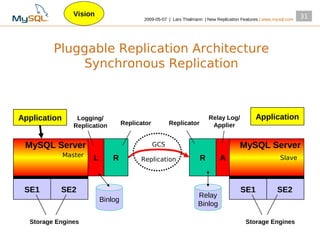
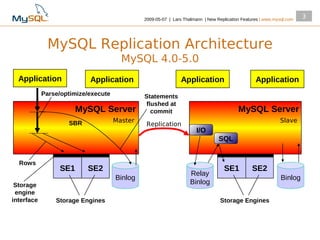
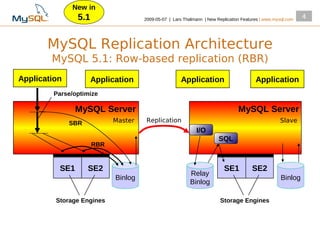
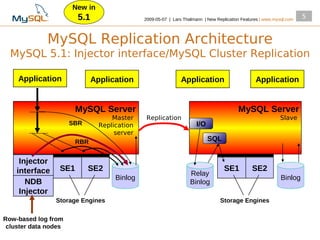
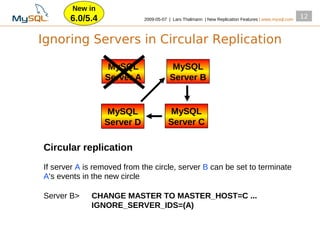
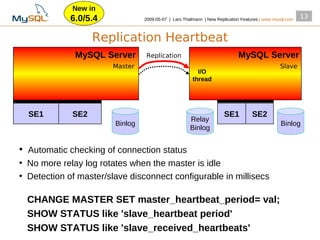
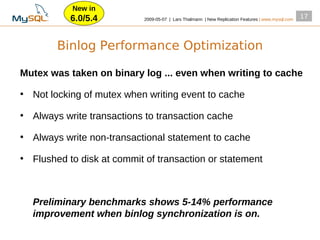
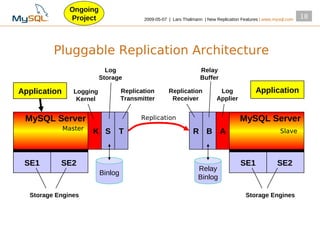
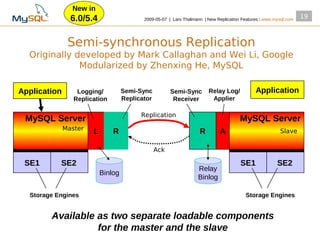
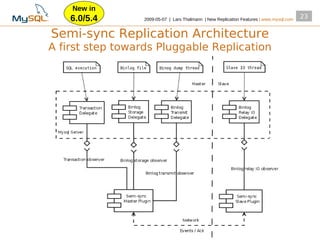
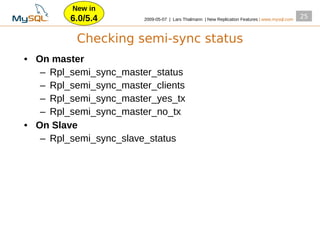
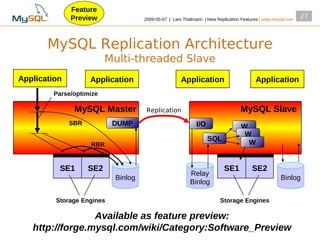
This document summarizes new replication features in MySQL versions 5.1, 6.0, and 5.4. Key features include row-based replication in 5.1, ignoring servers in circular replication in 6.0/5.4, replication heartbeat and slave position synchronization in 6.0/5.4, automatic relay log recovery in 6.0/5.4, and semi-synchronous replication as a pluggable architecture in 6.0/5.4. Ongoing projects previewed include multi-threaded replication slaves and time-delayed replication.



![Used for
5.1 20090507 | Lars Thalmann | New Replication Features | www.mysql.com
7
Assertions, ie, no diffbased test execution verification.
Execution report based on TAP output.
Tests are simple perl modules.
Platform independent (relies on perl VM).
MySQL Version independent tests.
$ ./bin/nuts.pl verbose test replication
1..7
ok 1 executing command CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS test
ok 2 executing command USE test
ok 3 executing command CREATE TABLE t (a int)
ok 4 executing command INSERT INTO t VALUES (10)
not ok 5 compare master slave contents
# Failed test 'compare master slave contents'
# at /home/acorreia/workspace.sun/repository.mysql/nuts0.1/suites/samples/replication.pm line 34.
ok 6 executing command DROP TABLE IF EXISTS t
ok 7 executing command DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS test
Failed 1/7 subtests
[06:39:06]
Test Summary Report
samples::replication (Wstat: 0 Tests: 7 Failed: 1)
Failed test: 5
Files=1, Tests=7, 37 wallclock secs ( 0.24 usr 0.12 sys + 1.98 cusr 1.22 csys = 3.56 CPU)
Result: FAIL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/090507-newreplicationfeatures2-091201100219-phpapp02/85/090507-New-Replication-Features-2-7-320.jpg)













![Feature
Preview 20090507 | Lars Thalmann | New Replication Features | www.mysql.com
30
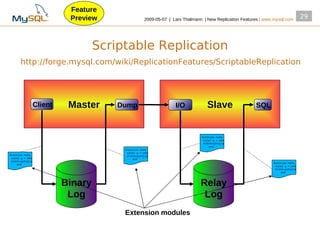
Scriptable Replication
Paul Tuckfield’s (Google/YouTube)
The “oracle” algorithm
module(..., package.seeall); require “luasql.mysql”
pattern = {
["UPDATE%s+(%w+).*%s(WHERE.*)"] = "SELECT * FROM %1 %2",
["DELETE%s+FROM%s+(%w+).*%s(WHERE.*)"] = "SELECT * FROM %1 %2",
}
env = luasql.mysql()
con = env:connect("test", “root”, “”, “localhost”, mysql.port)
function before_write(event)
local line = event.query
if not line then return end
for pat,repl in pairs(pattern) do
local str = string.gsub(line, pat, repl)
if str then con:execute(str); breakend
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/090507-newreplicationfeatures2-091201100219-phpapp02/85/090507-New-Replication-Features-2-30-320.jpg)