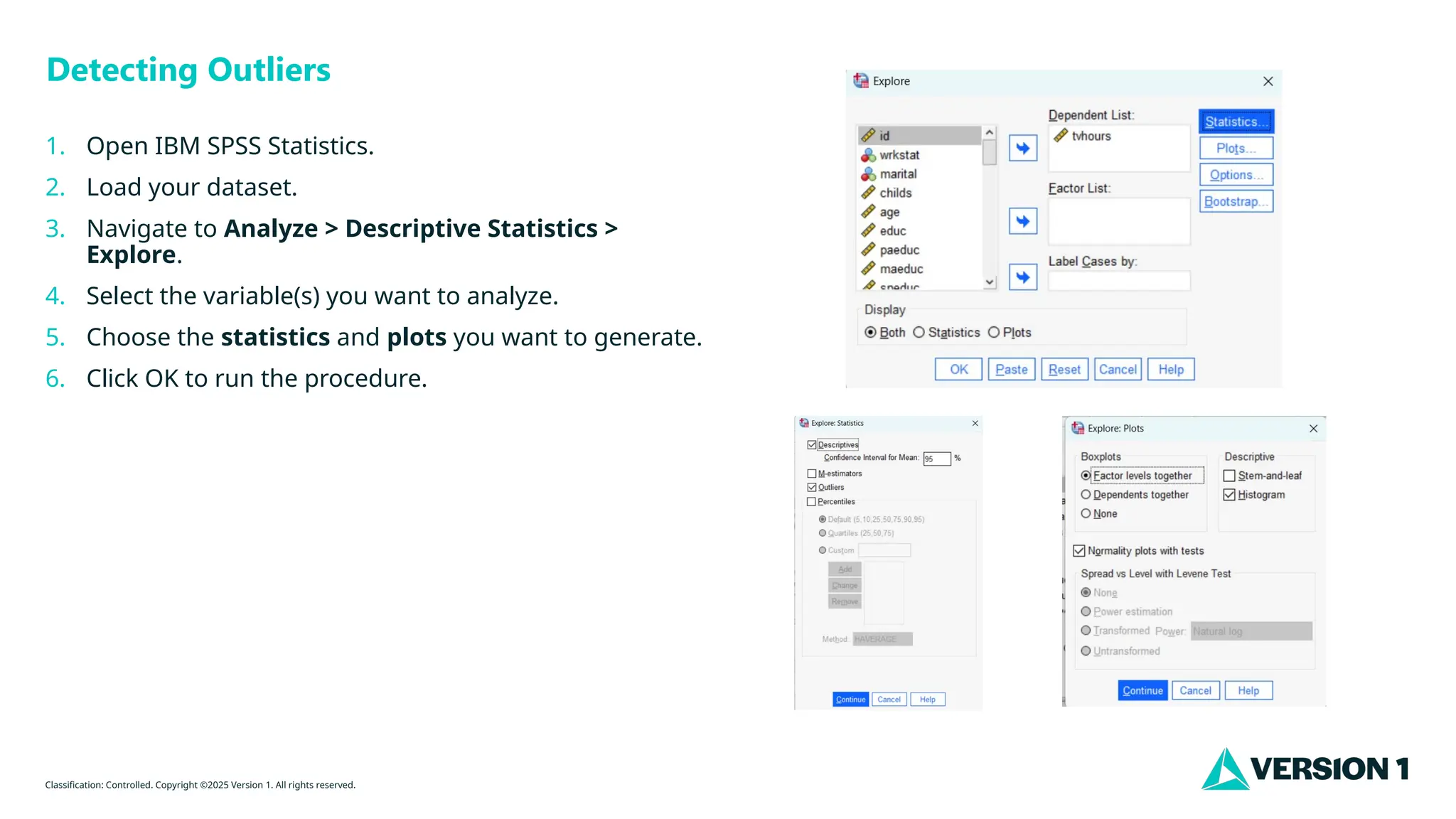
Detecting Outliers
1. Open IBM SPSS Statistics.
2. Load your dataset.
3. Navigate to Analyze > Descriptive Statistics >
Explore.
4. Select the variable(s) you want to analyze.
5. Choose the statistics and plots you want to generate.
6. Click OK to run the procedure.
- 3.
Classification: Controlled. Copyright©2025 Version 1. All rights reserved.
