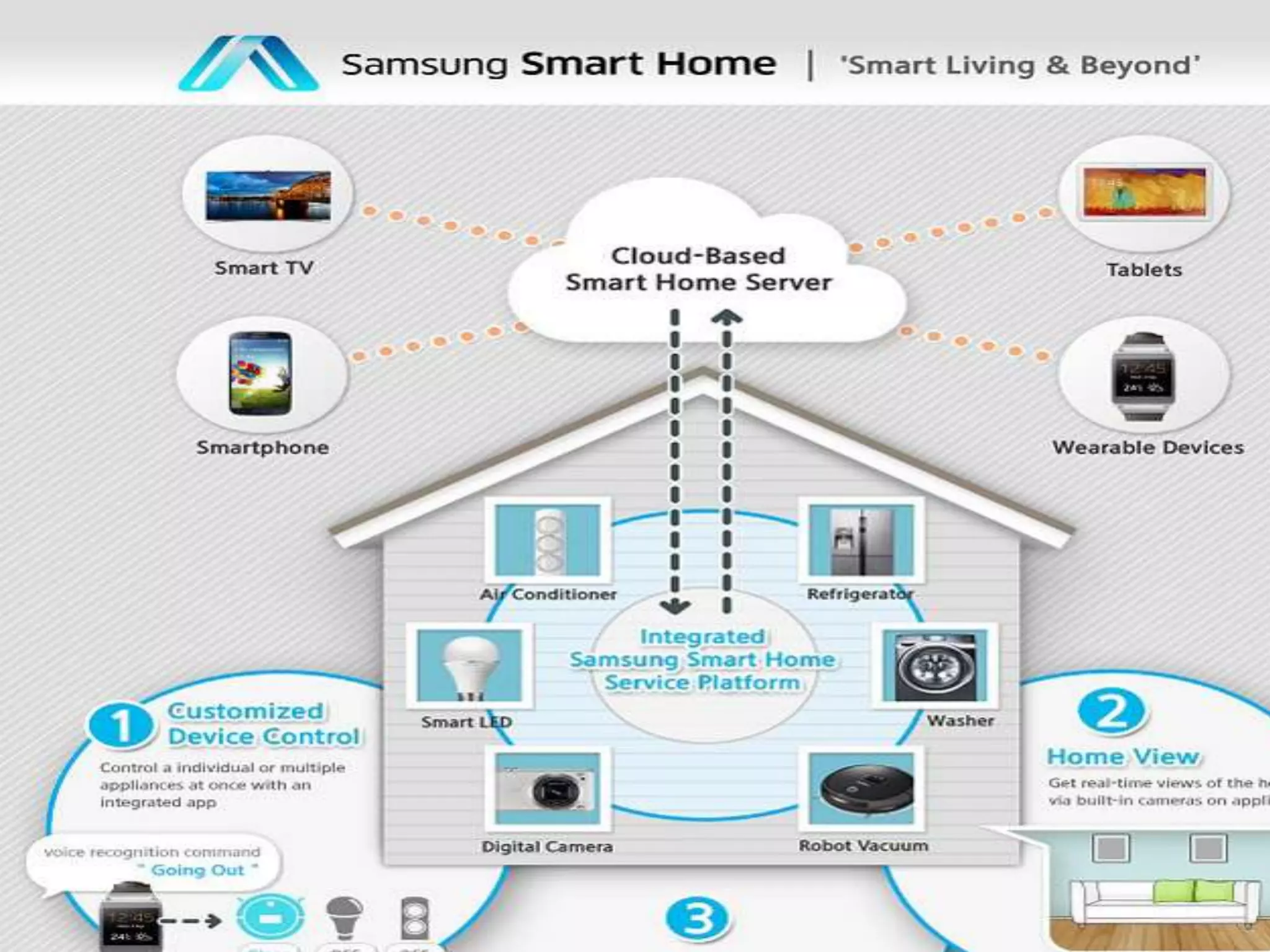
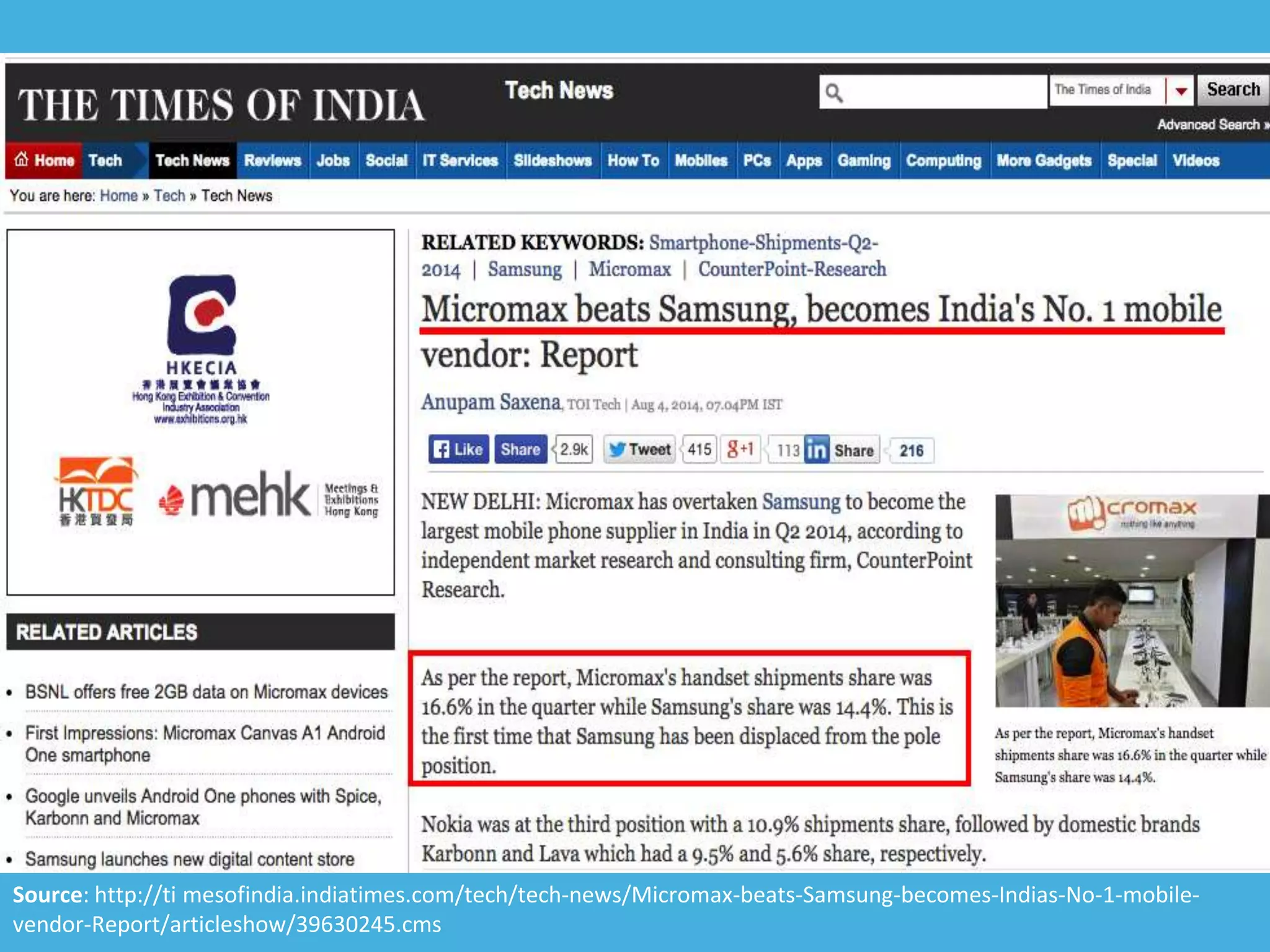
