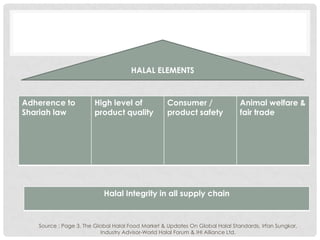
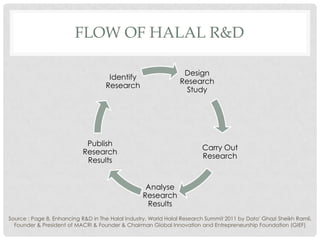
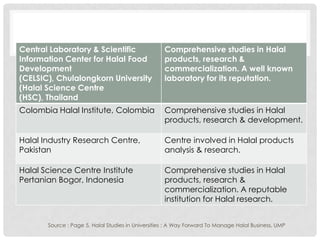
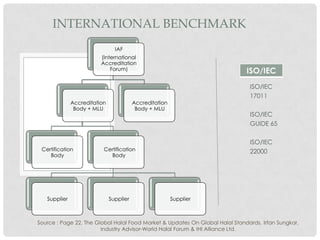
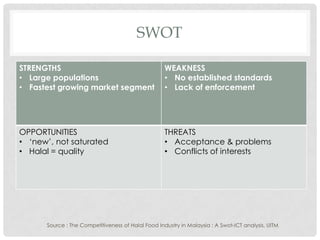
This document discusses Halal research and development. It defines research and outlines the key requirements for Halal R&D, including expertise in relevant fields, collaboration with international institutions, and adherence to Shariah law. It also examines the areas and challenges of Halal R&D, such as a lack of dedicated laboratories and standardized Halal standards. Benchmarking and strategies to strengthen Halal R&D are proposed, including specifying it as a focus area and building skills and expertise in both public and private research institutions.