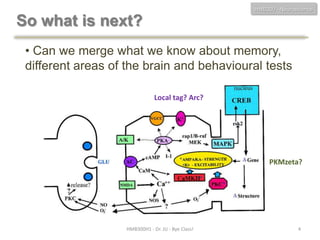
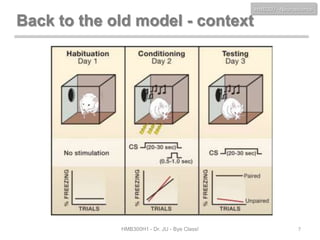
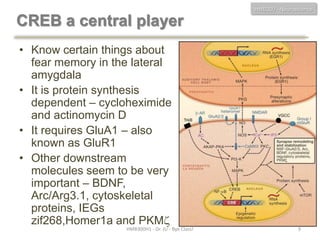
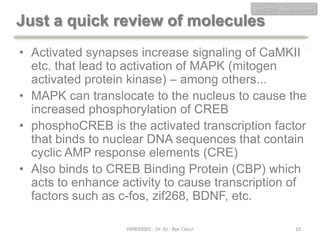
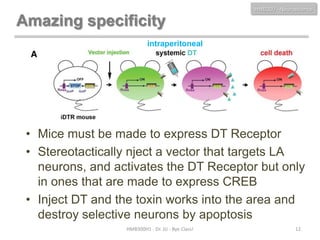
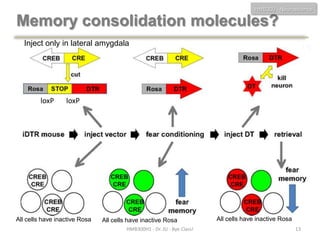
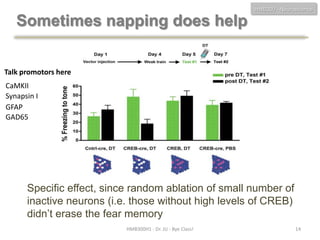
This document discusses neuroscience concepts related to memory and fear learning. It describes experiments using mice that were genetically engineered to express the diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) in all cells. Viruses were used to target neurons in the lateral amygdala that overexpressed cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) following fear conditioning. Injecting diphtheria toxin selectively ablated those CREB-overexpressing neurons and erased the previously learned fear memory, demonstrating that CREB plays a key role in fear memory consolidation in the amygdala. The document also reviews other molecules involved in fear memory such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor and discusses technical challenges to studying memory engrams at the neuronal level