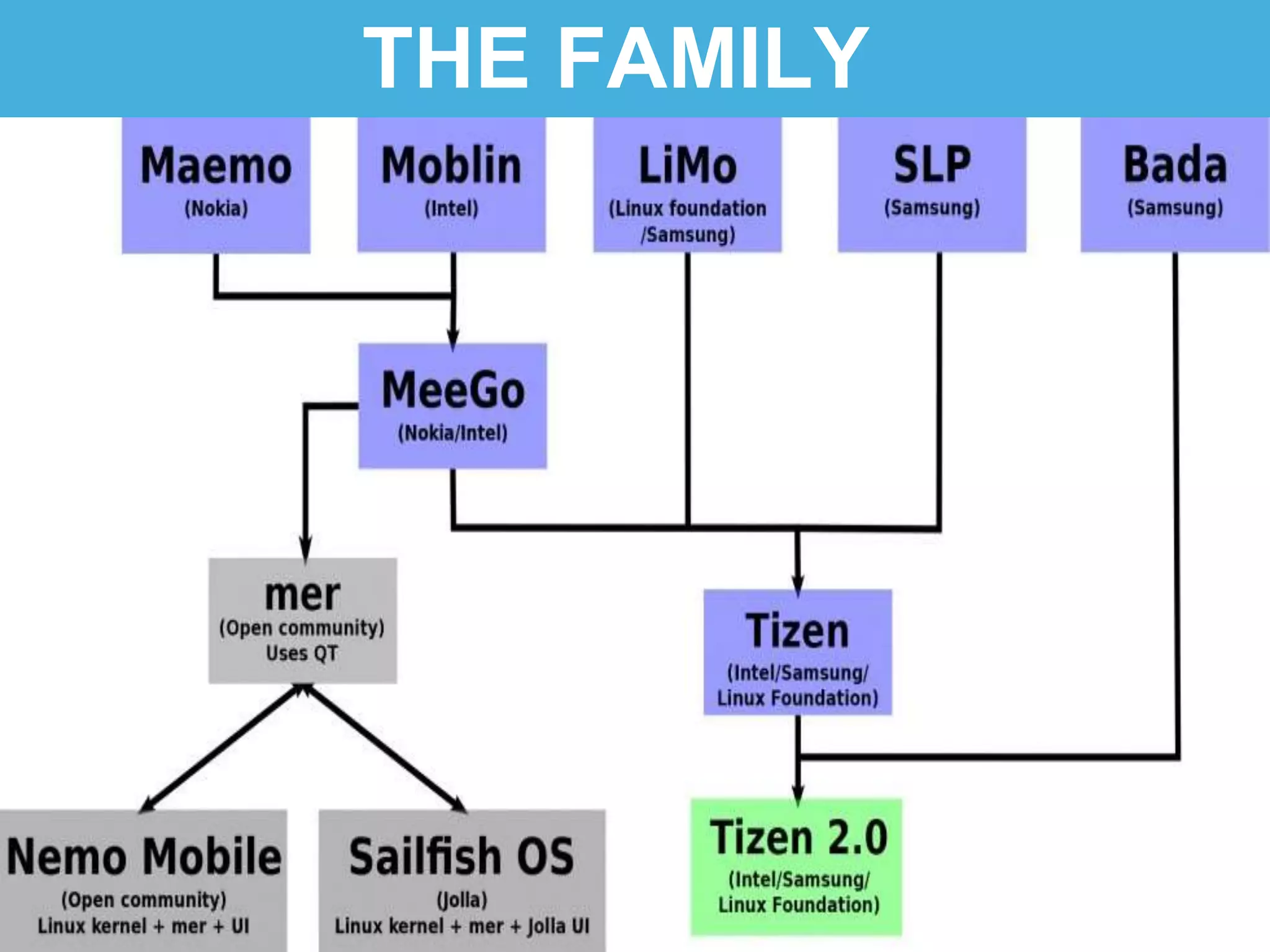
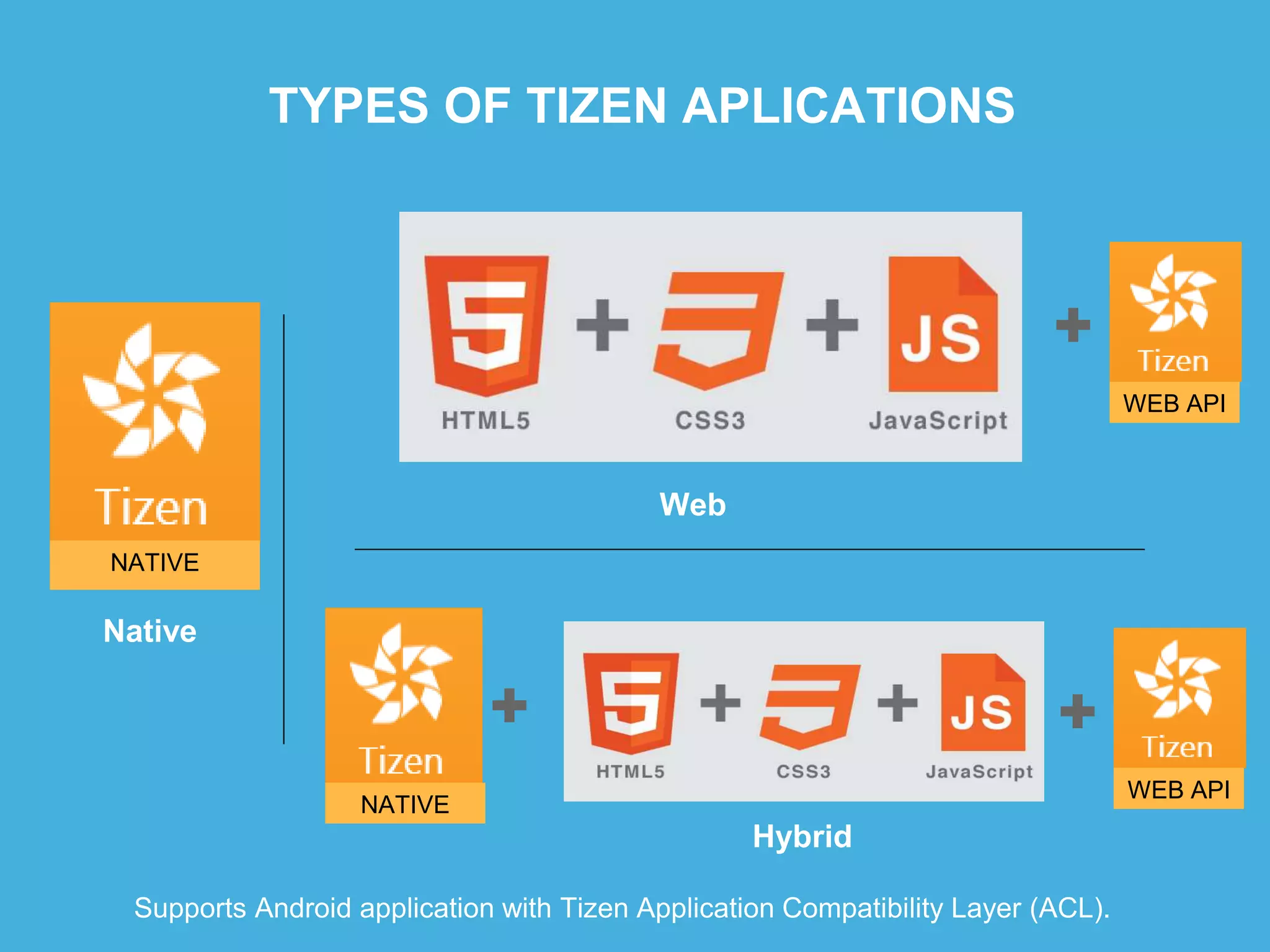
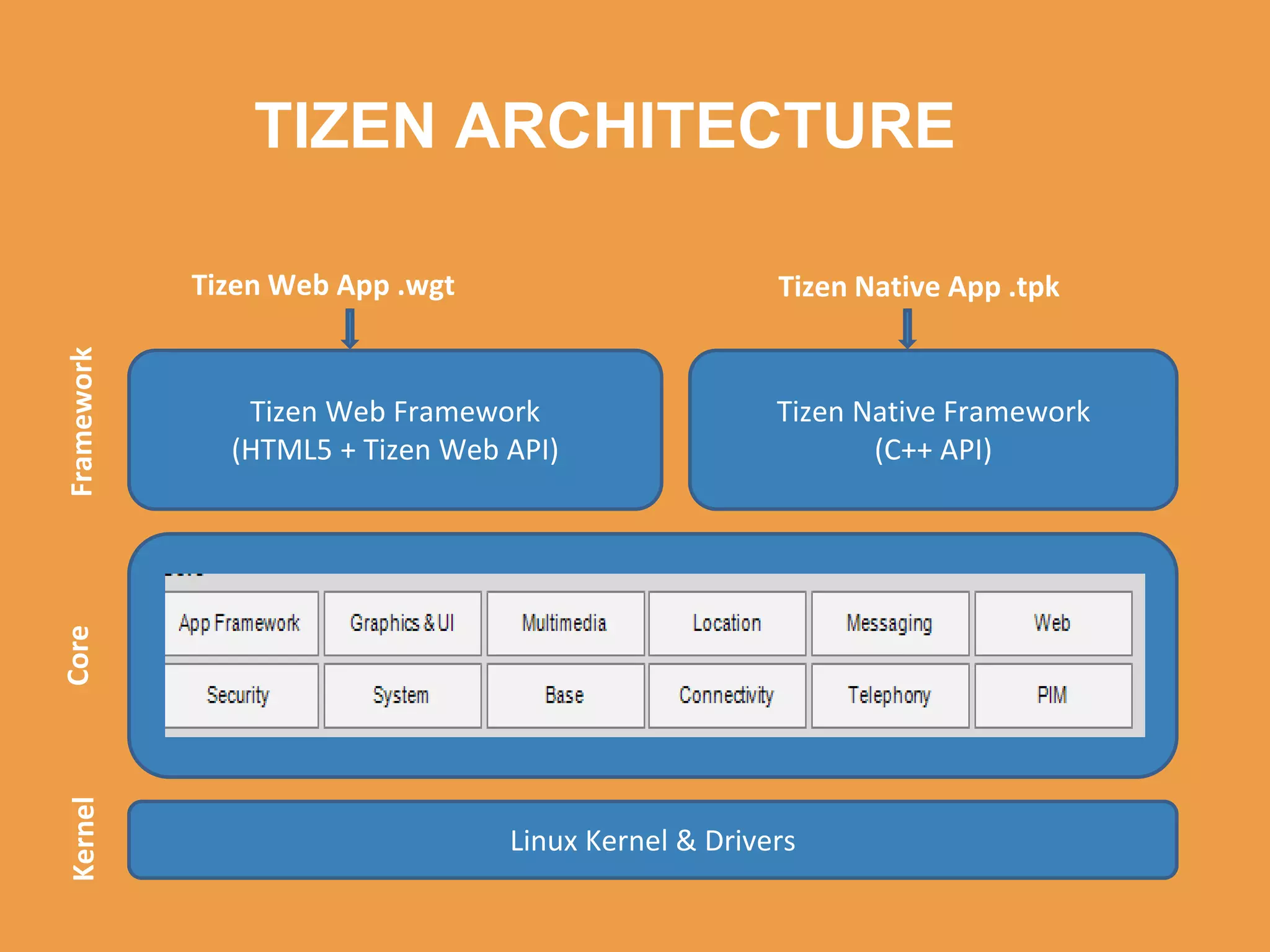
