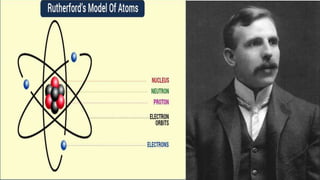
The ancient Greek philosophers Leucippus and Democritus first proposed the atomic theory in the 5th century BC. They believed that all matter is composed of indivisible atoms moving through empty space, and that different kinds of atoms exist which give matter its properties. John Dalton later expanded on this theory in the 19th century, stating that atoms are indivisible, indestructible particles that do not change during chemical reactions. J.J. Thomson's discovery of the electron led to the "plum pudding" atomic model, with electrons distributed throughout a sphere of positive charge. Ernest Rutherford then proposed the nuclear model of the atom as a tiny dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons.