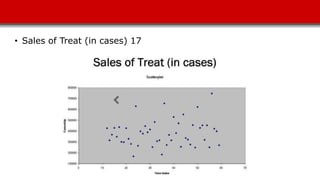
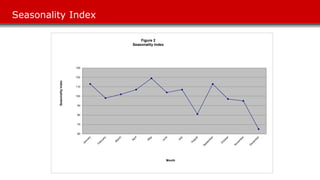
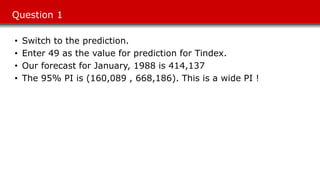
The document discusses sales forecasting techniques for Harmon Foods' breakfast cereal product Treat. It describes wide variability in past sales forecasts, ranging from 50-200% of actual sales. Various factors that influence demand are examined, including seasonality, promotions, and competitor strategies. The case study develops a regression model to forecast sales based on time trends, seasonality, consumer packs, and dealer allowances. Recommendations focus on timing promotions during high seasonal periods and emphasizing more effective dealer allowances over consumer packs.