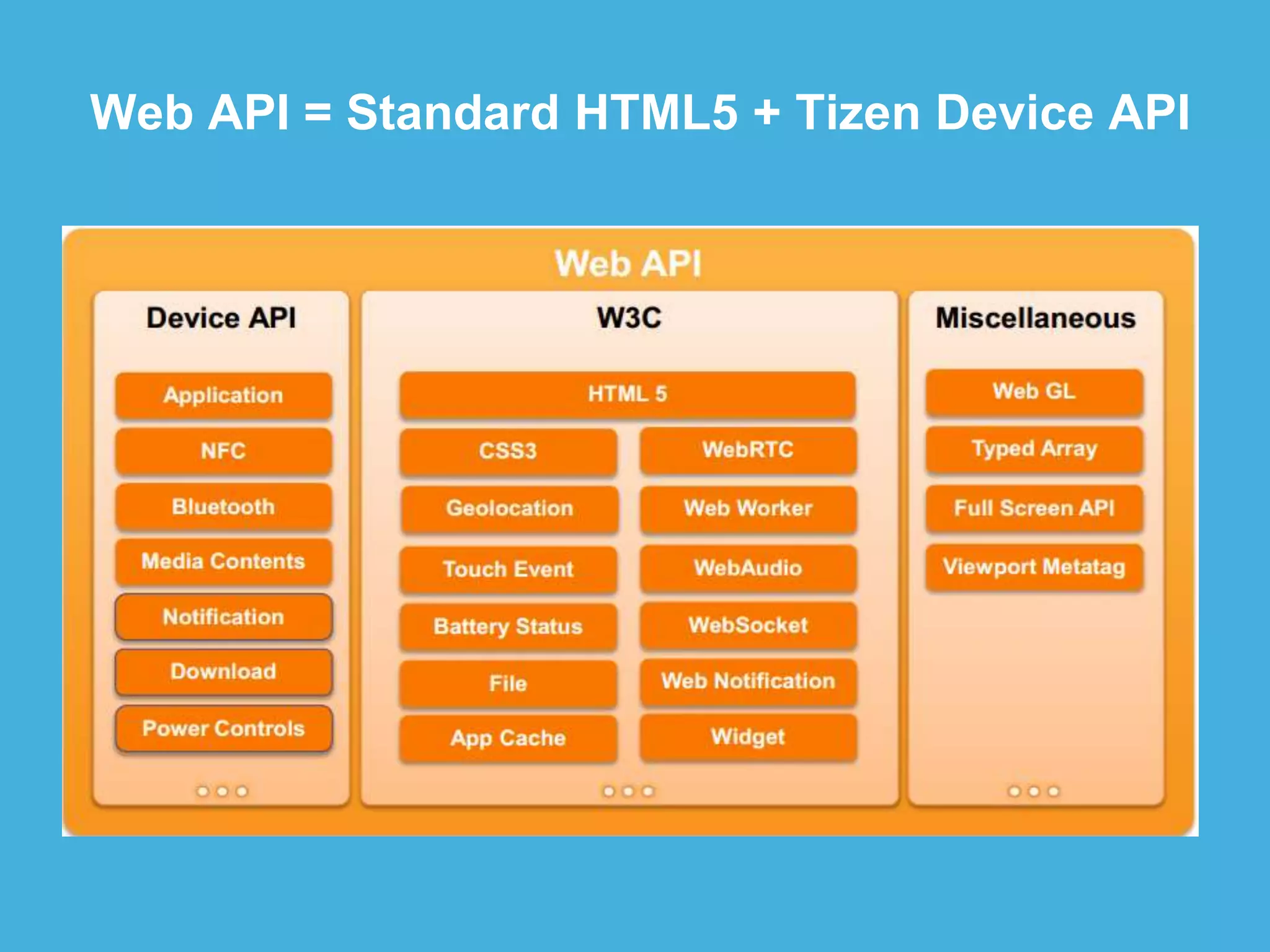
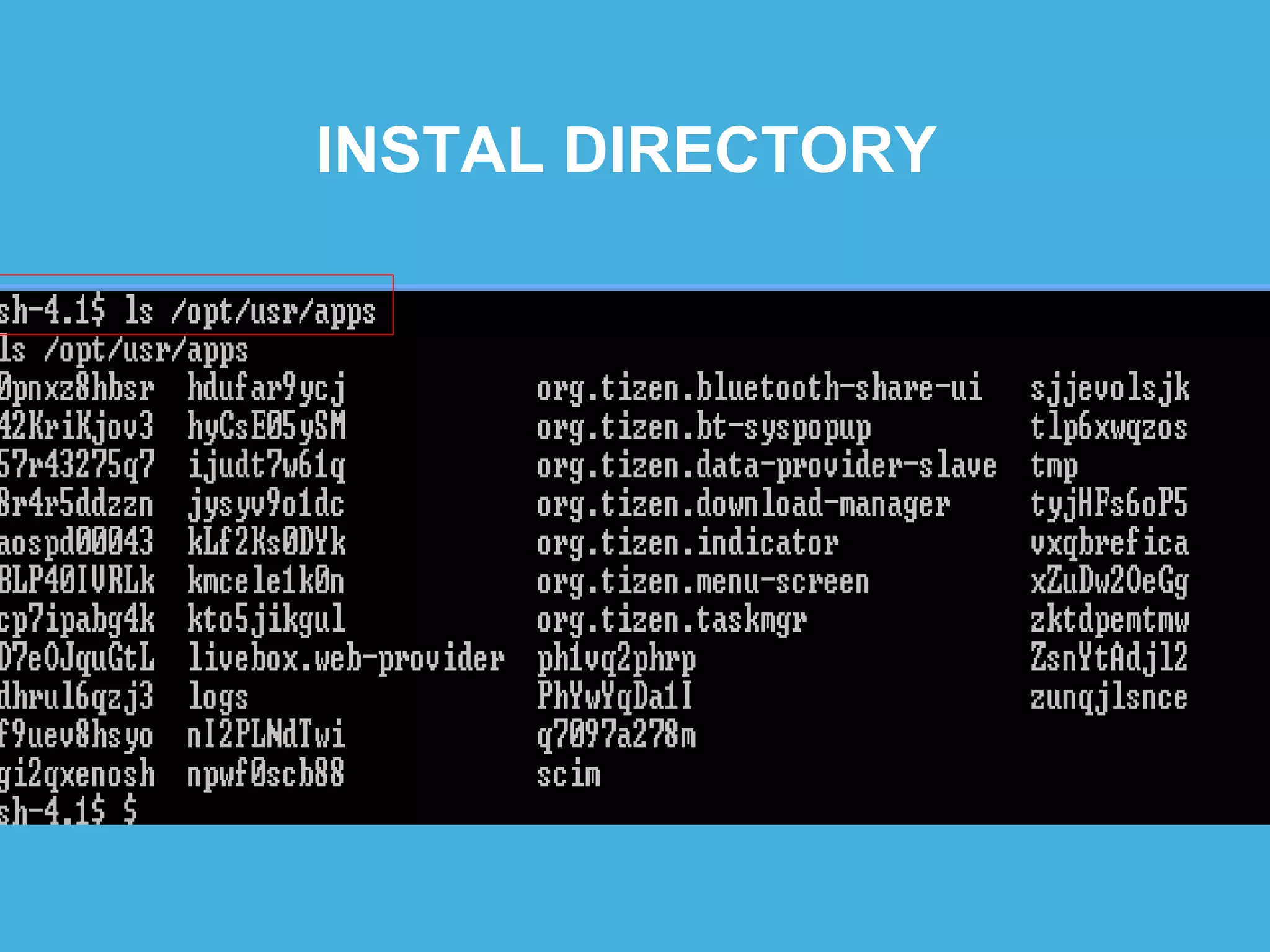
