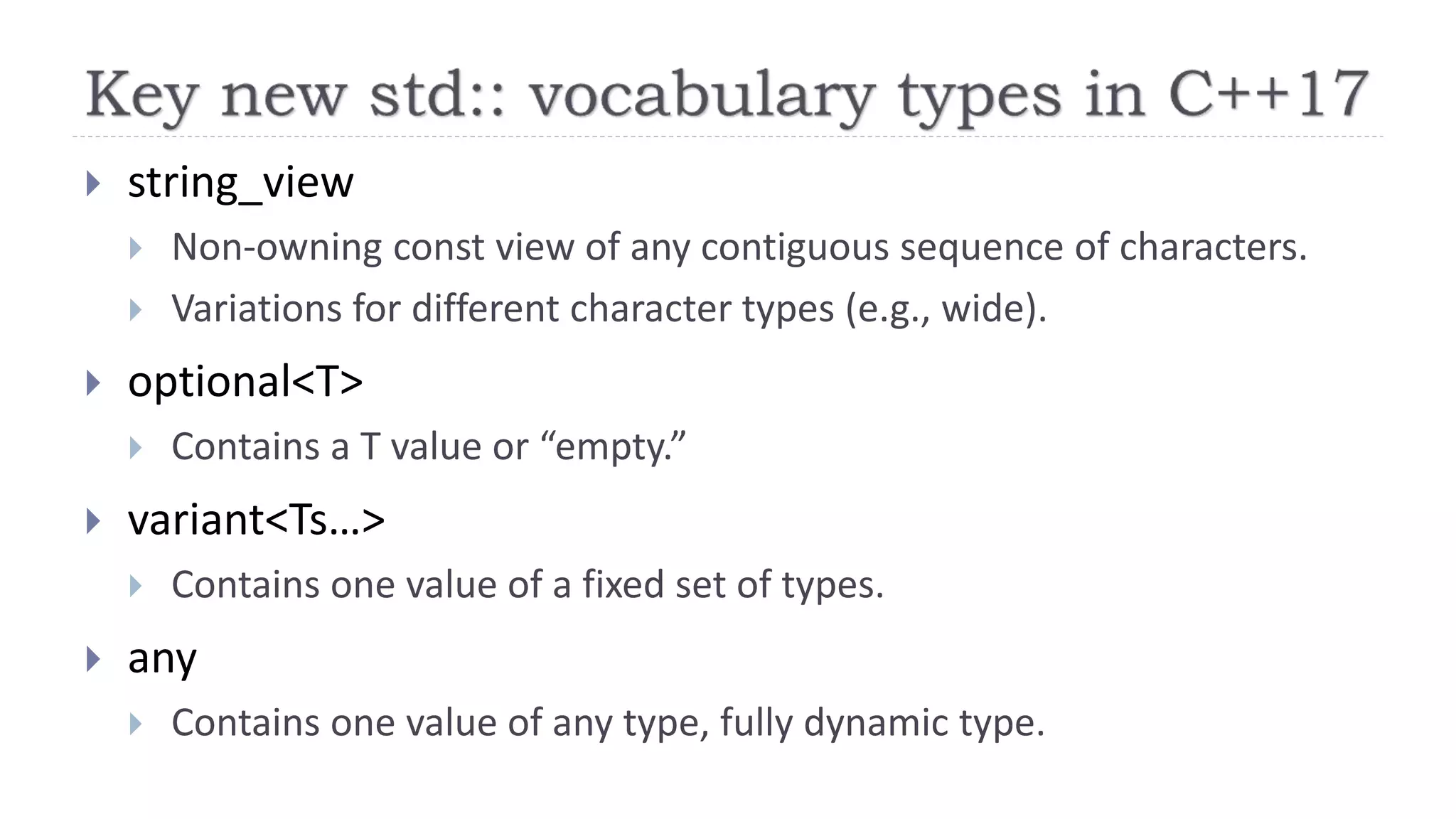
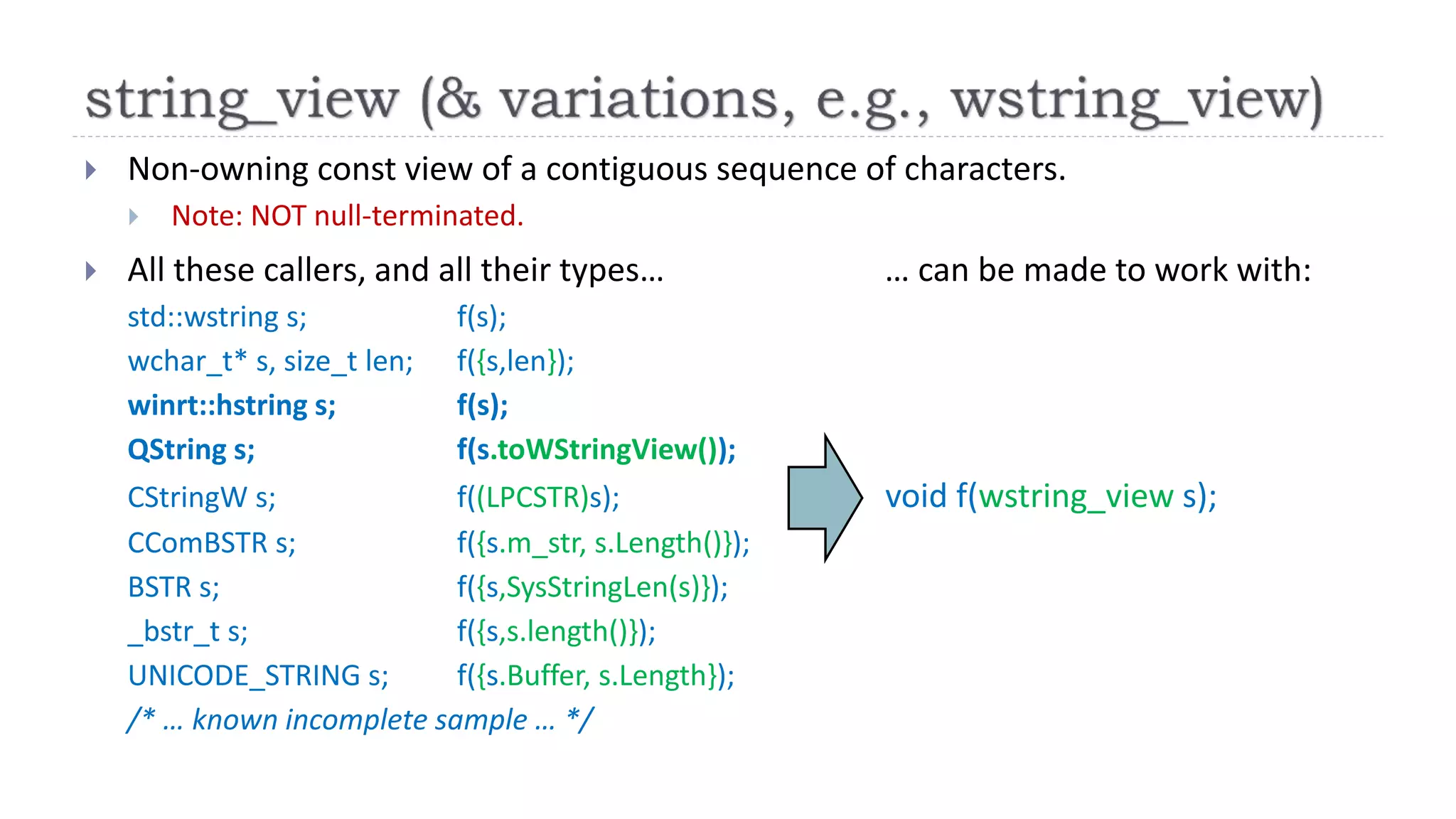
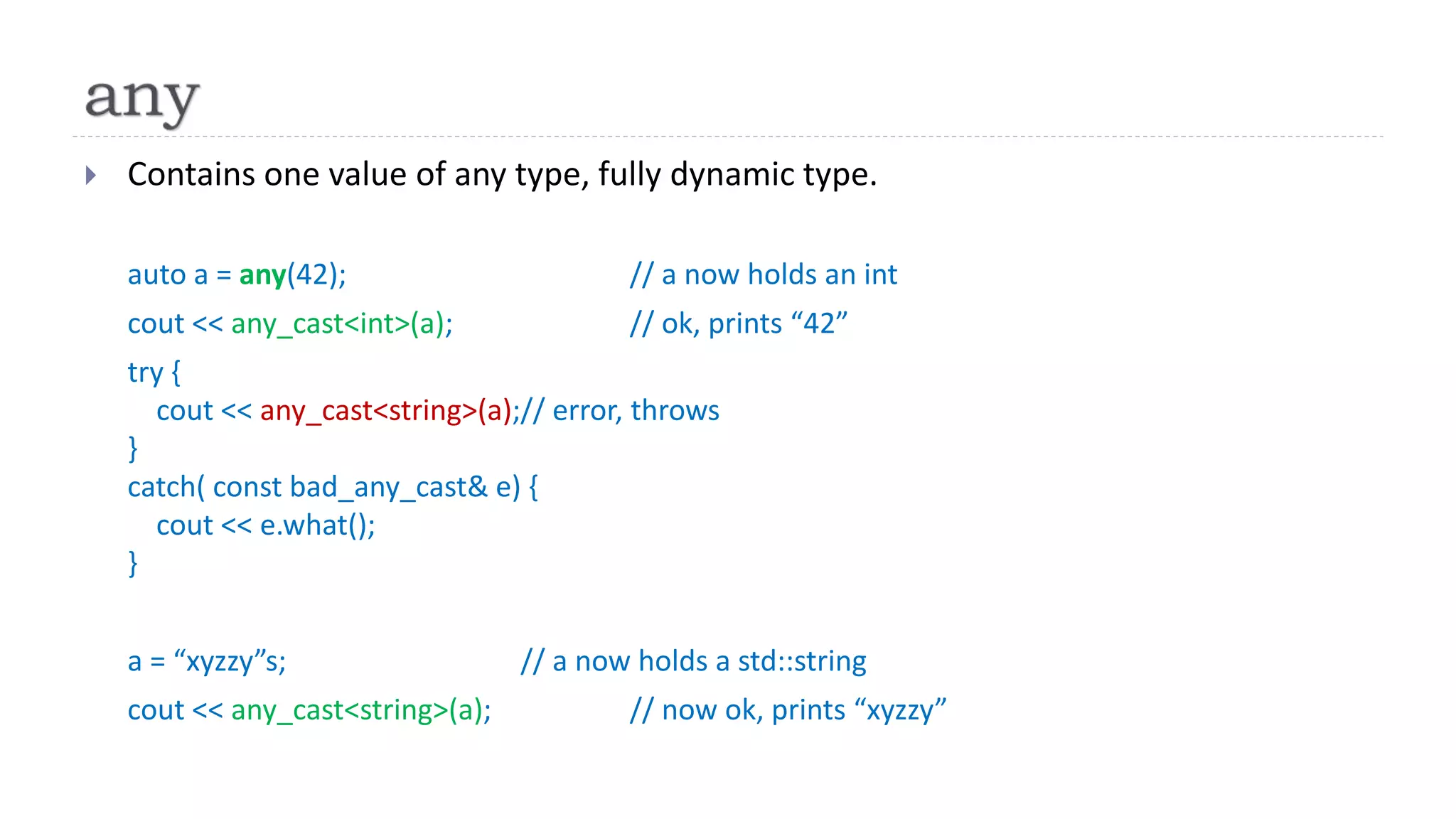
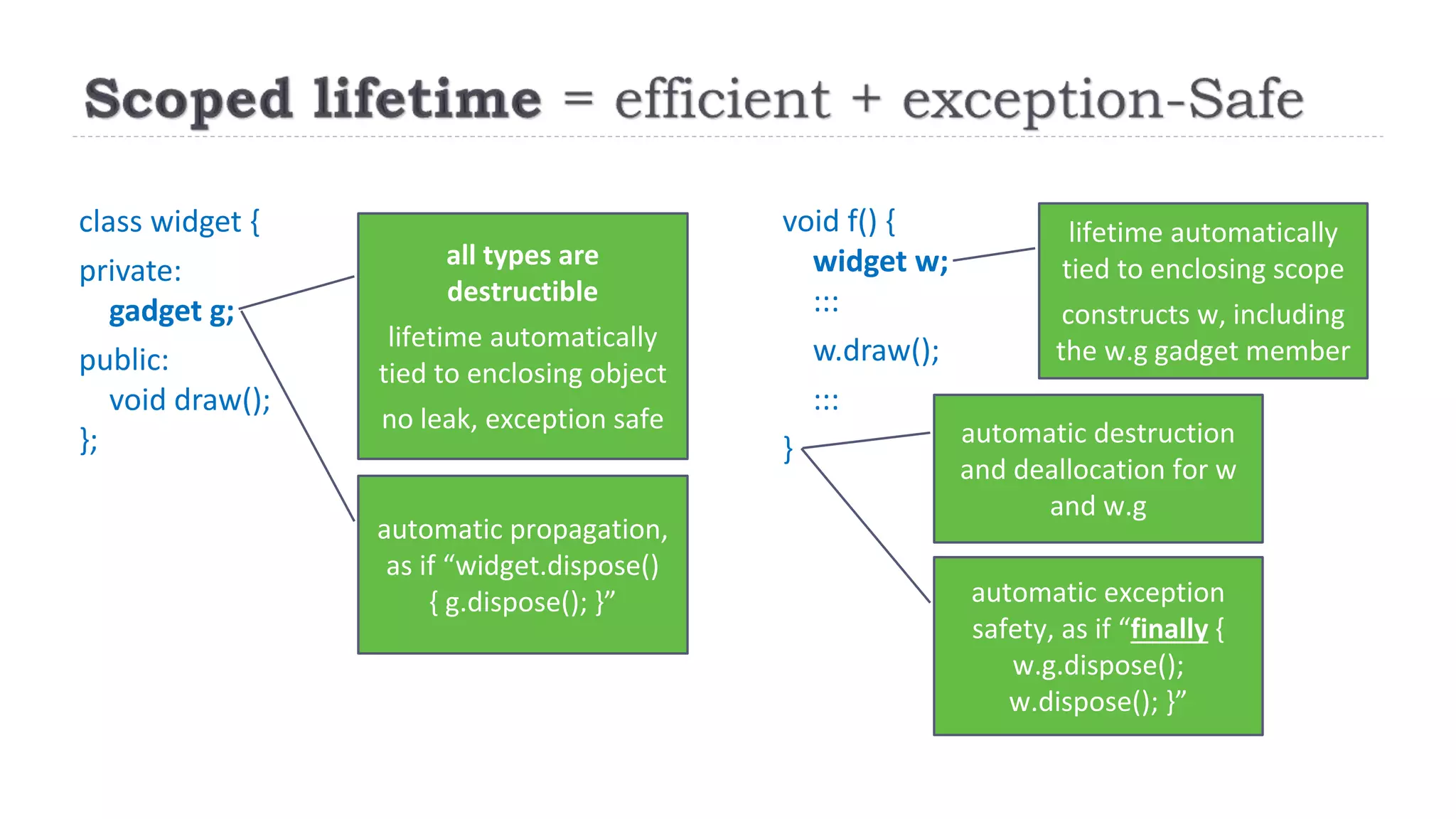
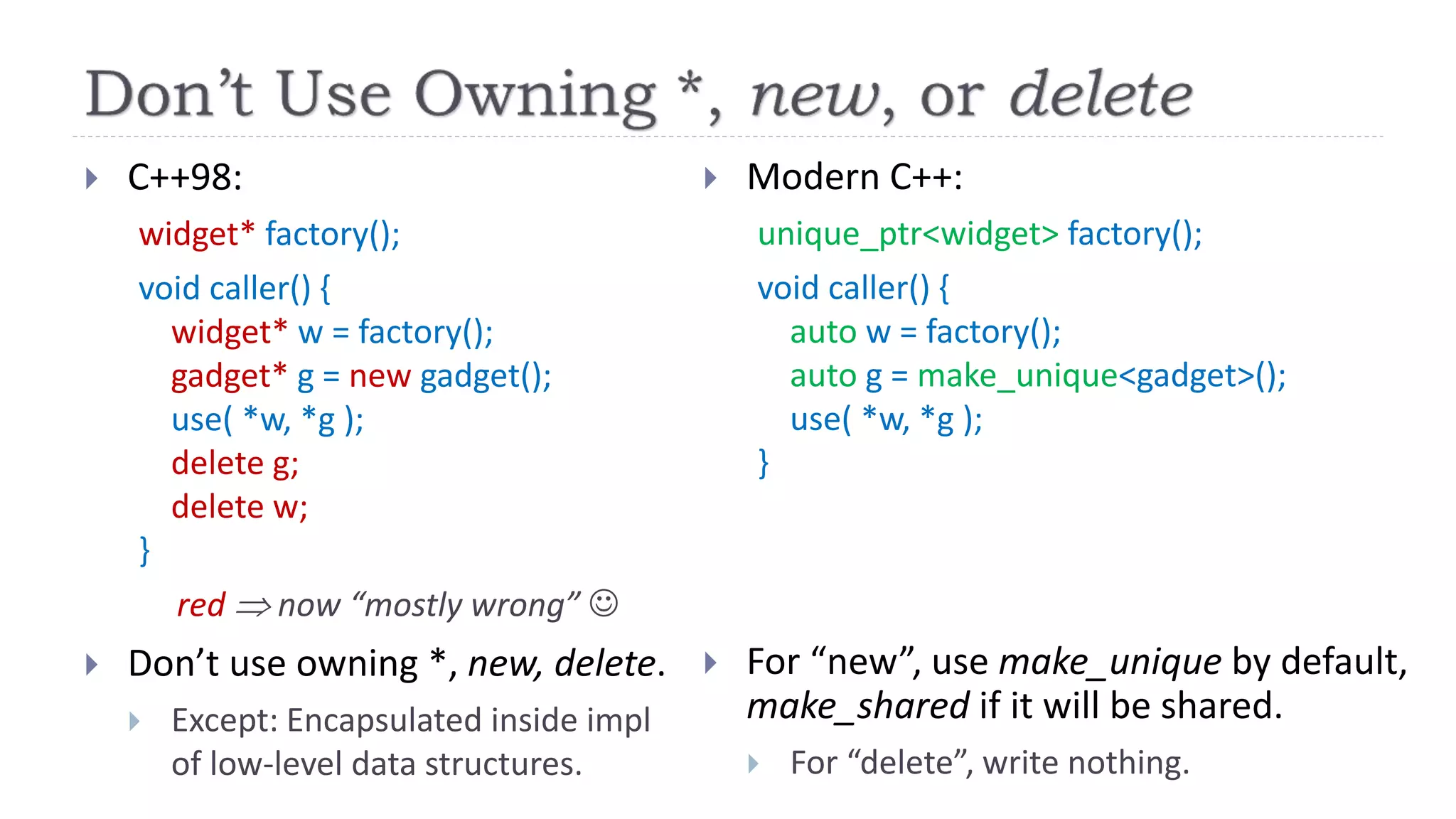
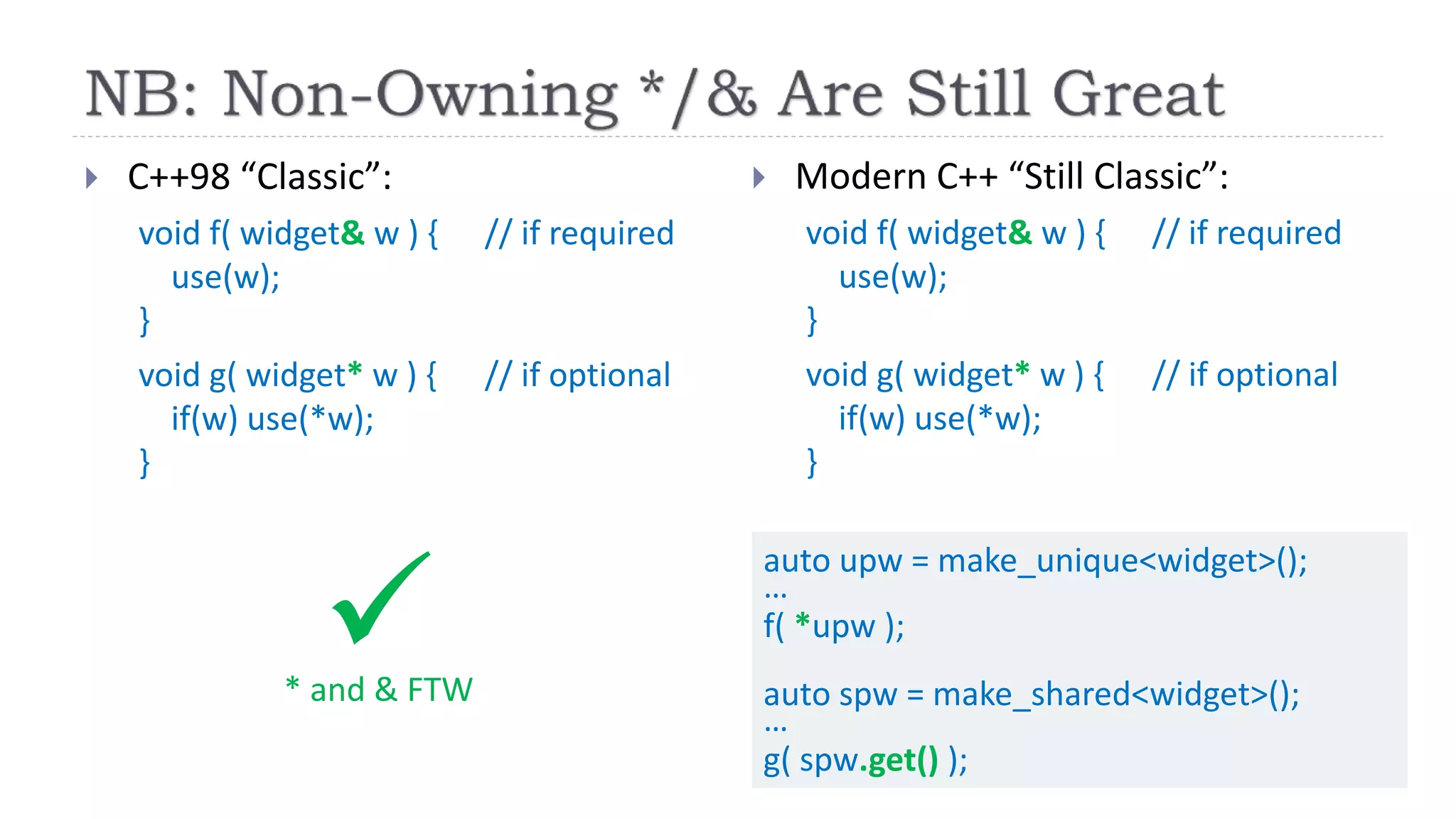
