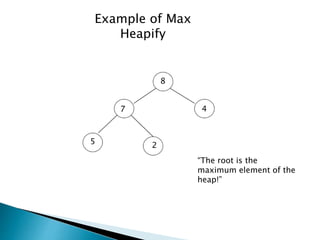
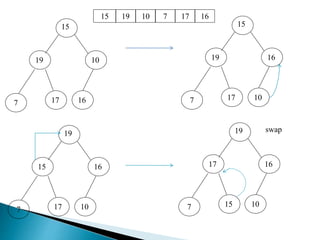
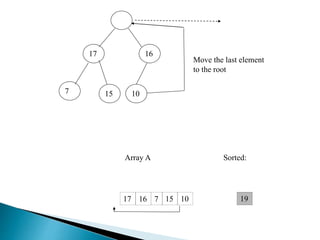
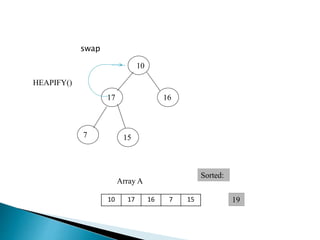
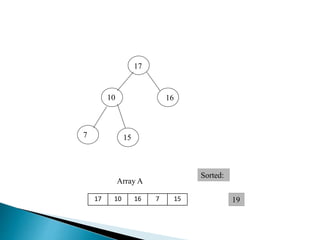
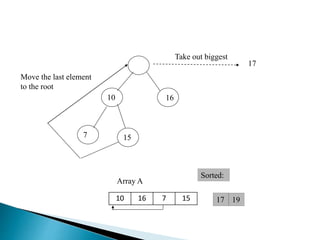
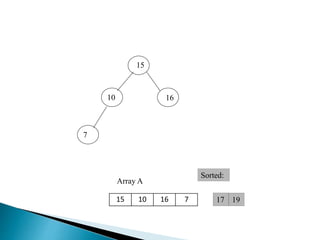
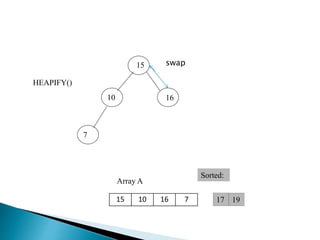
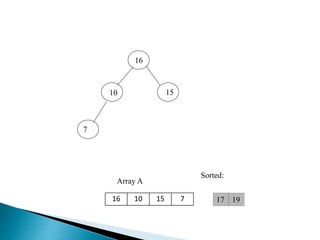
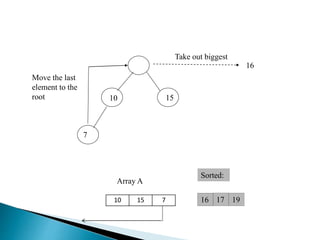
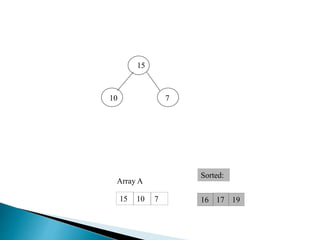
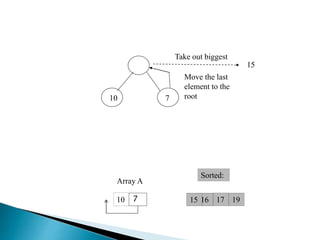
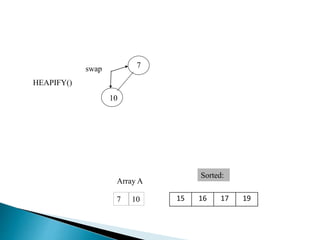
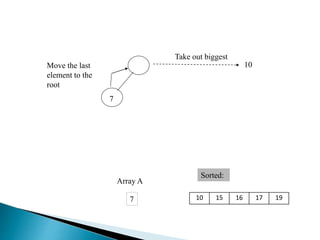
Heap is a complete binary tree represented as an array. There are two main types: min heap and max heap. A max heap has the largest element at the root and each parent is greater than or equal to its children. Heap sort uses the heap property to sort an array in O(n log n) time. It first builds a max heap from the array. Then it repeatedly removes the maximum element from the heap, adding it to the sorted portion of the array.

![Heap is a “complete” binary tree, usually
represented as an array.
Types:
Min Heap (largest element at root)
A[parent(i)]≥A[i]
Max Heap
A[parent(i)]≤A[i]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faizasaleemheapsortassigment120162020-180622140919/85/Heap-Sort-2-320.jpg)



![ BUILD‐MAX‐HEAP(A)
1. heap‐size[A] ← length[A]
2. for i ← ⌊length[A]/2⌋ downto 1
3. do MAX‐HEAPIFY(A,i)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faizasaleemheapsortassigment120162020-180622140919/85/Heap-Sort-20-320.jpg)