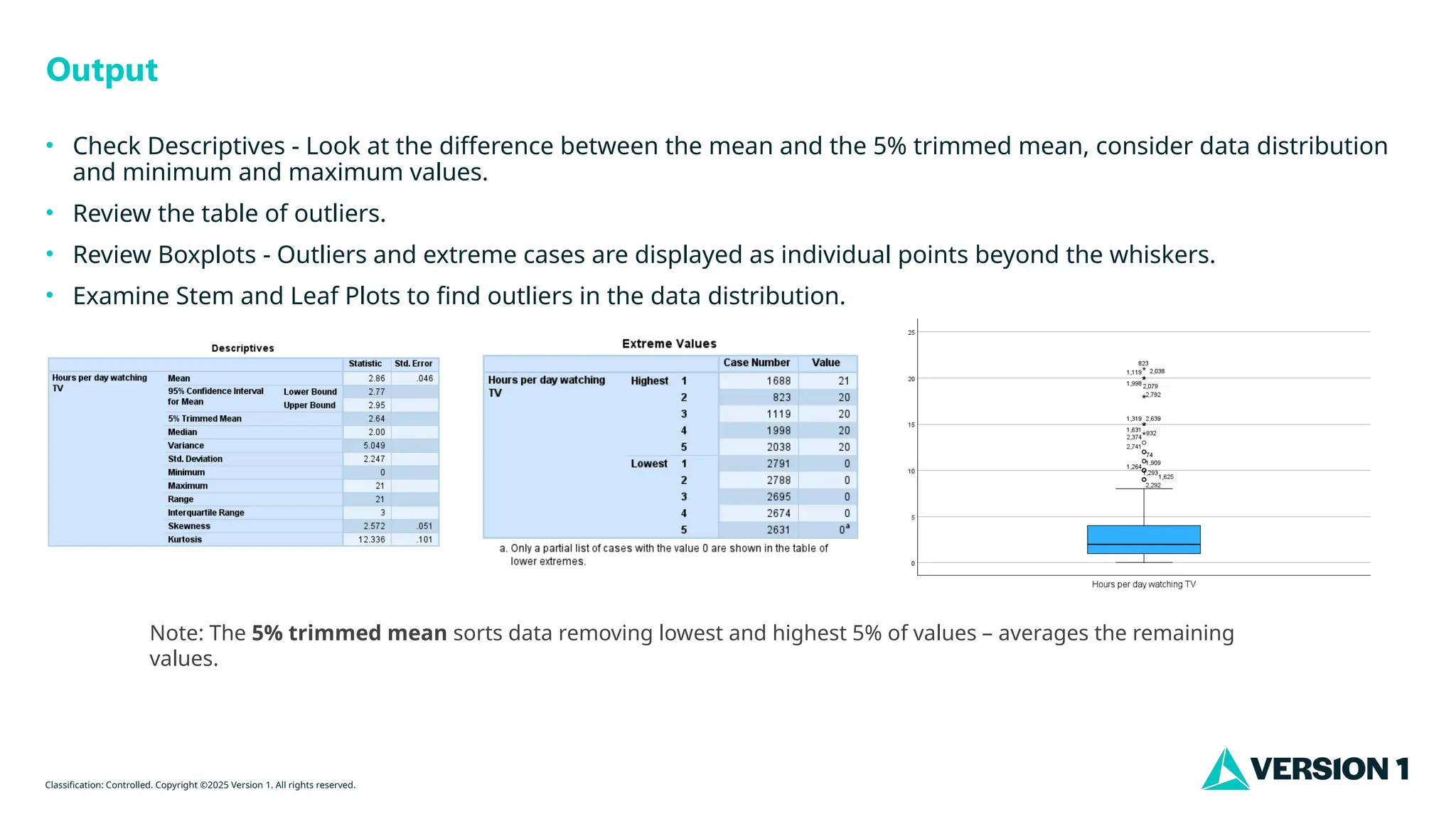
Output
• Check Descriptives - Look at the difference between the mean and the 5% trimmed mean, consider data distribution
and minimum and maximum values.
• Review the table of outliers.
• Review Boxplots - Outliers and extreme cases are displayed as individual points beyond the whiskers.
• Examine Stem and Leaf Plots to find outliers in the data distribution.
Note: The 5% trimmed mean sorts data removing lowest and highest 5% of values – averages the remaining
values.
- 4.
Classification: Controlled. Copyright©2025 Version 1. All rights reserved.
