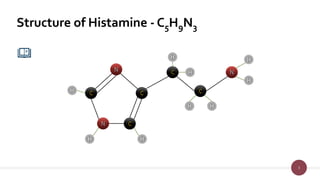
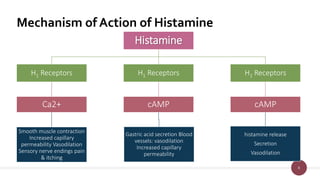
Histamine is a tissue amine abundant in animal tissues and plays critical roles in hypersensitivity and physiological processes. It is synthesized from histidine in mast cells and has notable pharmacological actions such as vasodilation and increased capillary permeability, mediated through H1 and H2 receptors. Adverse effects of histamine release can include itching, hypotension, and bronchospasm.