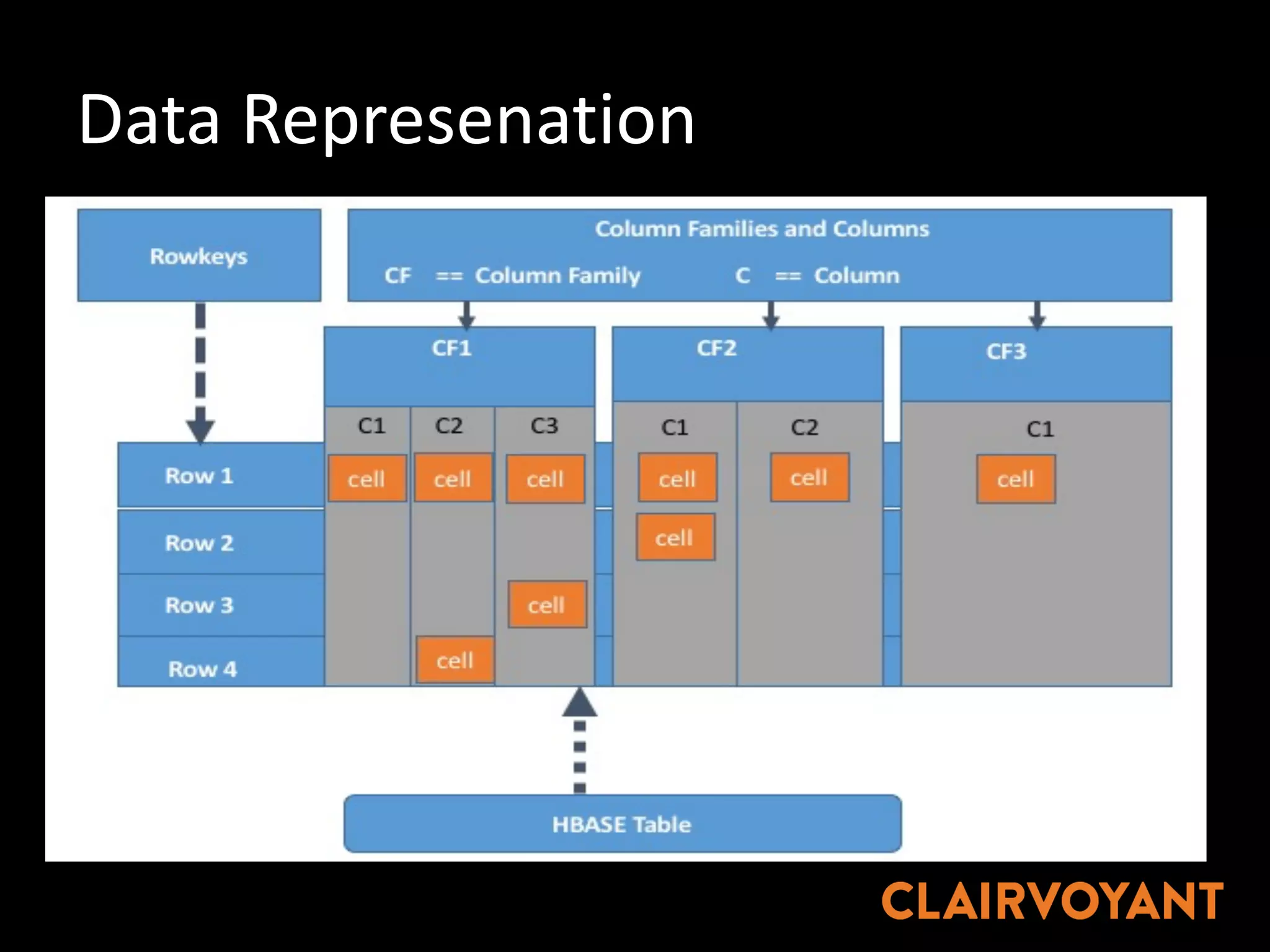
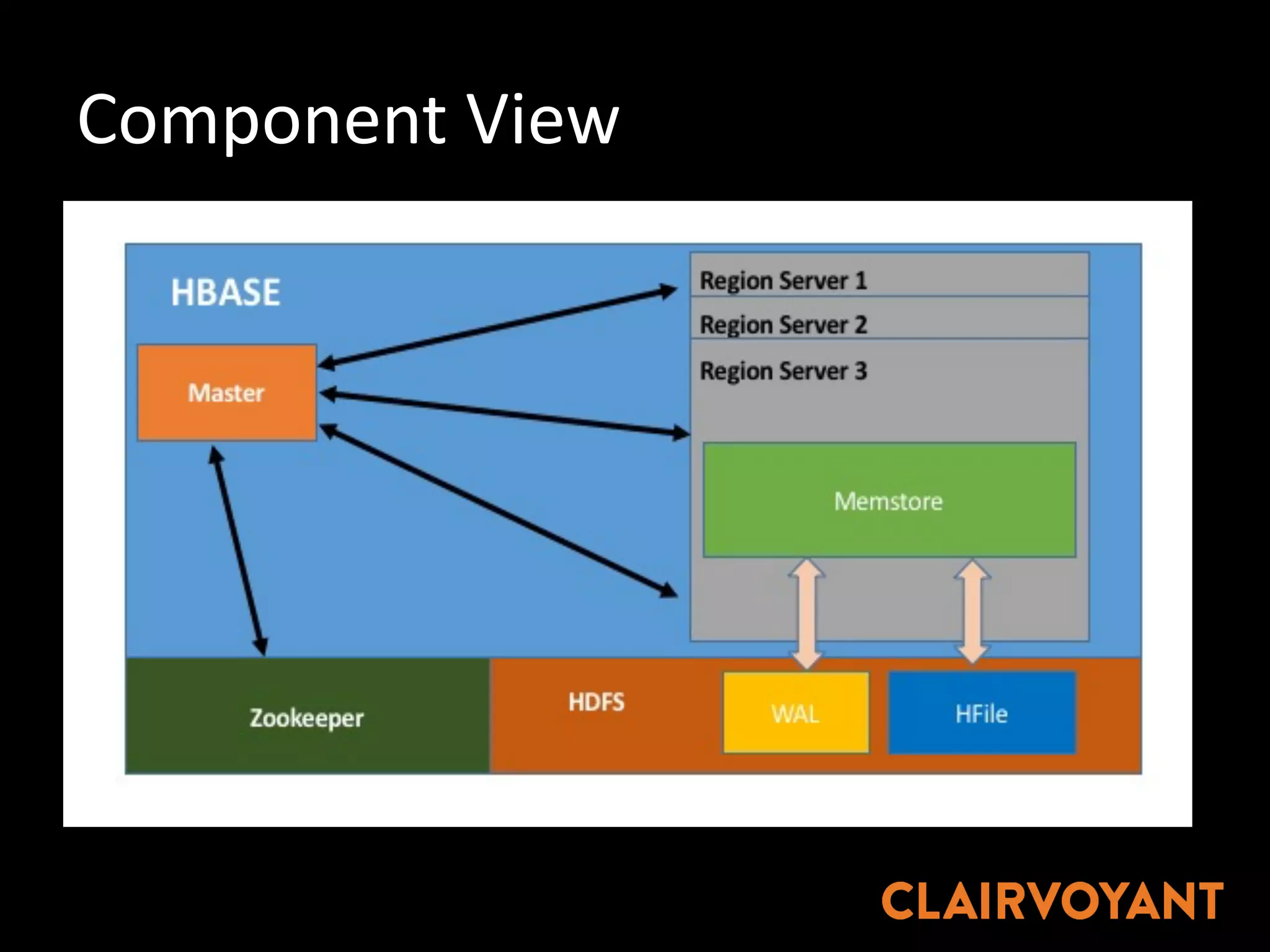
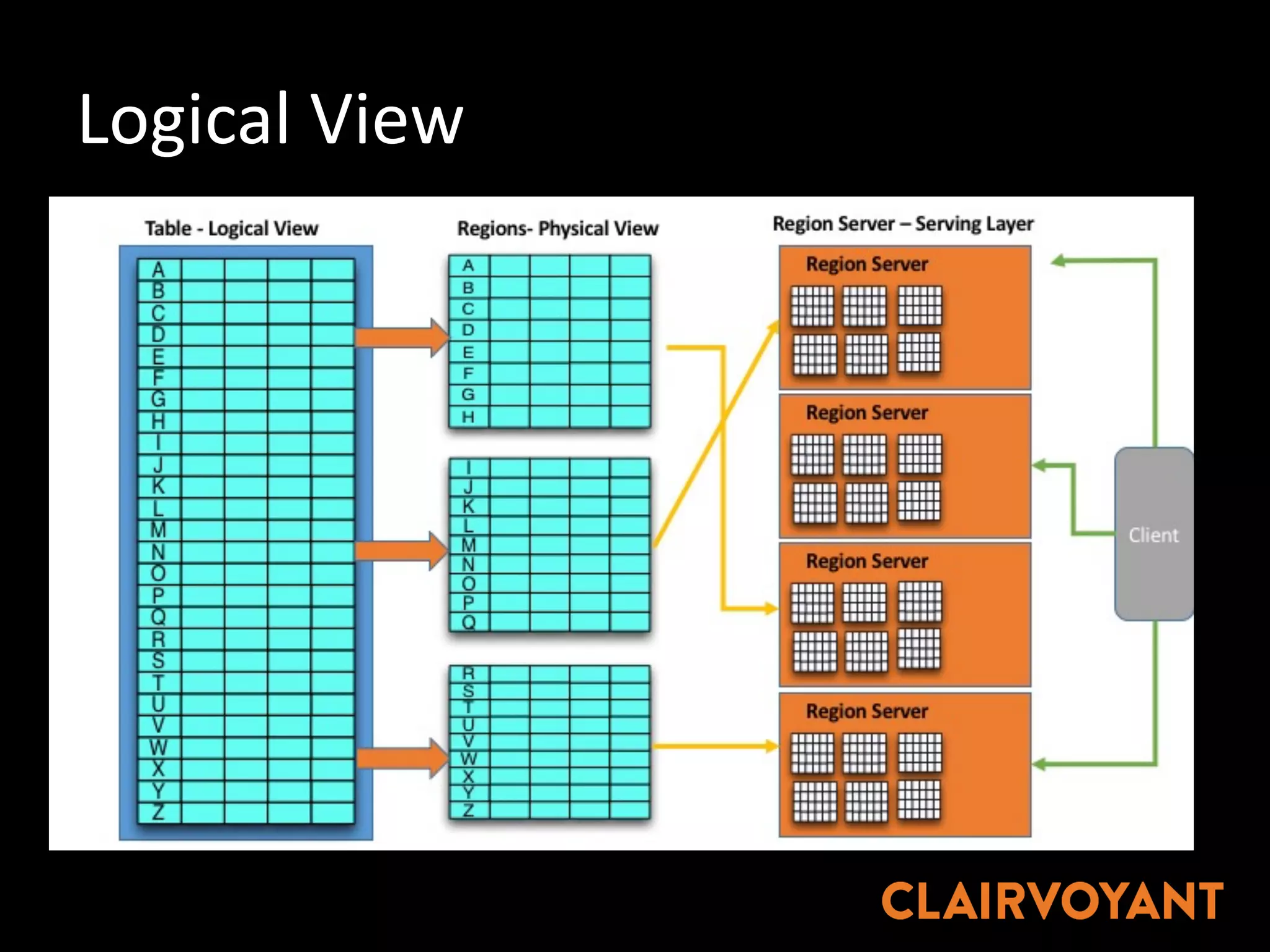
