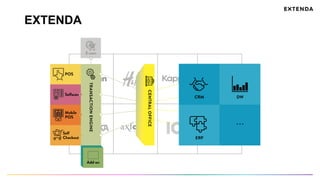
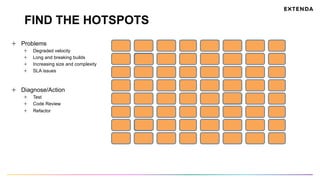
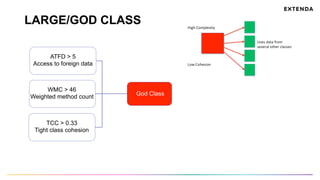
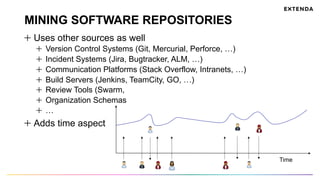
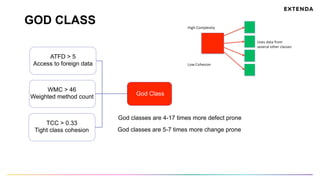
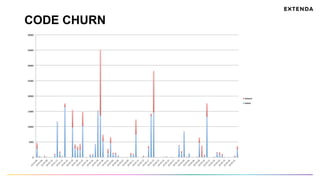
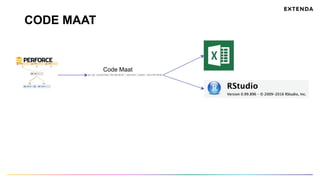
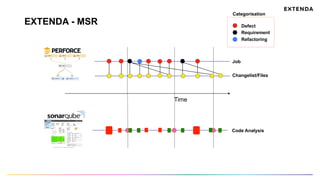
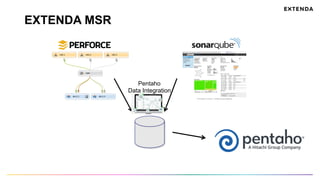
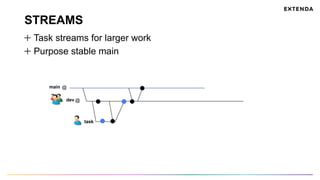
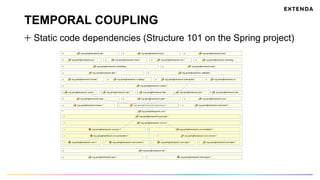
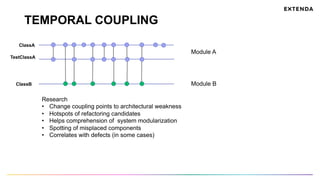
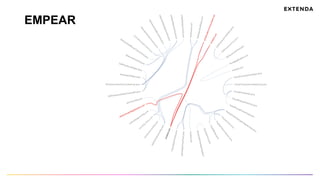
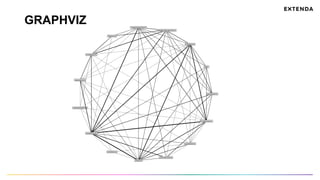
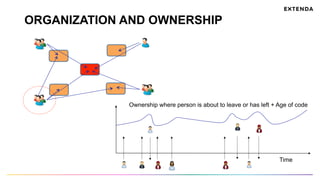
The document discusses the challenges of determining when and how to refactor code, emphasizing the importance of analyzing software evolution, code decay, and technical debt. It introduces methodologies for identifying 'god classes,' code churn, and architectural weaknesses through mining software repositories and utilizing tools like Code Maat. Ultimately, it aims to provide metrics that guide refactoring efforts by highlighting the business value and urgency of maintaining code quality.