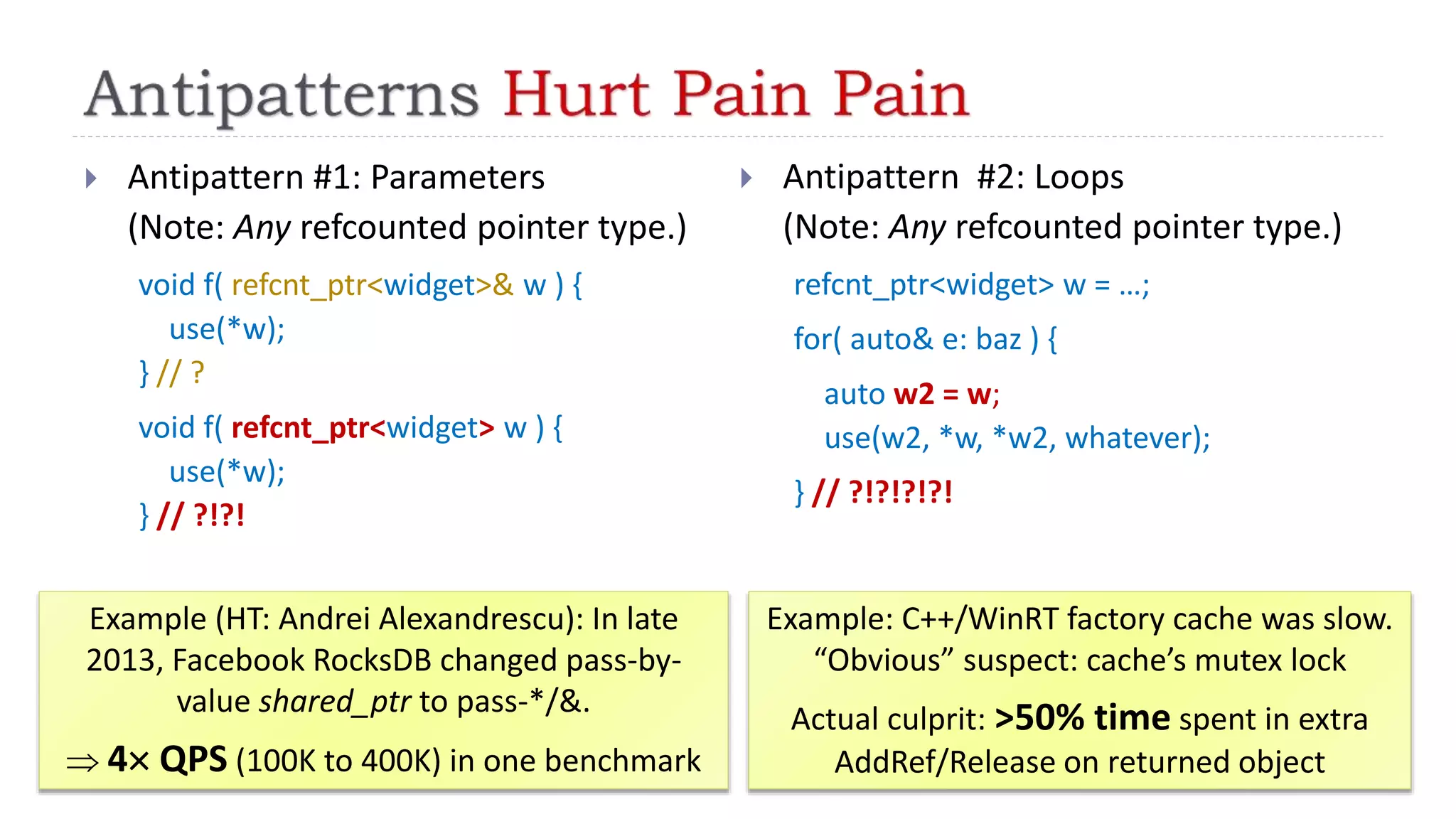
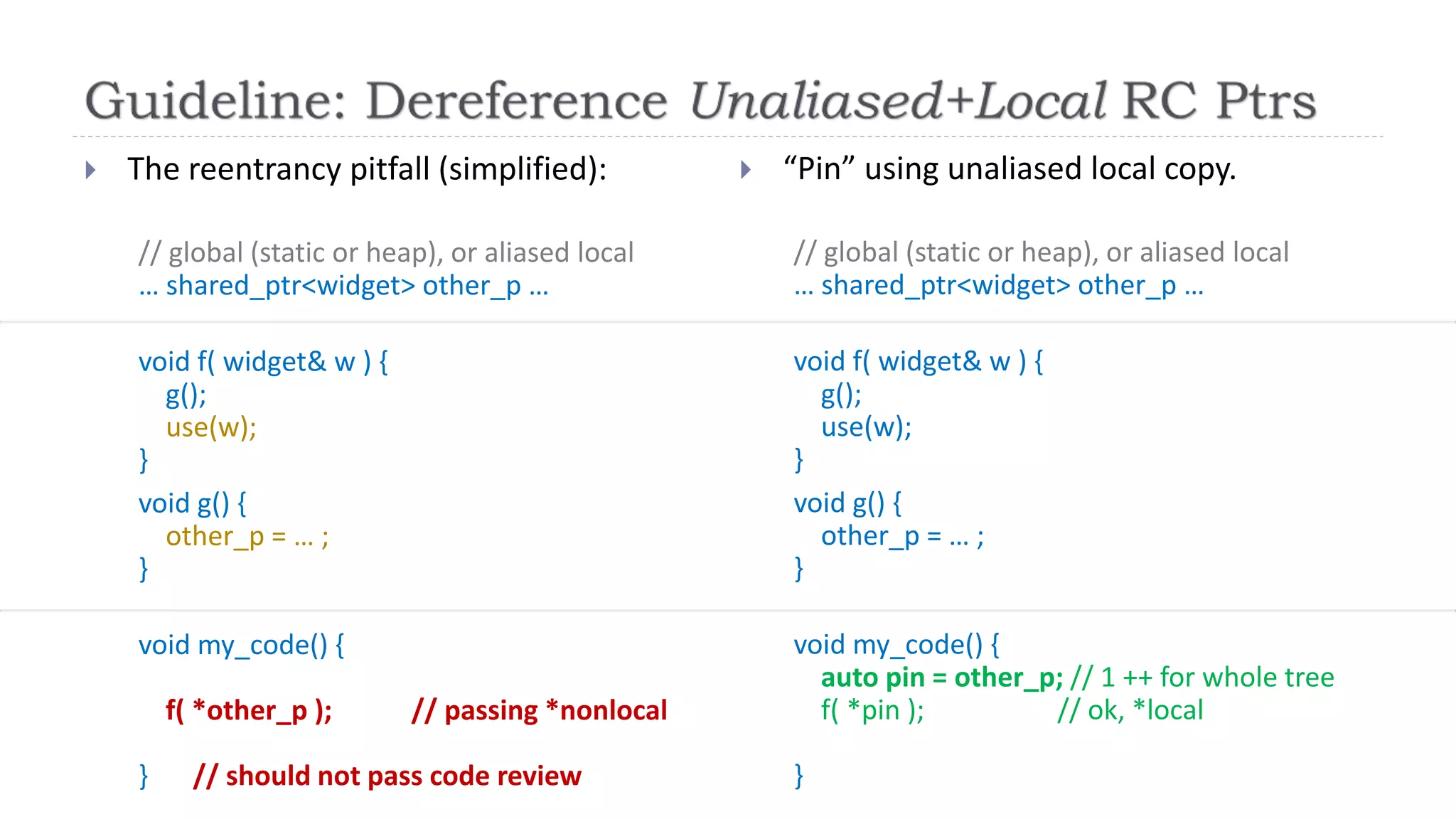
The document discusses the evolution from 'classic' to 'modern' C++, highlighting key concepts such as move semantics, error handling, and resource ownership through RAII. It