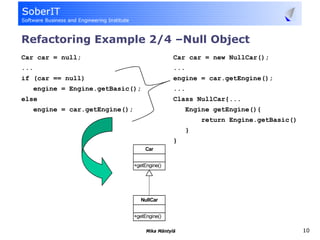
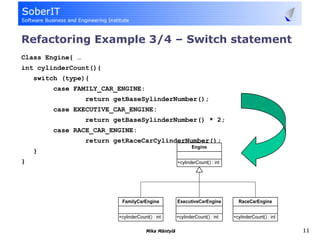
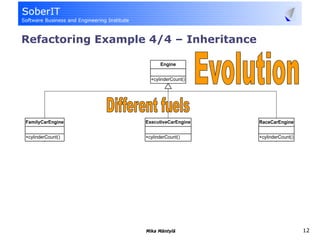
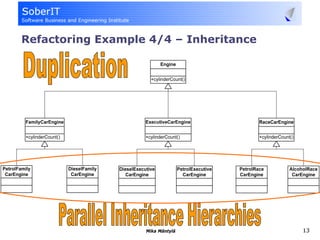
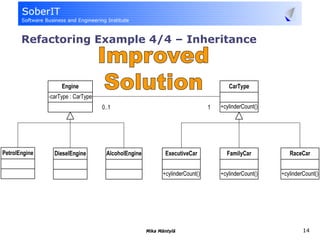
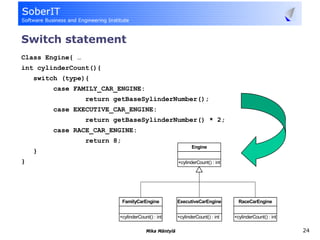
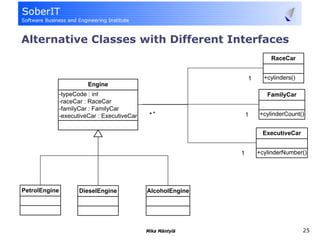
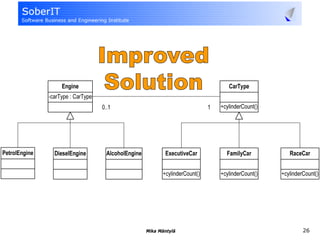
This document discusses software refactoring and provides examples. It defines refactoring as improving the design of existing code without changing its observable behavior. Refactoring is important for software evolution as designs inevitably become outdated. Examples of refactoring techniques include extracting methods, using null objects, replacing switch statements with polymorphism, and inheritance. The document also discusses bad code smells and anti-patterns that refactoring can help address, such as long methods, large classes, duplicate code, and high coupling between classes.