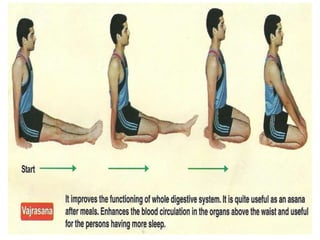
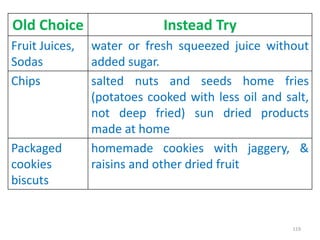
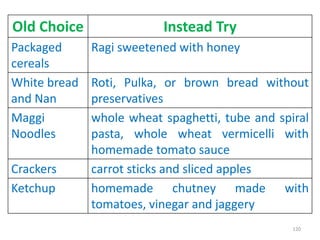
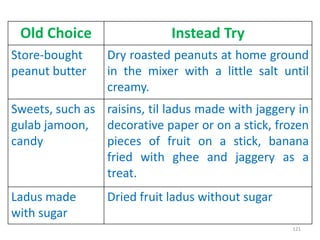
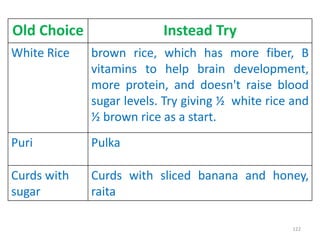
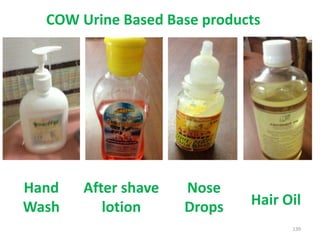
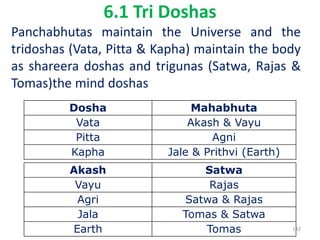
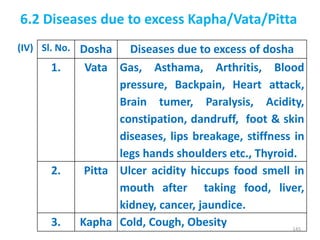
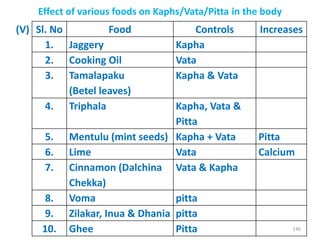
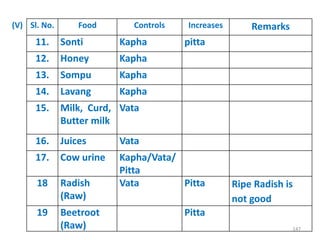
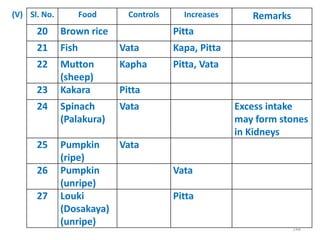
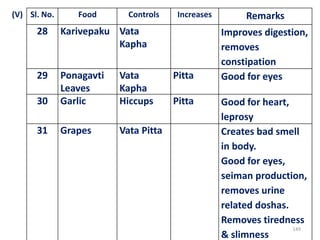
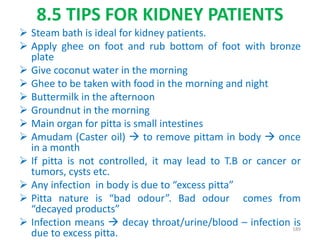
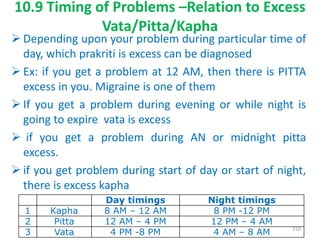
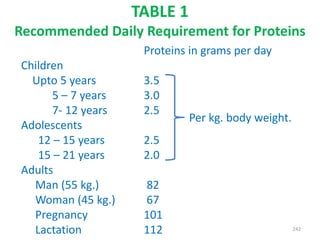
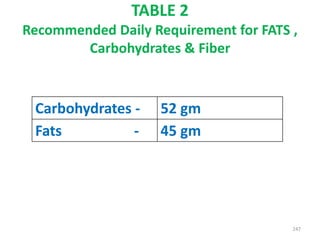
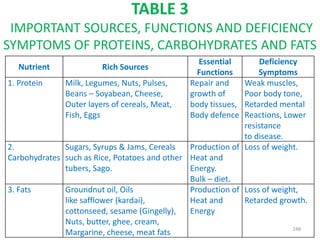
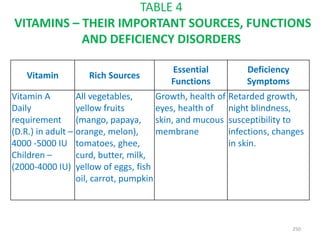
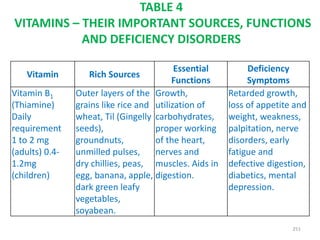
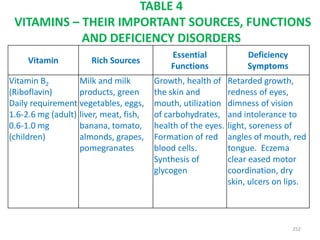
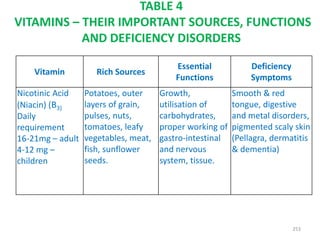
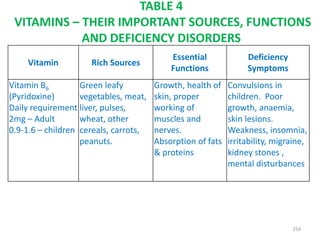
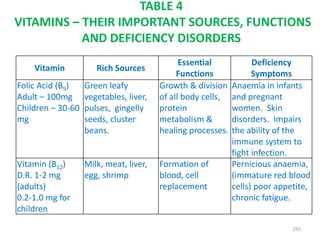
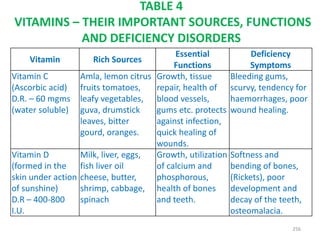
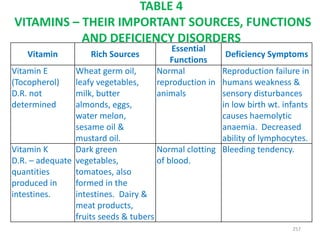
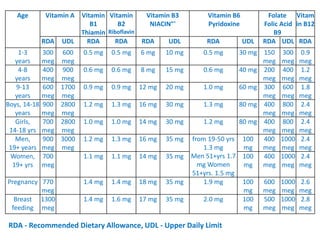
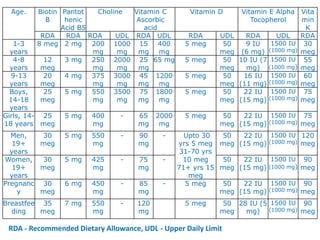
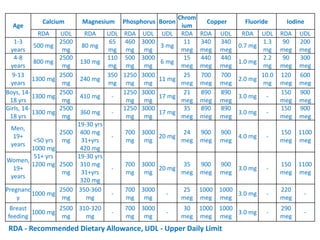
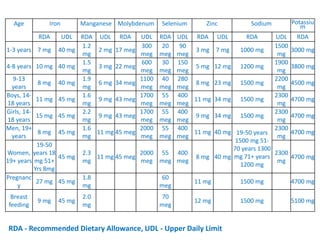
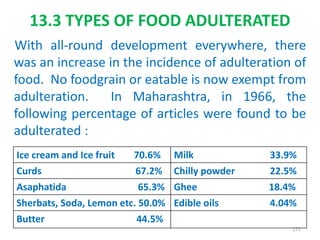
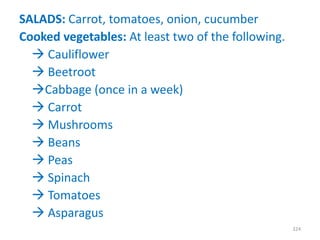
