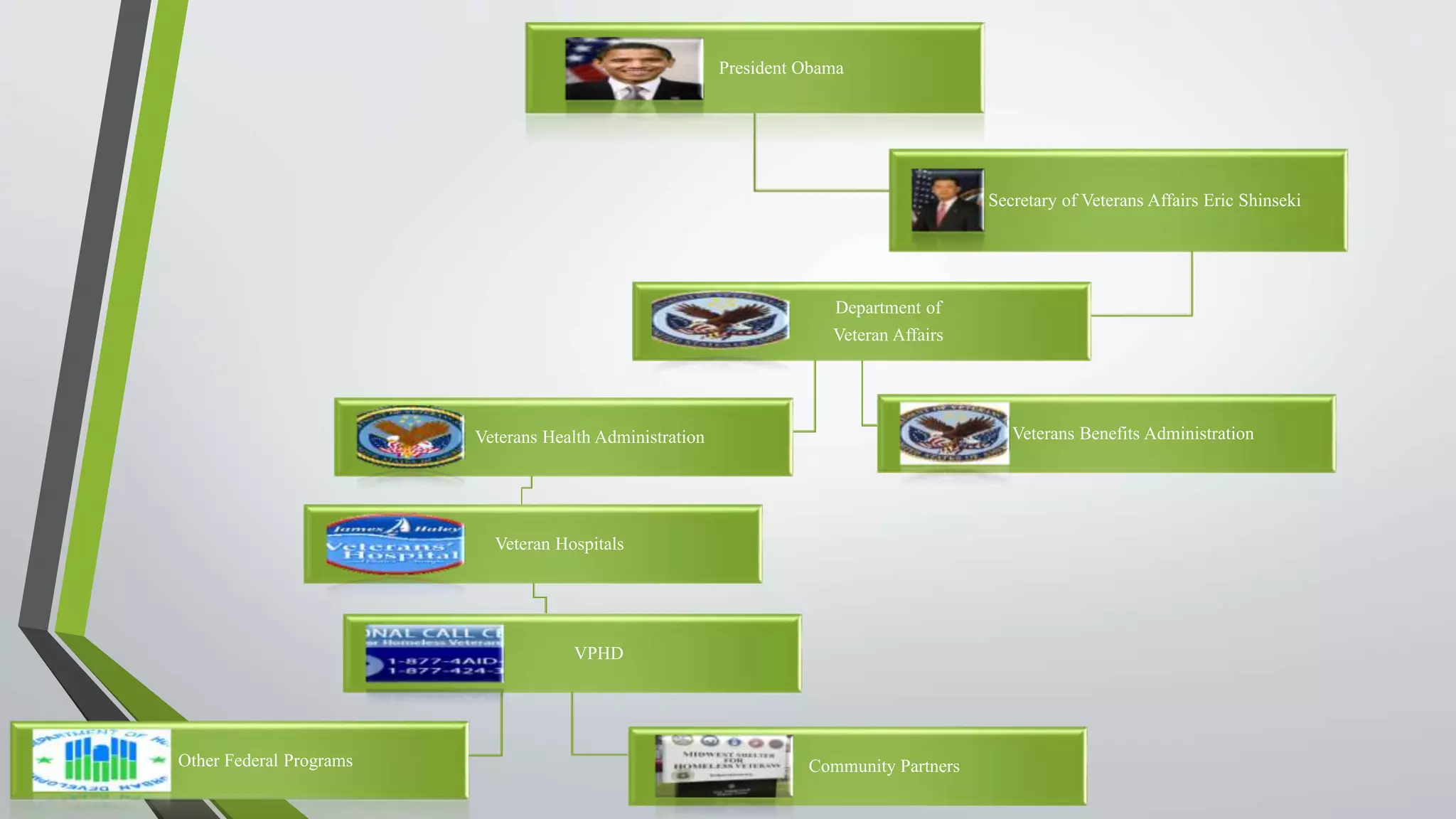
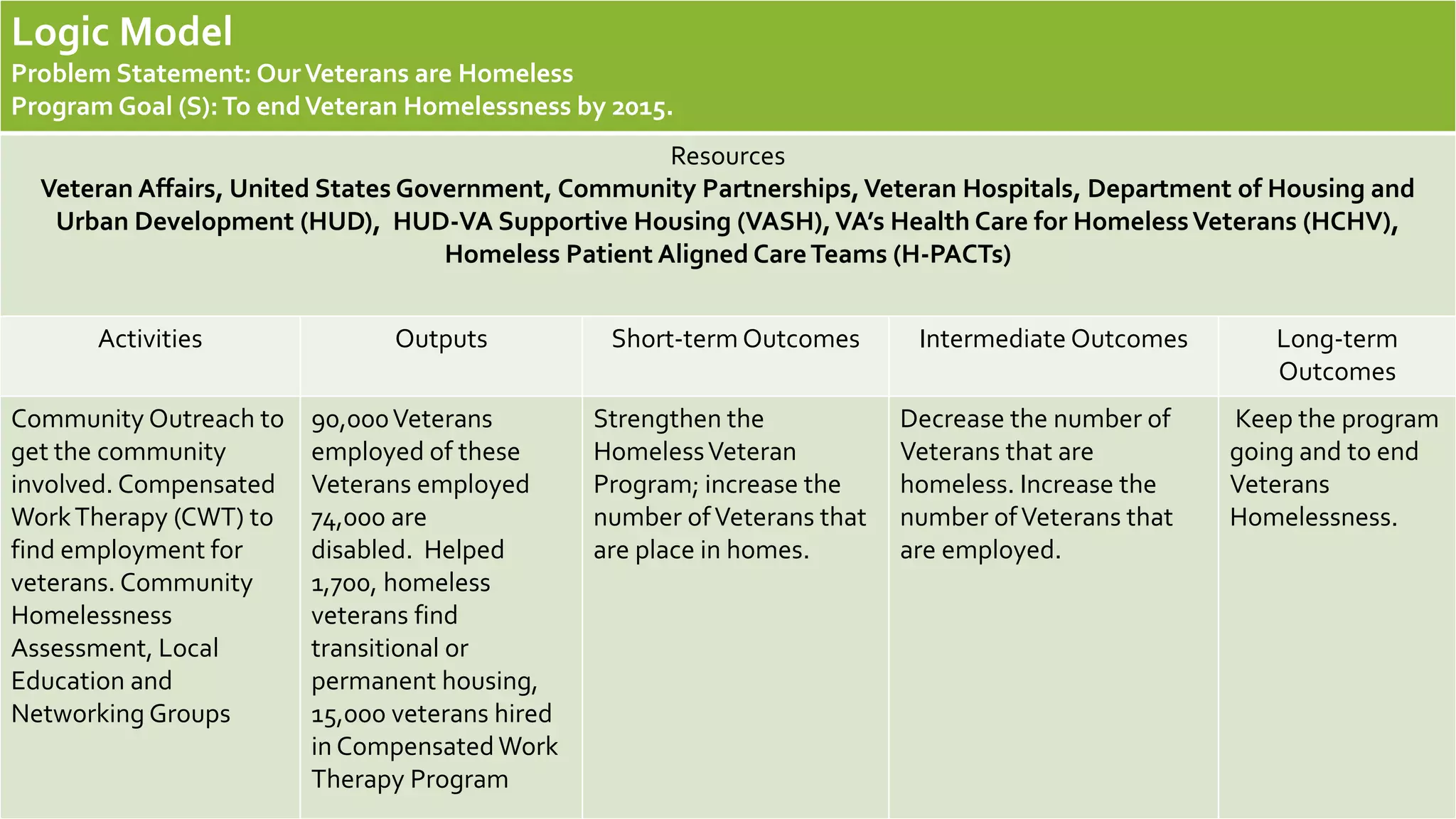
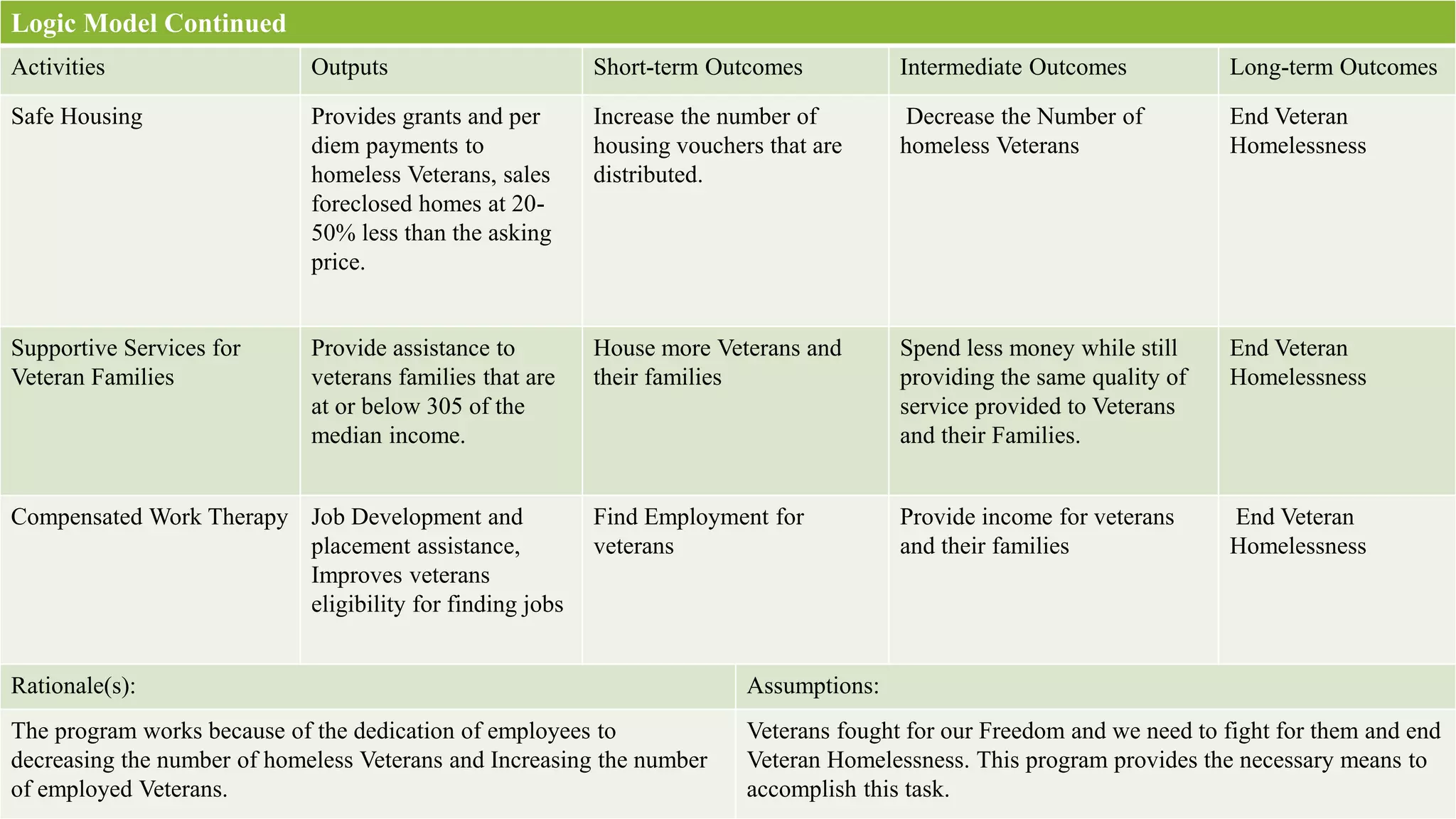
The document outlines an evaluation plan for assessing the effectiveness of the Veterans Homelessness Prevention Demonstration Program (VHPD). The evaluation aims to determine if VHPD's current strategies are working to end veteran homelessness and identify any shortcomings. A logic model is presented showing the program's resources, activities, outputs, and short and long-term outcomes. Key stakeholders are identified and evaluation questions are proposed to assess whether VHPD is achieving its goals. Methods such as a literature review and longitudinal study are suggested for collecting data, which will be reported in a paper and presentation. Effectiveness will be measured using statistical tests. Preliminary results indicate VHPD has reduced homelessness and is on track to meet its objective