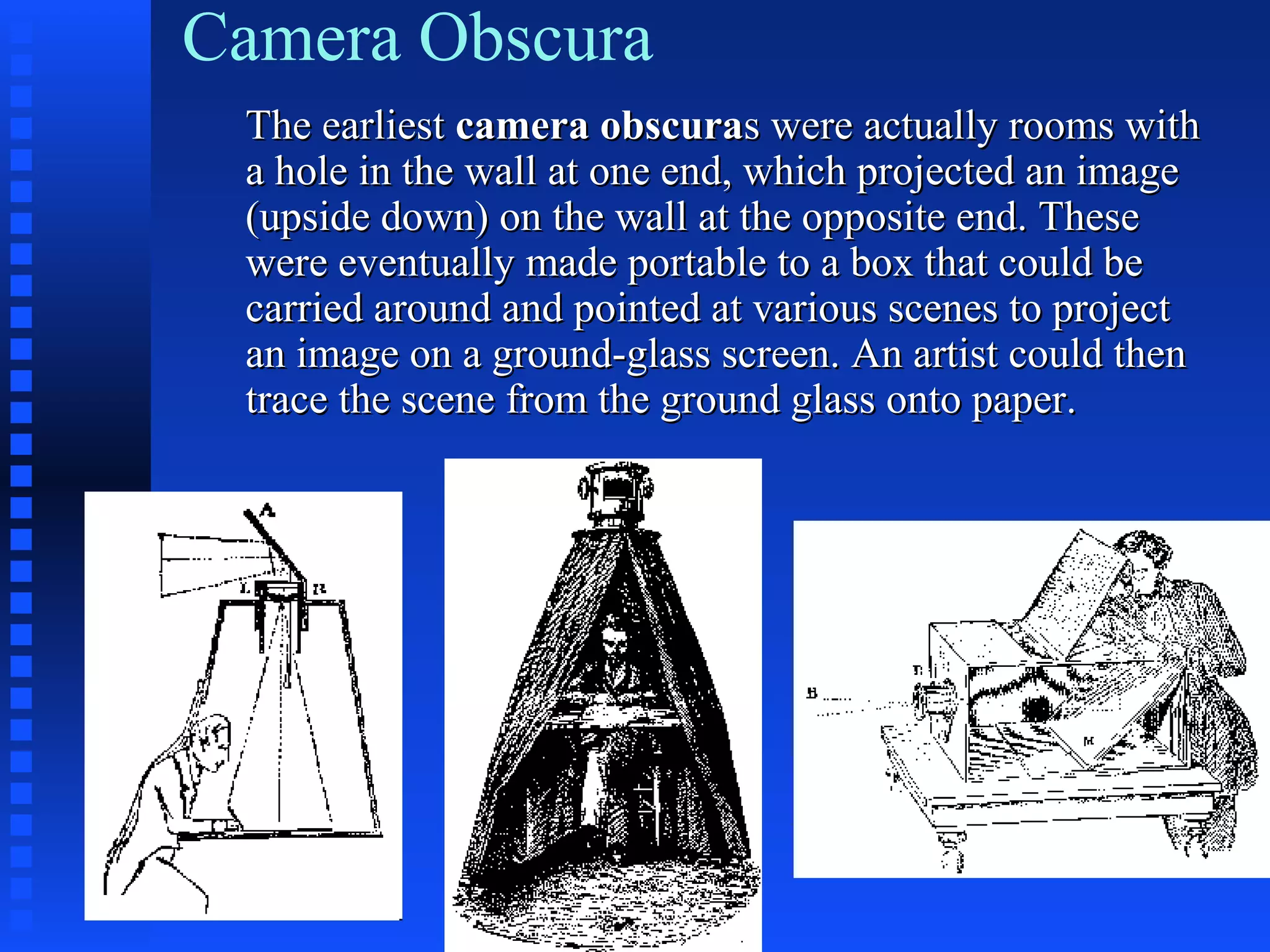
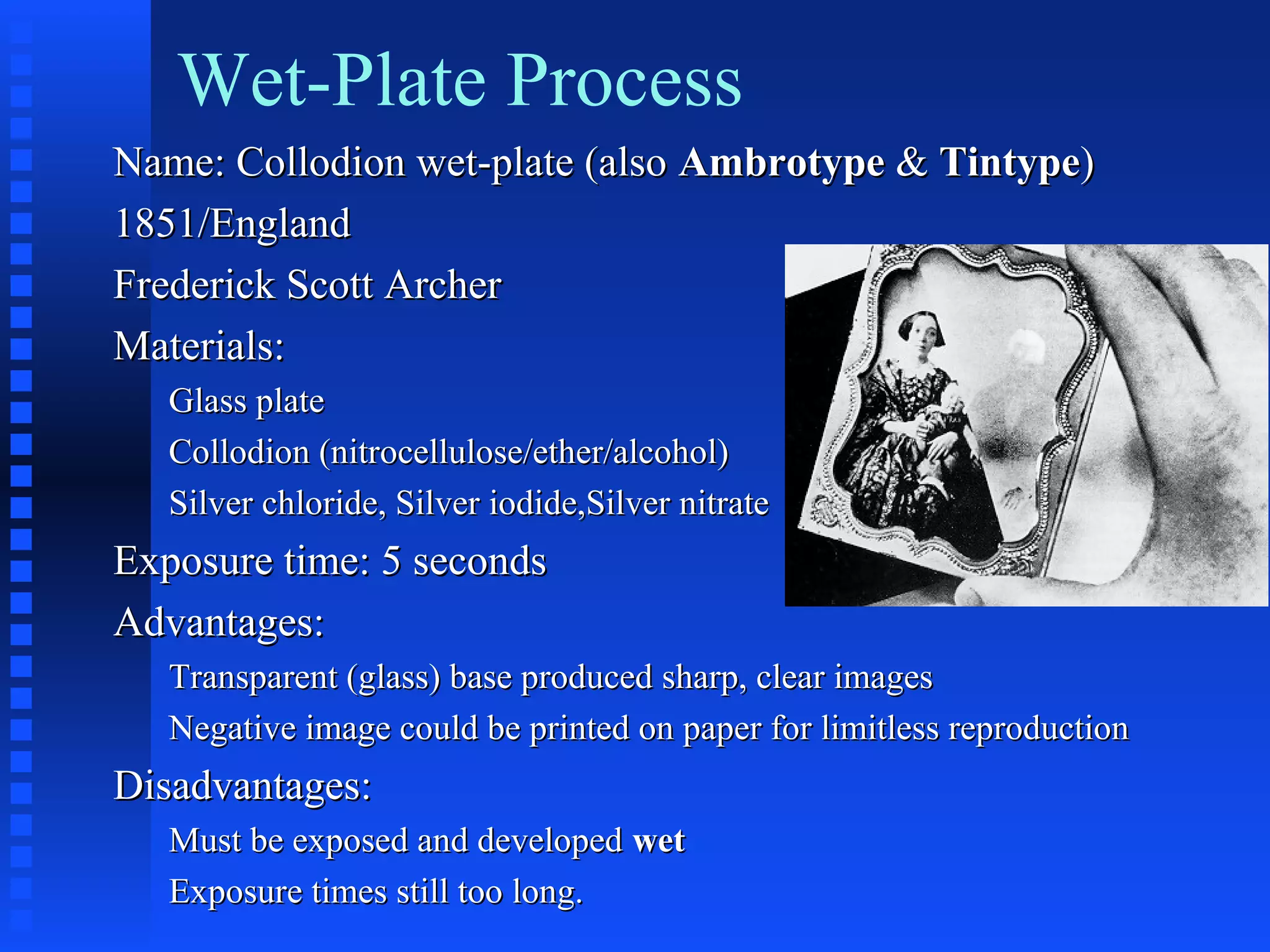
The document traces the history of imaging from early cave art and hieroglyphics through developments in camera obscura, the first photograph or "heliograph" created by Nicéphore Niépce in 1826, and the introduction of the daguerreotype and calotype processes. It discusses improvements including the wet plate collodion process, gelatin dry plates, film, color photography technologies like Kodachrome, and digital developments like the first digital SLR and camera phones. Key events and inventors in the transition from manual to chemical to digital capture are highlighted.