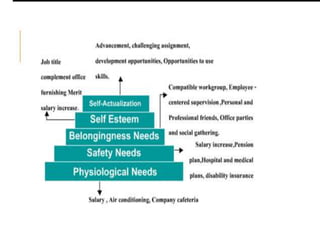
This document discusses motivation and reward systems. It covers several theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, ERG theory, McClelland's acquired needs theory, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. It also discusses process theories of motivation such as Vroom's expectancy theory, Adams' equity theory, and Locke's goal setting theory. The document then covers types of rewards including intrinsic and extrinsic rewards. It discusses reinforcement theory and different reinforcement schedules. It defines job analysis, job description, job evaluation, and different approaches to reward systems such as skill-based pay.