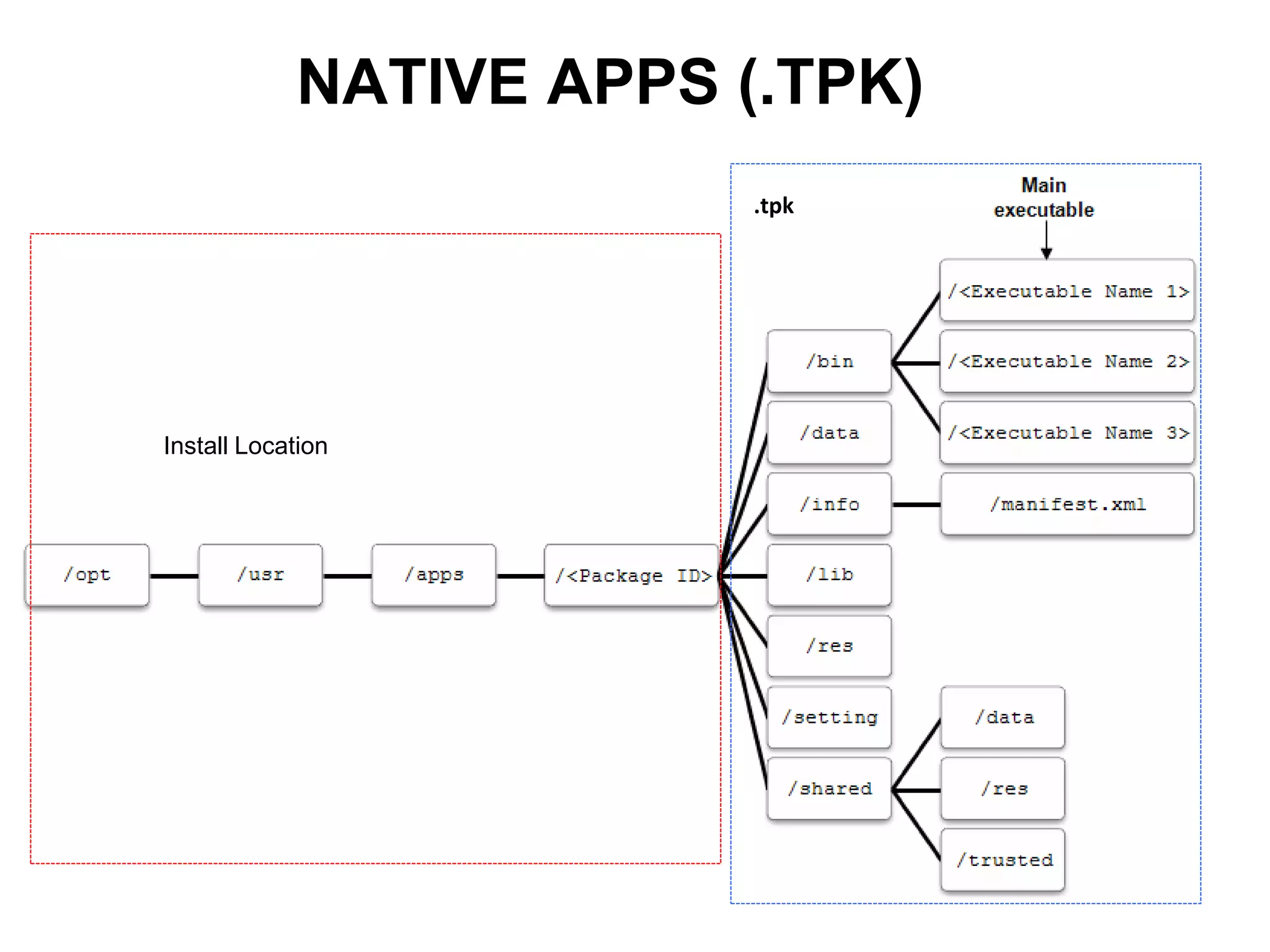
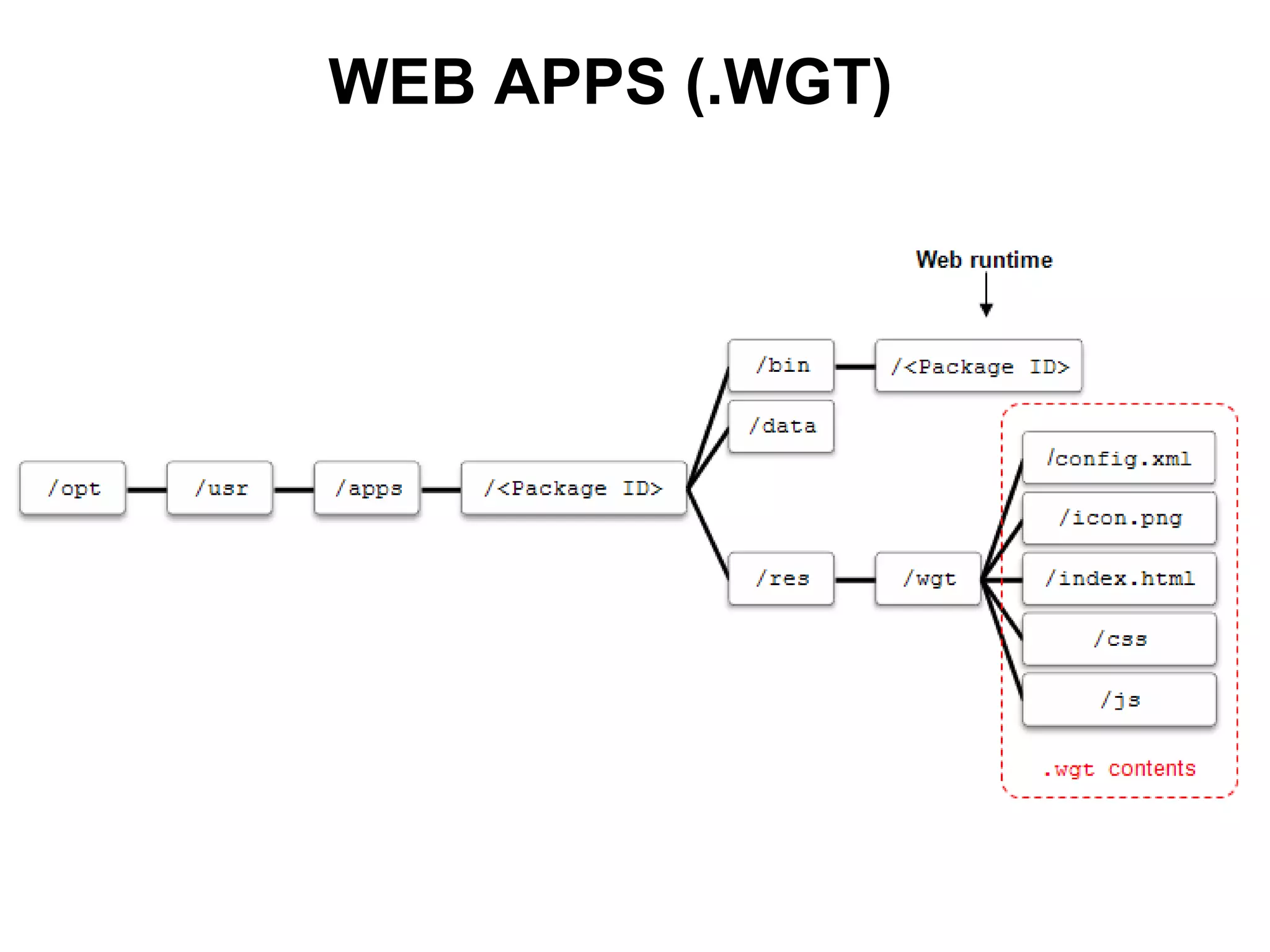