emphasizes the importance of using smart pointers like unique_ptr and shared_ptr for memory management, and presents practical code examples illustrating the differences between older C++ paradigms and contemporary practices. The document also notes ongoing updates for the C++17 standard, making modern C++ more efficient and easier to teach.




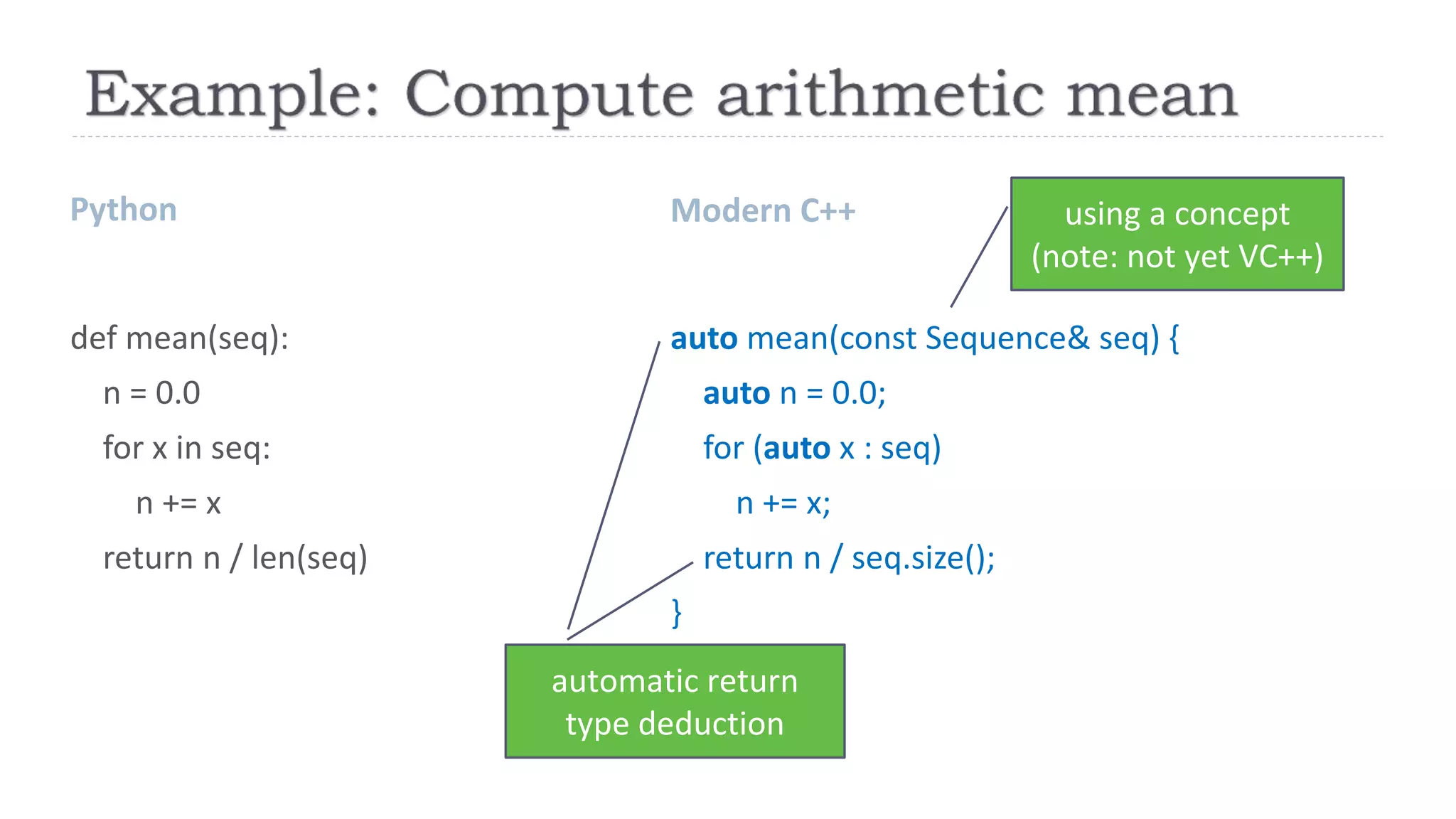

{ return reduce(begin(seq),end(seq)) / seq.size(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brk2146-180509203