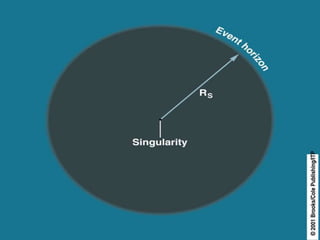
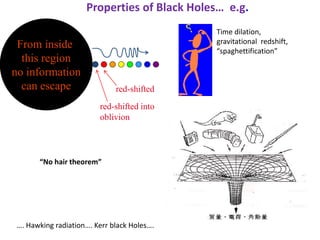
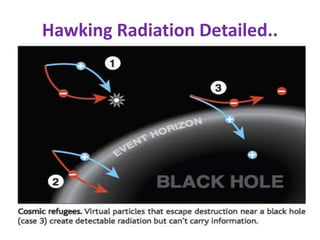
Hawking radiation is a theoretical prediction of blackbody radiation emitted by black holes due to quantum effects near their event horizon, proposed by physicist Stephen Hawking in 1974. This phenomenon leads to black hole evaporation, where the mass of the black hole decreases over time, eventually causing it to disappear. The document also covers the properties and types of black holes, along with resources for further understanding of Hawking radiation.