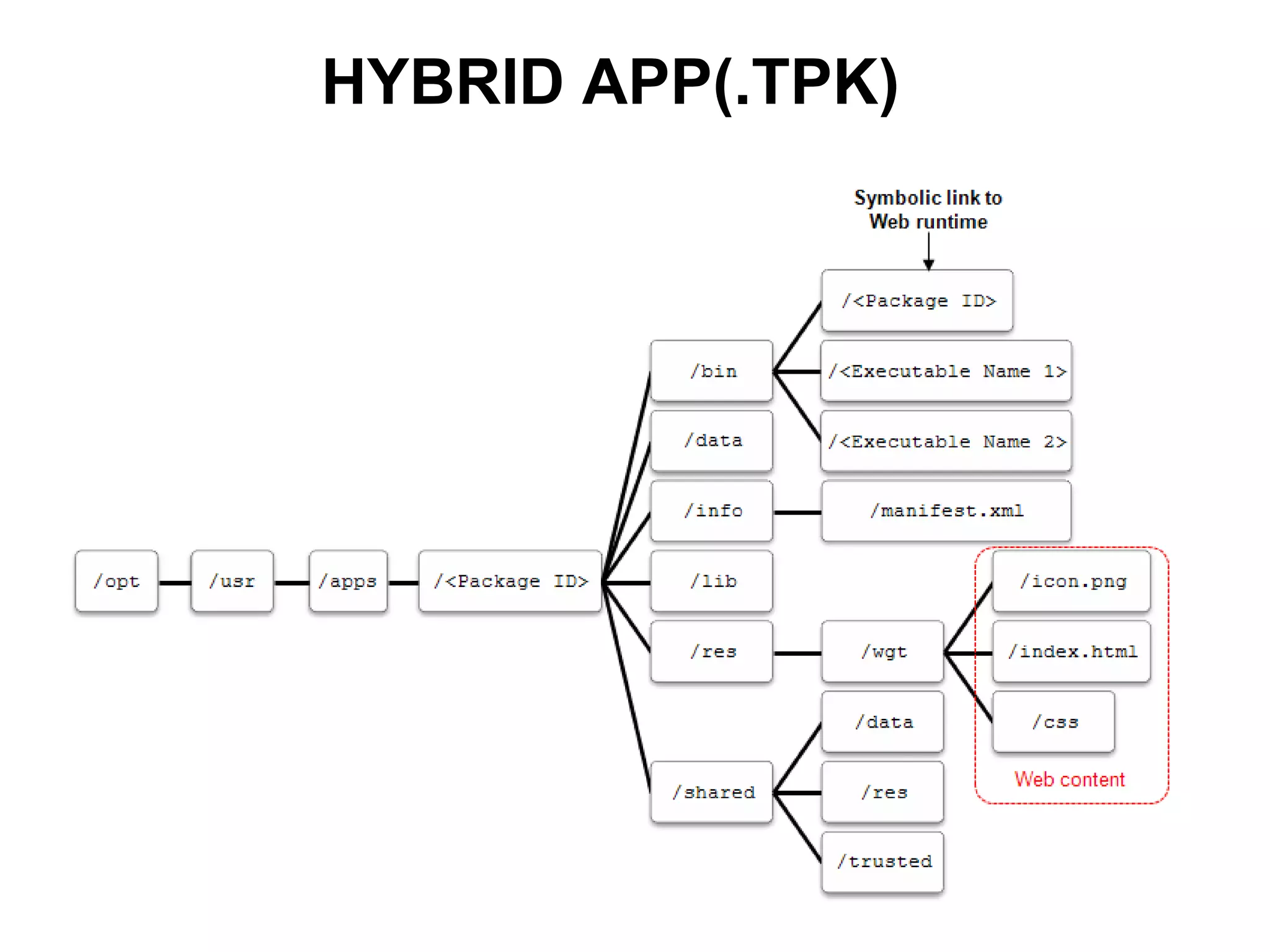
