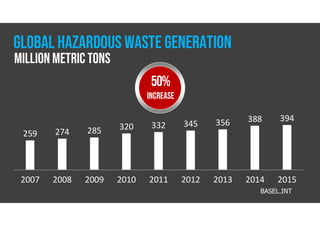
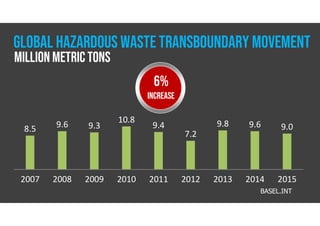
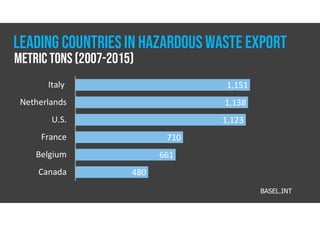
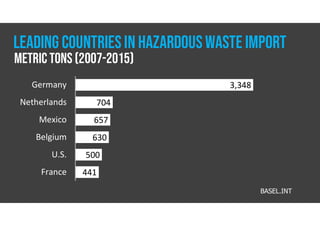
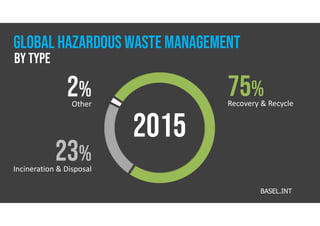
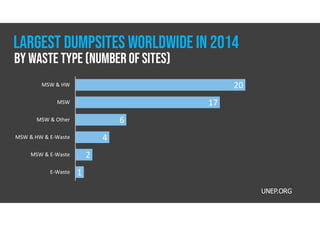
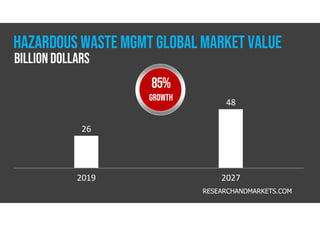
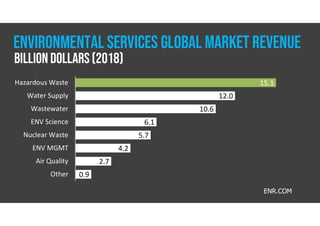
The document discusses hazardous waste, defining it as waste that poses dangers to humans and the environment, and outlines the management process established by the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). It details the roles of hazardous waste generators, transporters, and treatment facilities, emphasizing the importance of recycling and safe disposal. Additionally, it presents statistics on global hazardous waste generation and transboundary movement, highlighting the need for sustainable waste management practices.