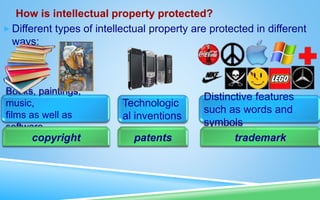
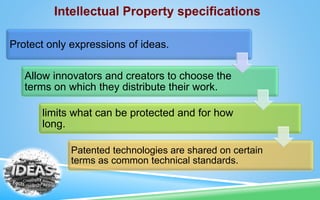
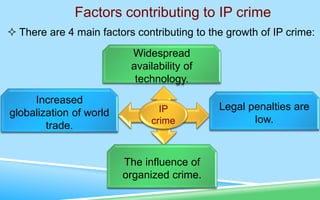
This document discusses intellectual property and related topics. It defines intellectual property as creations of the mind like inventions, literary works, symbols and designs. Intellectual property is protected through copyright for creative works, patents for inventions, and trademarks for distinctive features. The growth of the internet has challenged these protections by making information easily copied. Issues around ownership of knowledge, fair use, and managing intellectual property crimes in the digital age are discussed.