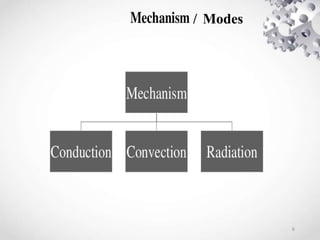
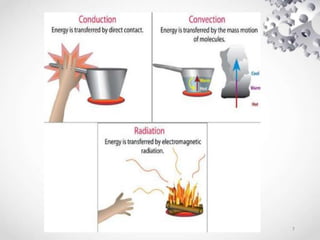
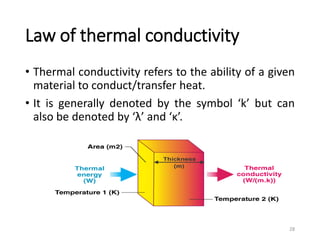
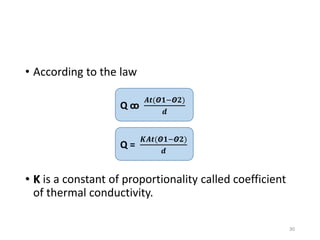
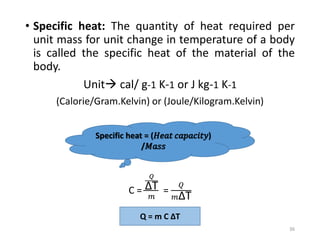
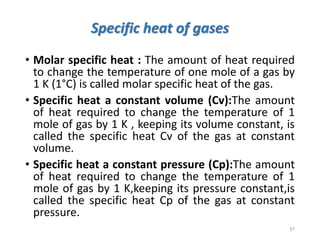
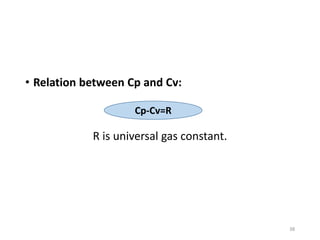
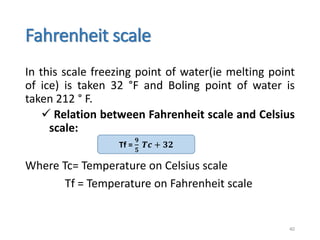
The document provides an overview of thermodynamics, focusing on key concepts such as heat transfer mechanisms, thermal conductivity, and the properties of black bodies. It discusses the implications of thermal conductivity in real-world applications, specific heat, and introduces important temperature scales and their conversions. Additionally, it touches upon foundational laws in thermodynamics, including Kirchhoff's law and the Stefan-Boltzmann law.