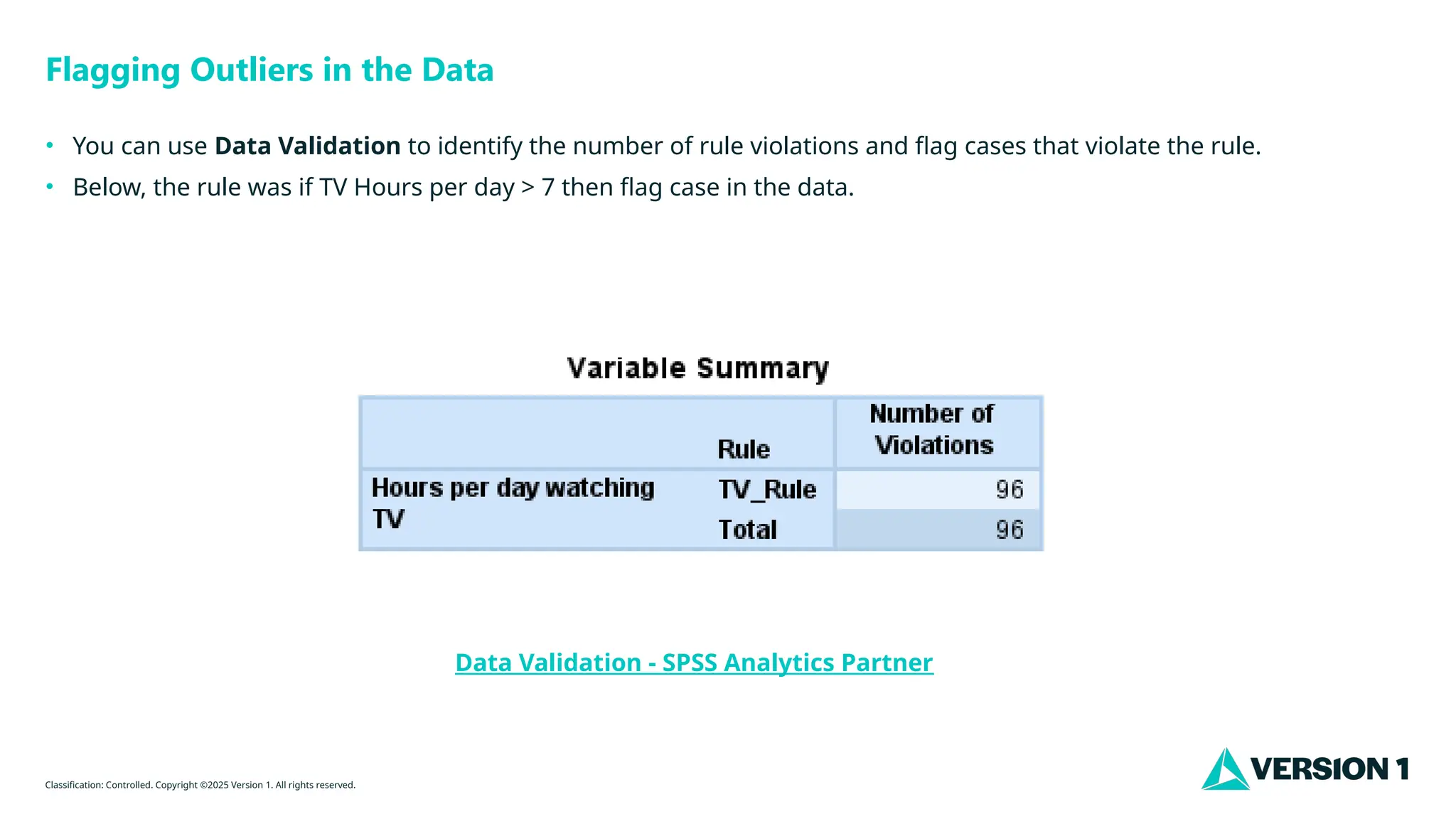
Flagging Outliers in the Data
• You can use Data Validation to identify the number of rule violations and flag cases that violate the rule.
• Below, the rule was if TV Hours per day > 7 then flag case in the data.
Data Validation - SPSS Analytics Partner
- 5.
Classification: Controlled. Copyright©2025 Version 1. All rights reserved.
Tips and Best Practices
• Visualise data to spot outliers.
• Recognize the effect of outliers on your analysis.
• Verify outliers using methods like Boxplots and Data Validation.
• Document and explain your approach to handling outliers.
• Outlier: A data point far outside the normal range, potentially valid or erroneous.
• Anomalous case: Any data point that deviates from expected patterns, including outliers and errors.
• Data understanding and examination is crucial!
- 6.