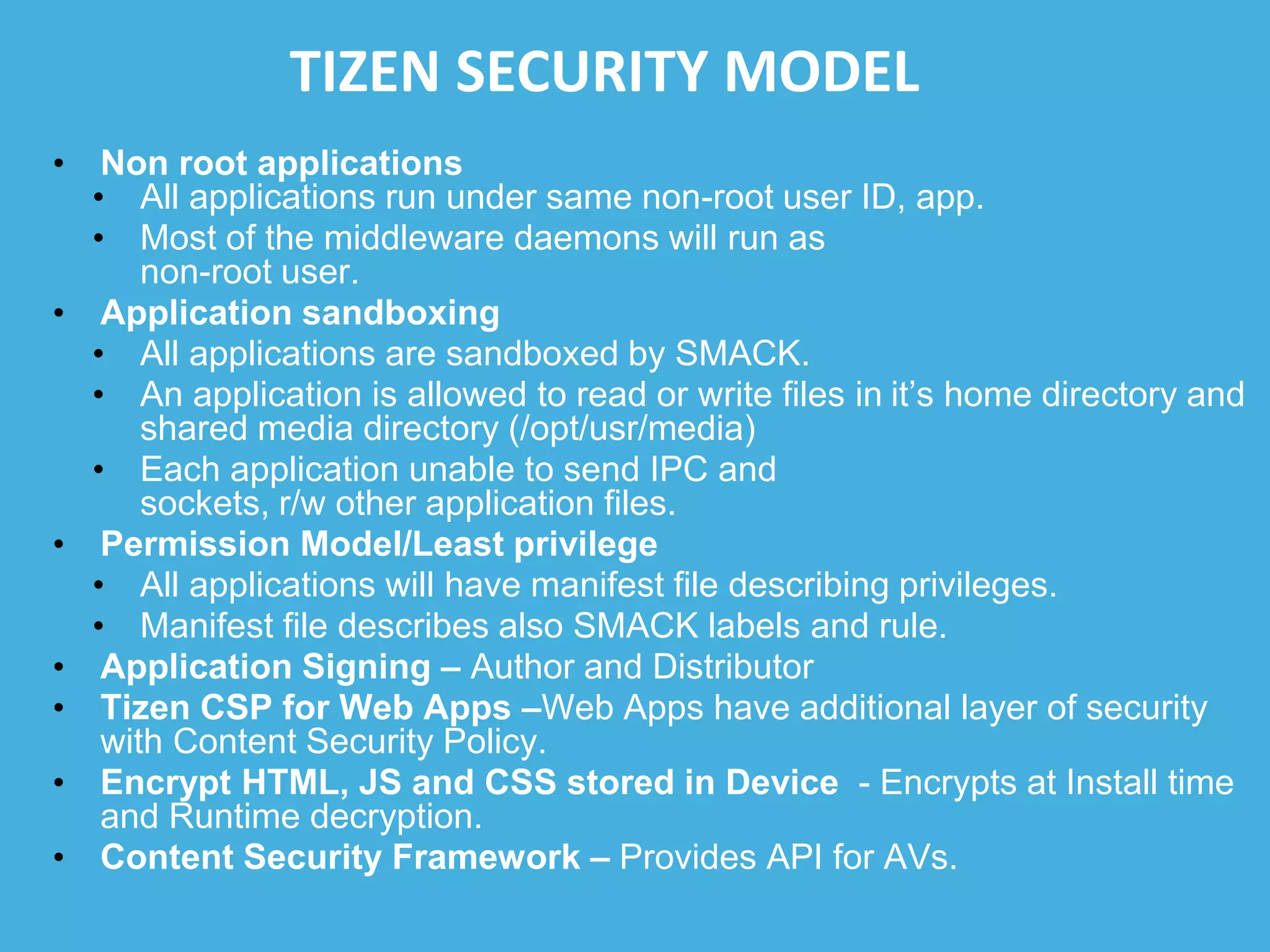
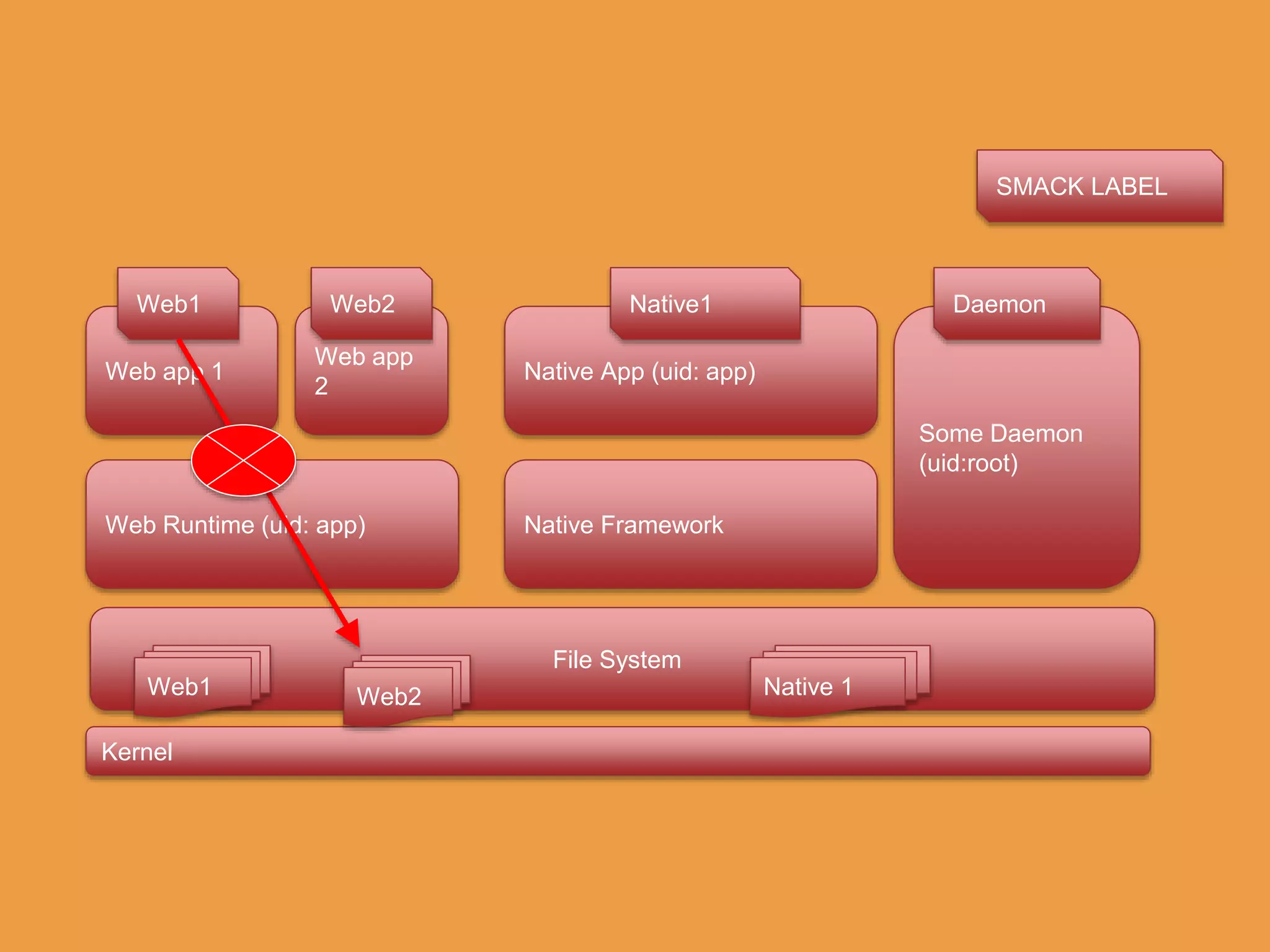