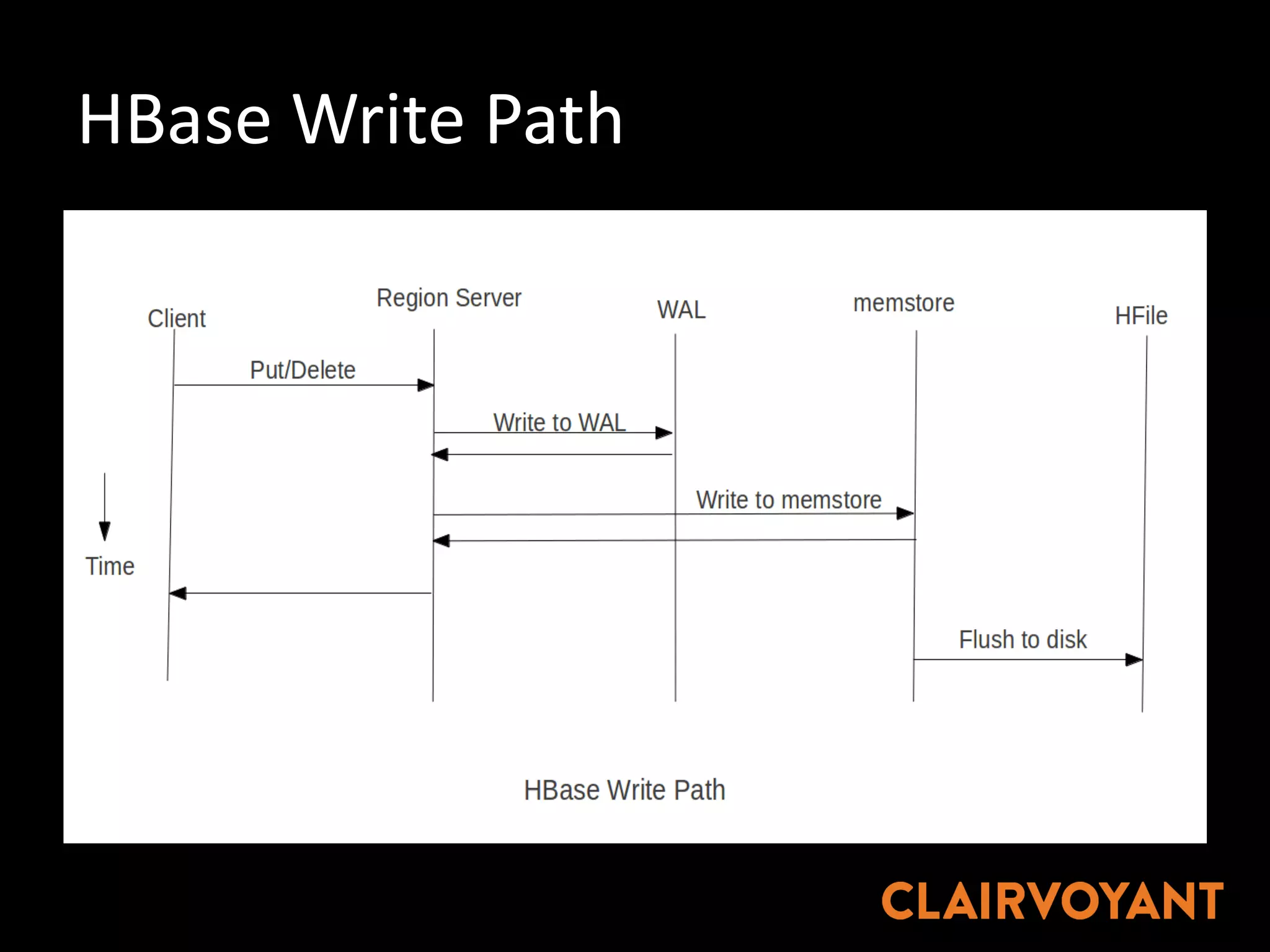
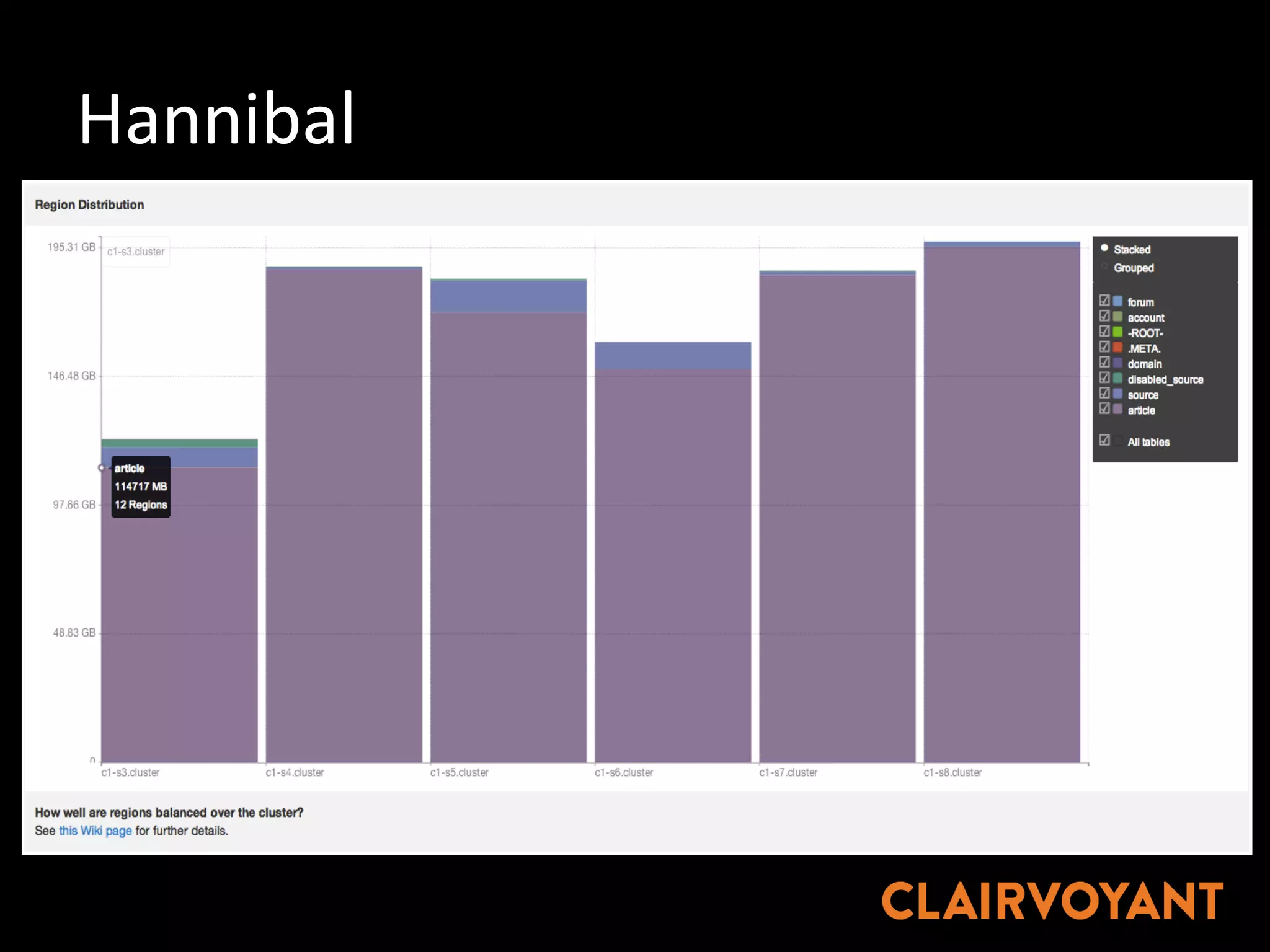
