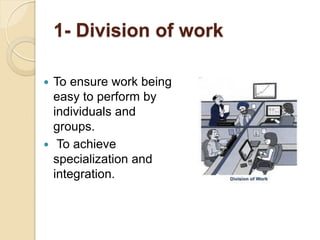
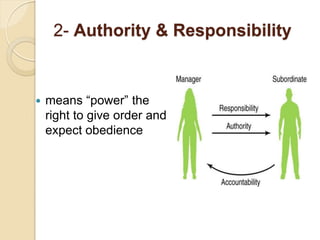
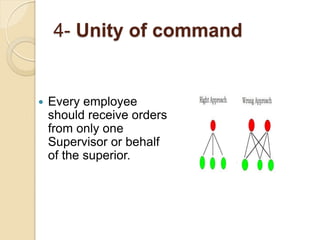
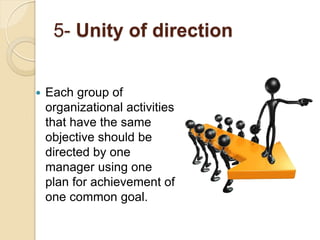
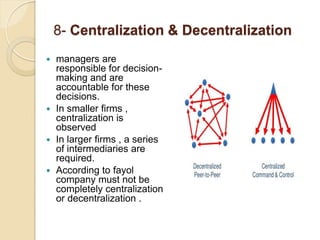
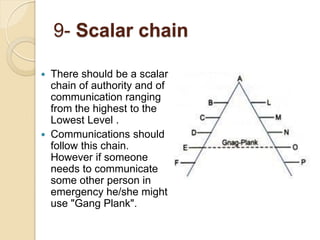
Henri Fayol developed 14 principles of management that aim to increase organizational efficiency. The principles include division of work, authority and responsibility, discipline, unity of command, and subordination of individual interests to group goals. Fayol also identified six management functions - planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, controlling - and argued that managers should follow principles like order, equity, stability of personnel, and esprit de corps. His work contributed to establishing administrative management theory and emphasizing data-driven decision making.