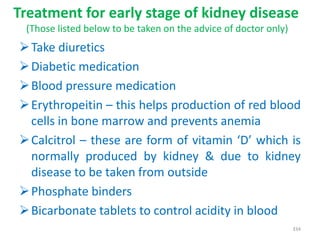
This document provides an introduction to holistic health principles from Ayurveda as described by Maharshi Vagbhata. It discusses how Indian culture and practices were historically suited to the climate but Western influence has led to the adoption of habits detrimental to health. Key tips are summarized, including avoiding processed foods; cooking with air and sunlight; drinking water properly; balancing doshas; and controlling vata, pitta, and kapha. Spreading awareness of these principles through various community channels is also recommended.














































![3.1 (e) Effect of taking water after food
Enzymes secrete immediately after eating like
when a switch is ‘ON’, bulb glows.
• When digestion is going, if water is taken,
enzymes become calm and food becomes stale.
• Gas generates due to stale food & cholesterol
increases due to stale food.
• Gases spread throughout body & difficult to
control.
• 103 diseases caused due to such gas. Example,
Acidity, Piles, Cancer etc.
• Bad Cholesterol i.e. LDL is produced when food is
in stale condition
How much water to be taken?
• Water intake = [Weight / 10 – 2] 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/healthtipslatest-160714051920/85/Health-tips-48-320.jpg)