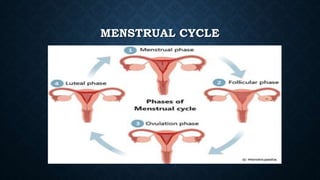
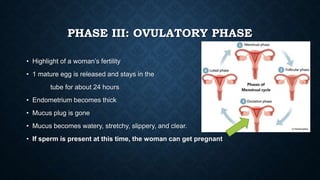
This document provides information about puberty, reproductive health, sexually transmitted infections, and HIV/AIDS for adolescents. It defines puberty and the physical and emotional changes that occur. It discusses the male and female reproductive systems and menstrual cycle. It aims to provide adolescents with accurate information to make responsible decisions about relationships and sexuality while dispelling common myths. The key messages are that menstruation is a normal part of development and communication between partners is important for family planning and preventing STIs including HIV.