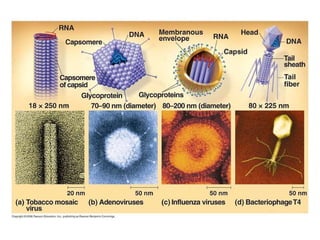
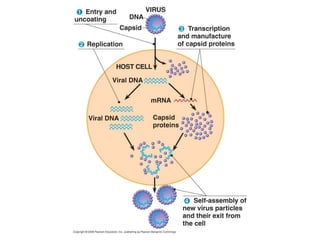
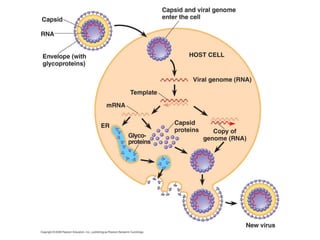
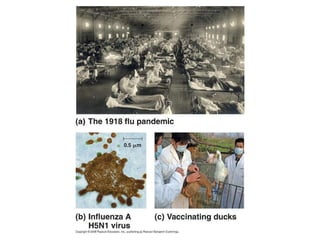
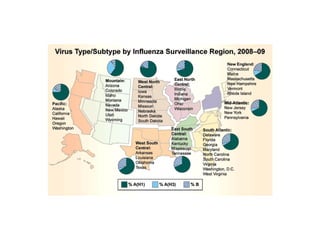
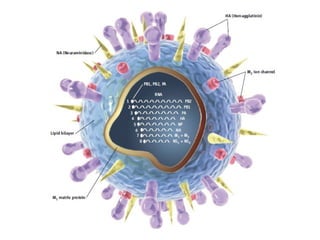
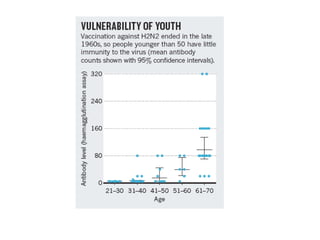
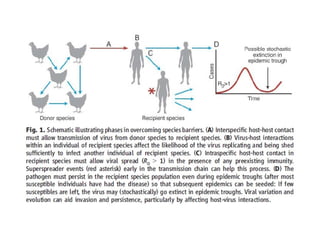
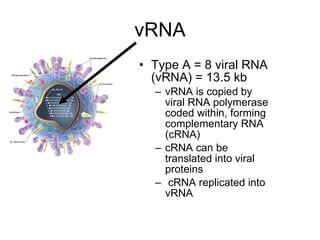
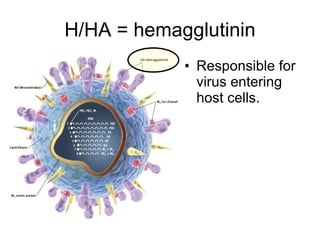
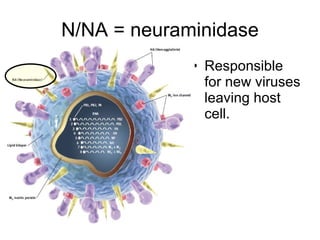
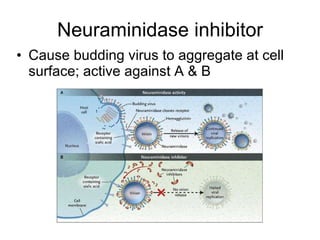
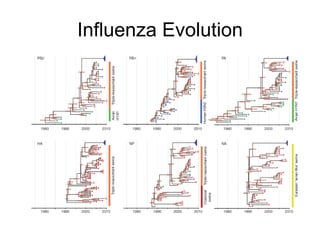
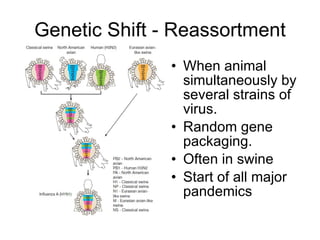
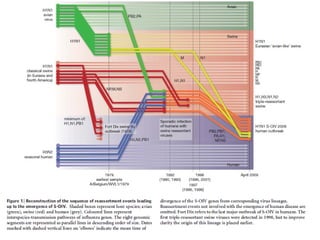
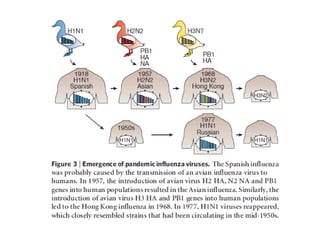
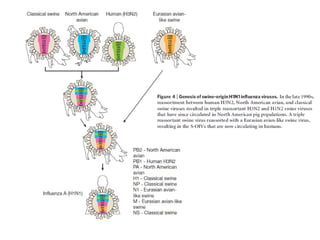
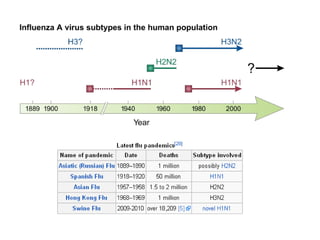
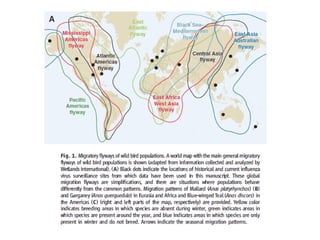
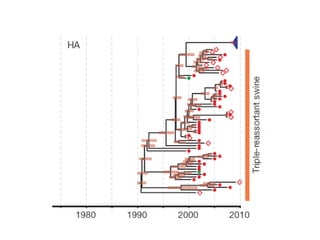
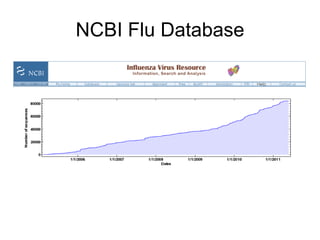
Influenza is caused by RNA viruses of type A or B. Type A influenza evolves rapidly through antigenic drift and shift, causing seasonal epidemics and pandemics when new strains emerge that humans have no immunity against. The 2009 H1N1 pandemic originated from genetic reassortment between human, avian, and swine influenza viruses. While H5N1 avian influenza is a pandemic threat, it has so far not achieved efficient human-to-human transmission. Genetic sequencing of influenza viruses allows public health officials to track their evolution and spread globally.