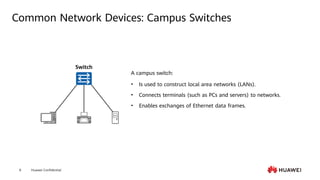
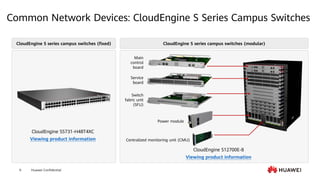
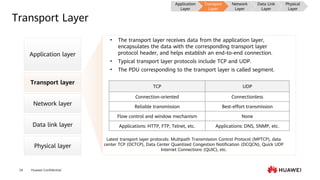
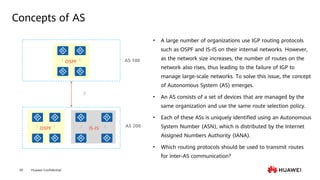
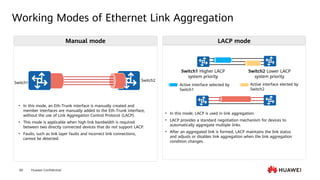
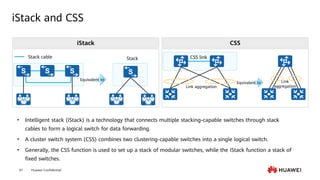
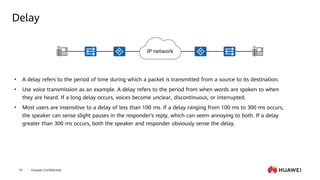
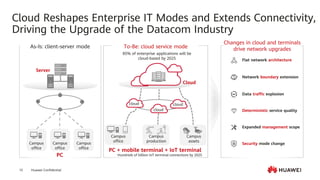
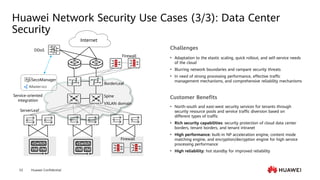
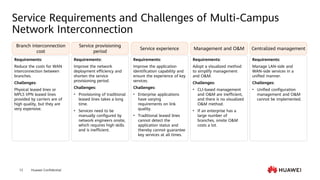
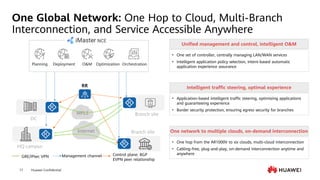
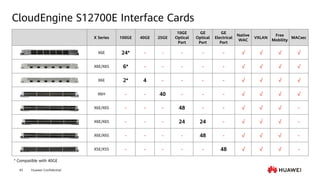
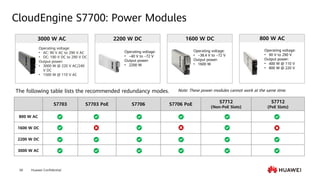
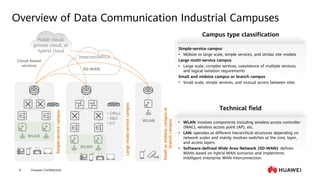
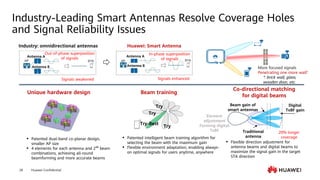
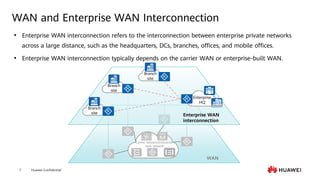
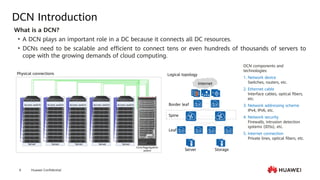
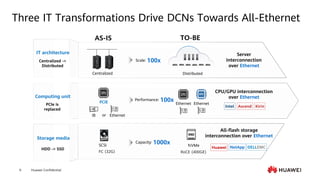
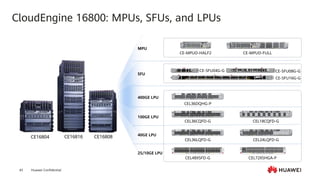
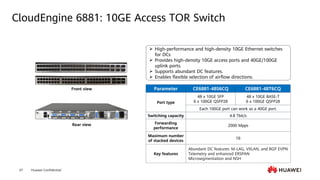
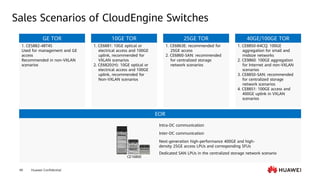
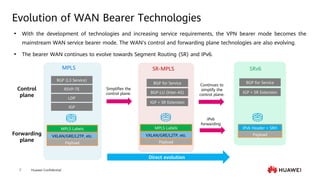
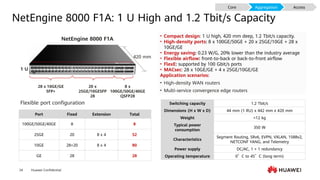
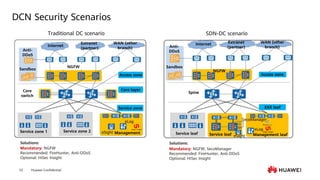
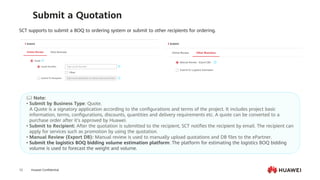
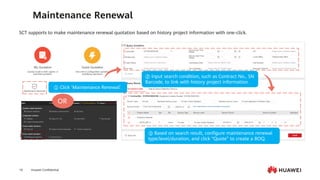
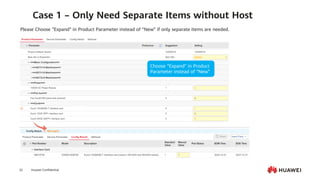
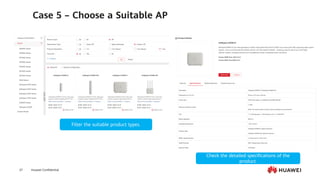
This document provides an overview of data communication network basics. It discusses the common components of a data communication network including routers, switches, firewalls, wireless controllers, access points, PCs, printers and servers. It then describes some of the basic concepts around IP routing, Ethernet switching, network security, WAN technologies, network management and QoS. The objectives are to describe common network architectures, devices and their functions, as well as introduce basic protocols and models including TCP/IP, IPv4, IPv6, routing, switching and the OSI model. The document is an introductory course that covers these fundamental network concepts.