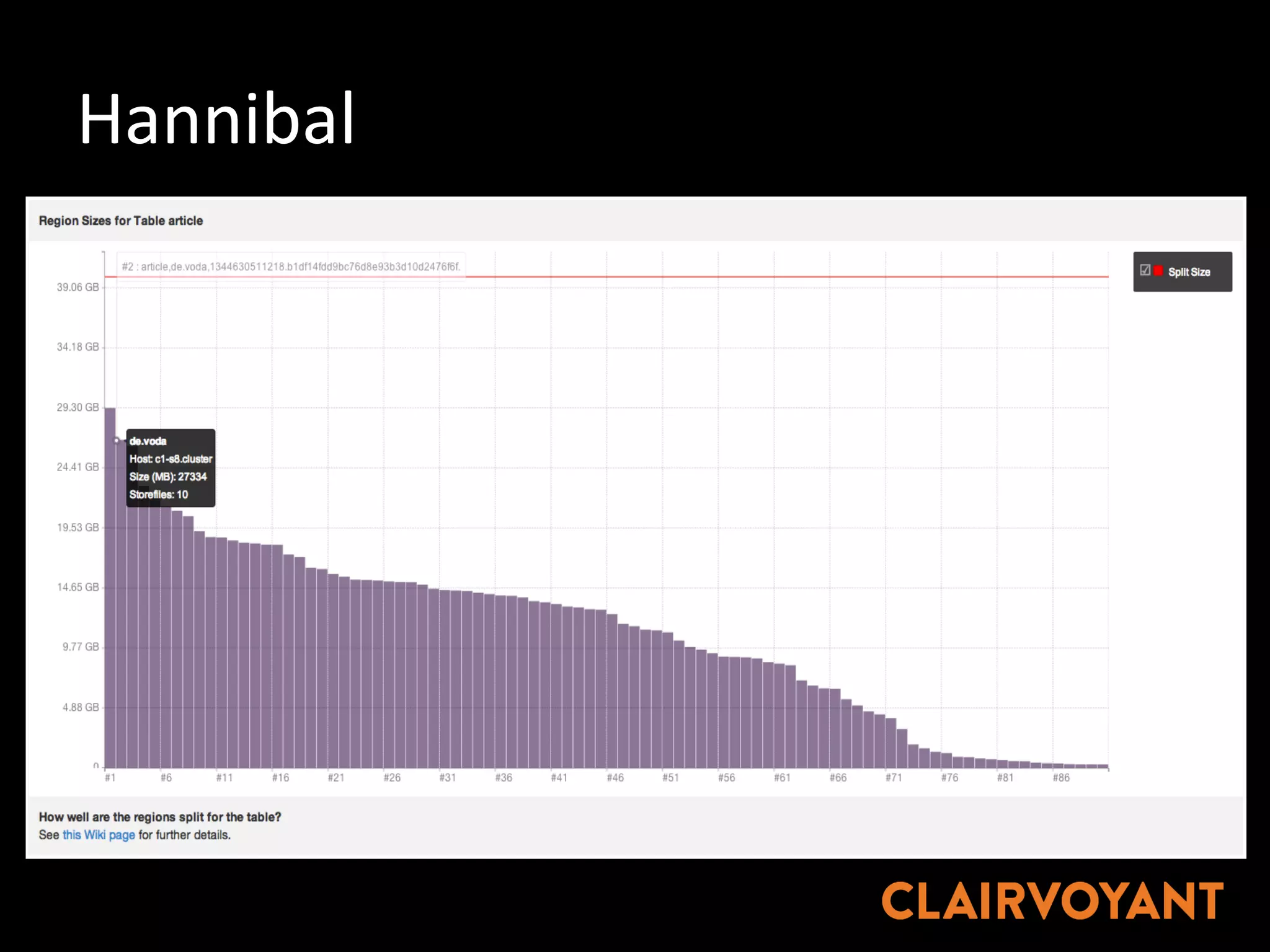
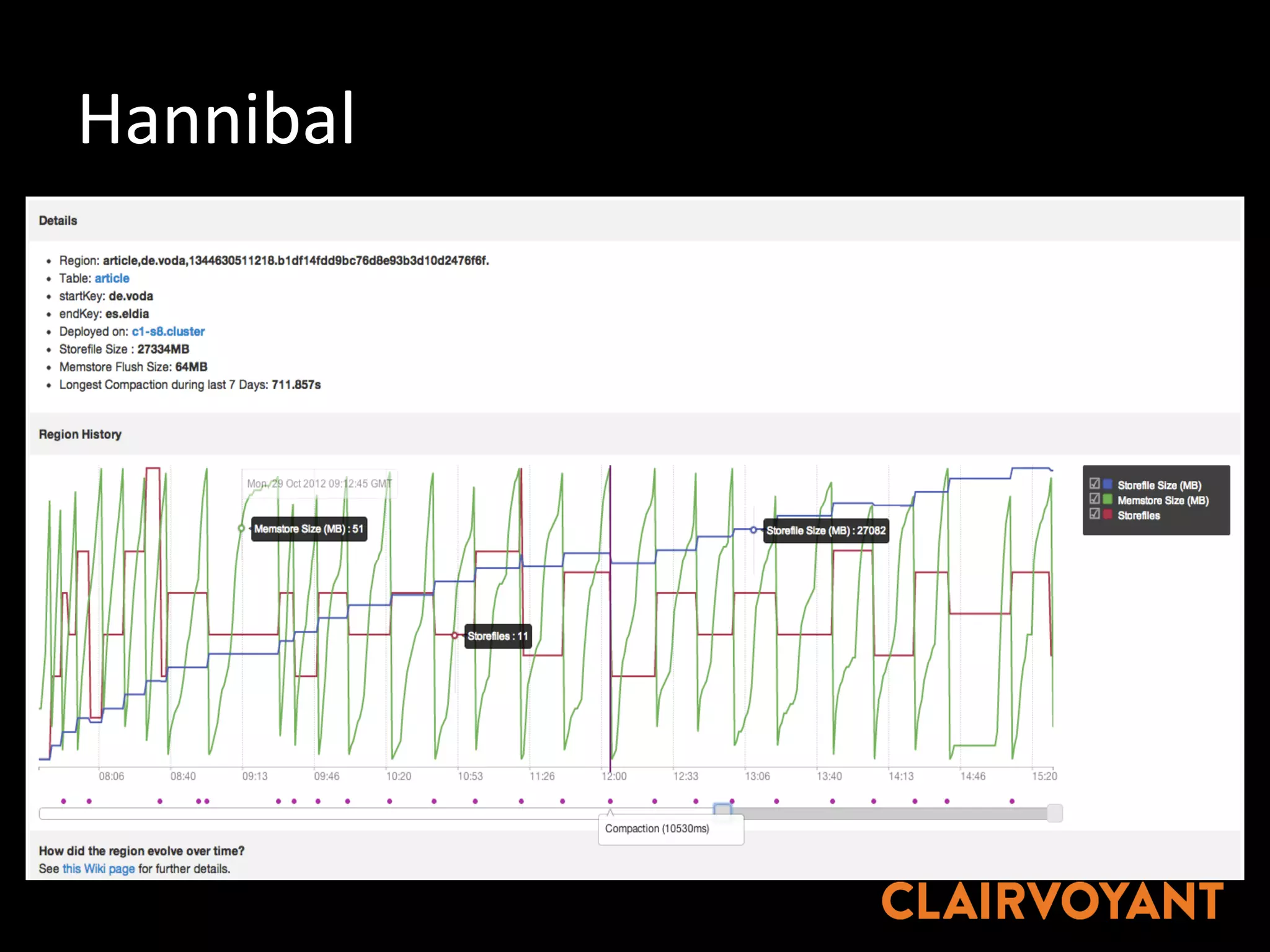
The document provides an extensive overview of HBase, a non-relational, distributed column-oriented database, detailing its architecture, data model, and common operational challenges. It discusses best practices for deployment, data representation, write and read paths, performance tuning, and tools like Apache Phoenix for SQL support. The document also addresses troubleshooting techniques, monitoring, and the importance of proper key design for optimal data retrieval.