307/75/How-to-Adopt-Modern-C-17-into-Your-C-Code-8-2048.jpg)
 {
return reduce(par_unseq,begin(seq),end(seq))
/ seq.size();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brk2146-180509203307/75/How-to-Adopt-Modern-C-17-into-Your-C-Code-9-2048.jpg)









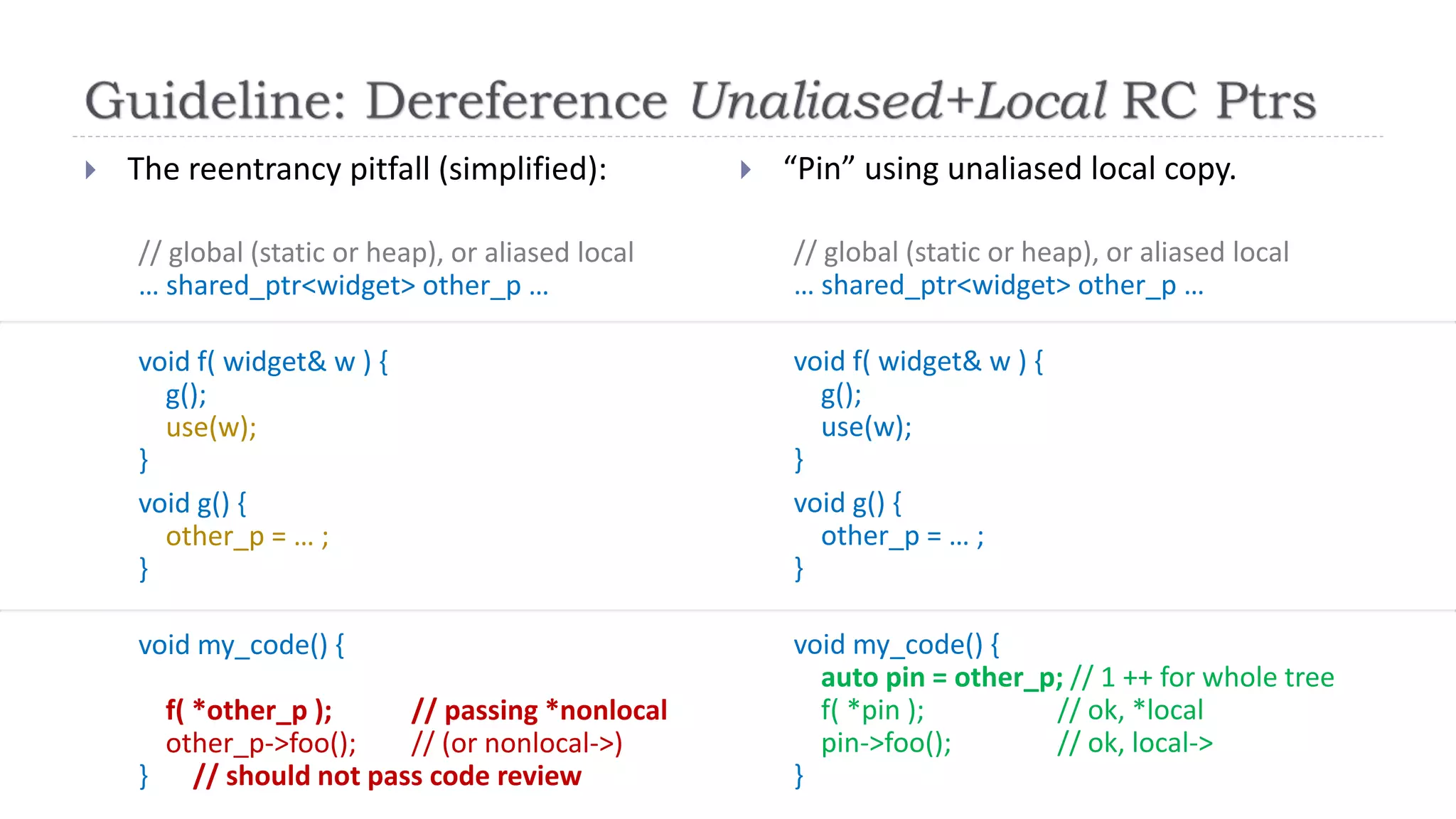
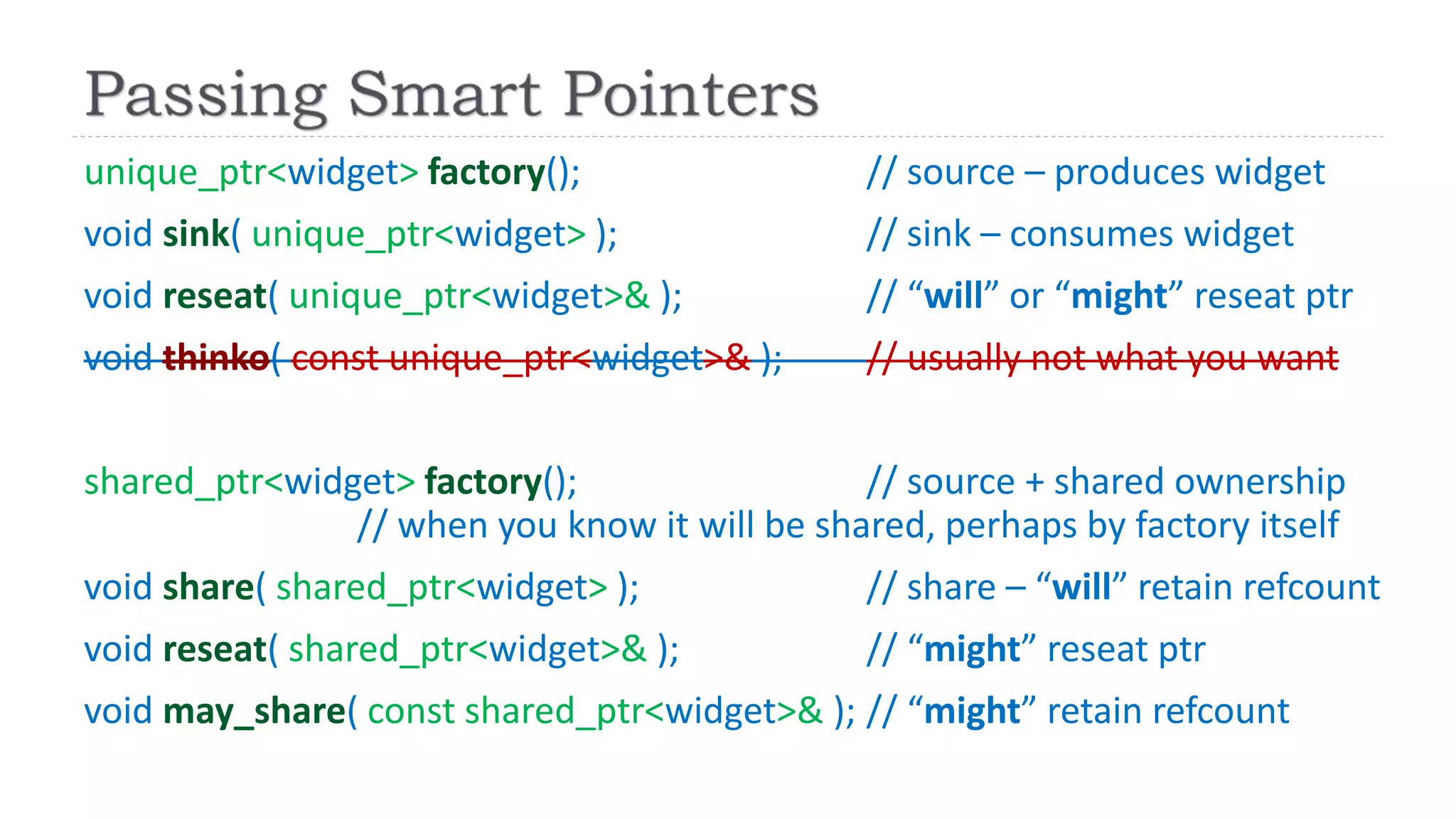



![ … and it turns out we’ve already been doing it.
Given a set<string> myset, consider:
// C++98
pair<set<string>::iterator,bool> result = myset.insert( “Hello” );
if (result.second) do_something_with( result.first ); // workaround
// C++11 – sweet backward compat
auto result = myset.insert( “Hello” ); // nicer syntax, and the
if (result.second) do_something_with( result.first ); // workaround still works
// C++17
auto [ iter, success ] = myset.insert( “Hello” ); // normal return value
if (success) do_something_with( iter );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brk2146-180509203307/75/How-to-Adopt-Modern-C-17-into-Your-C-Code-33-2048.jpg)