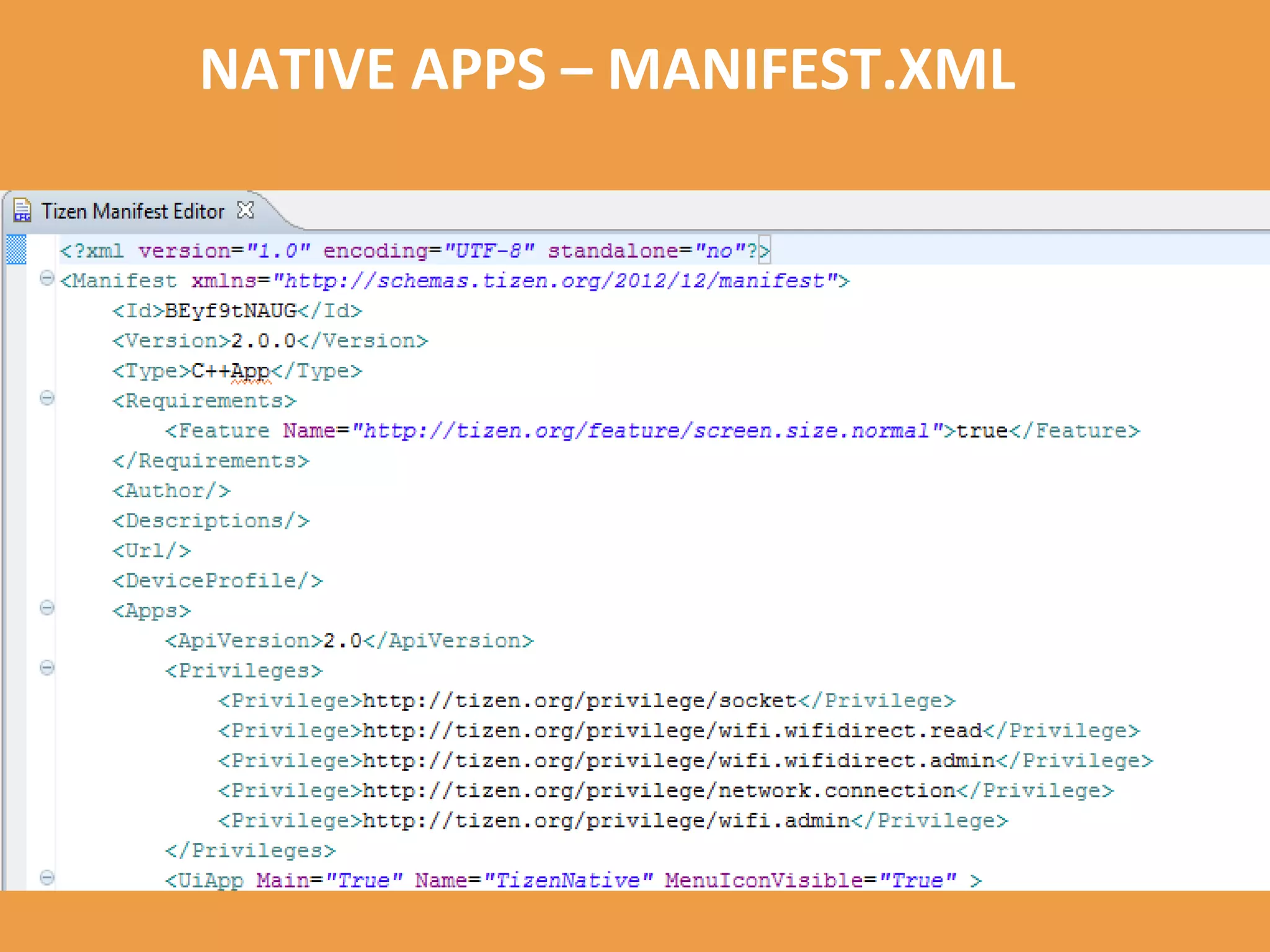
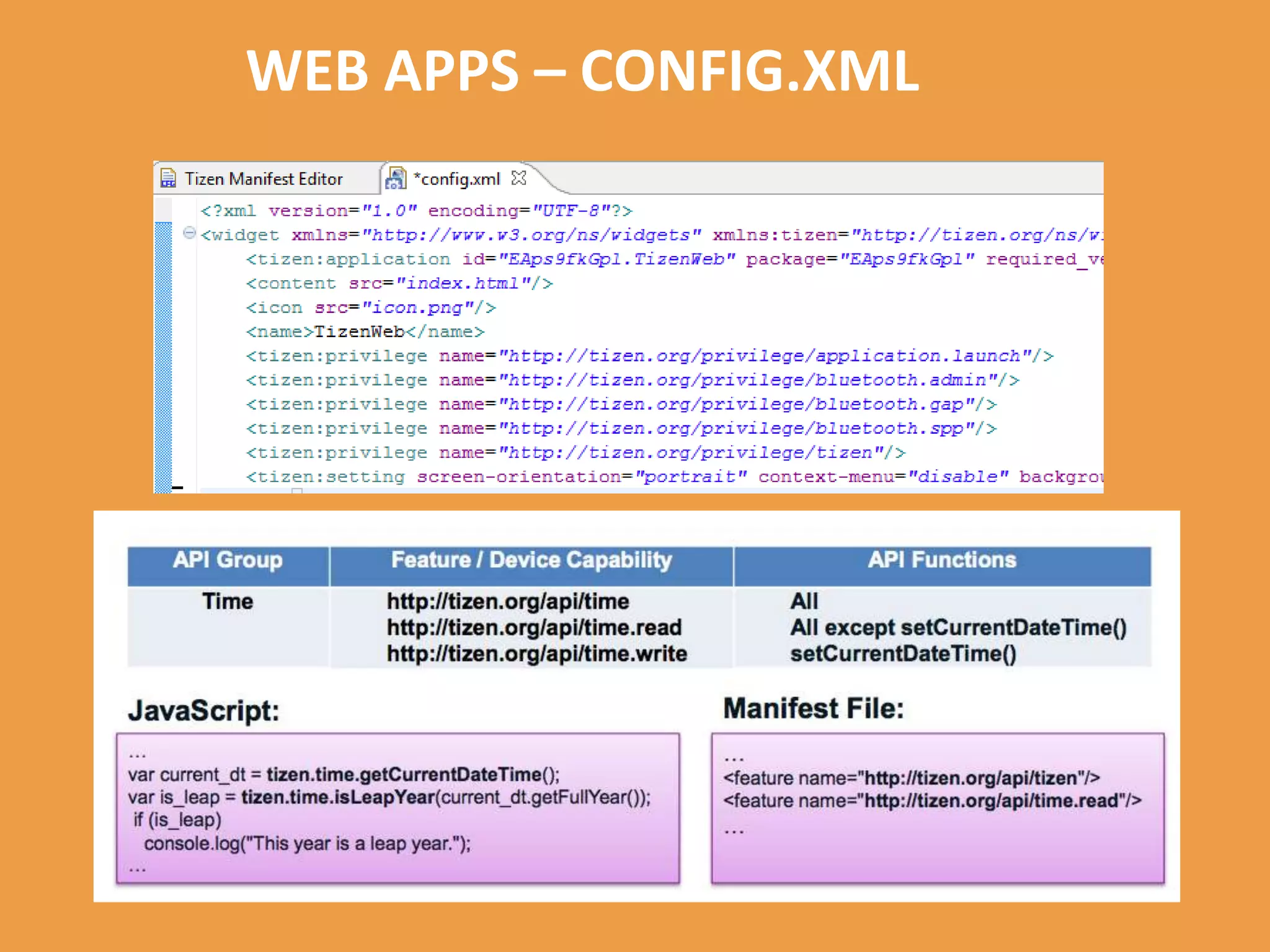
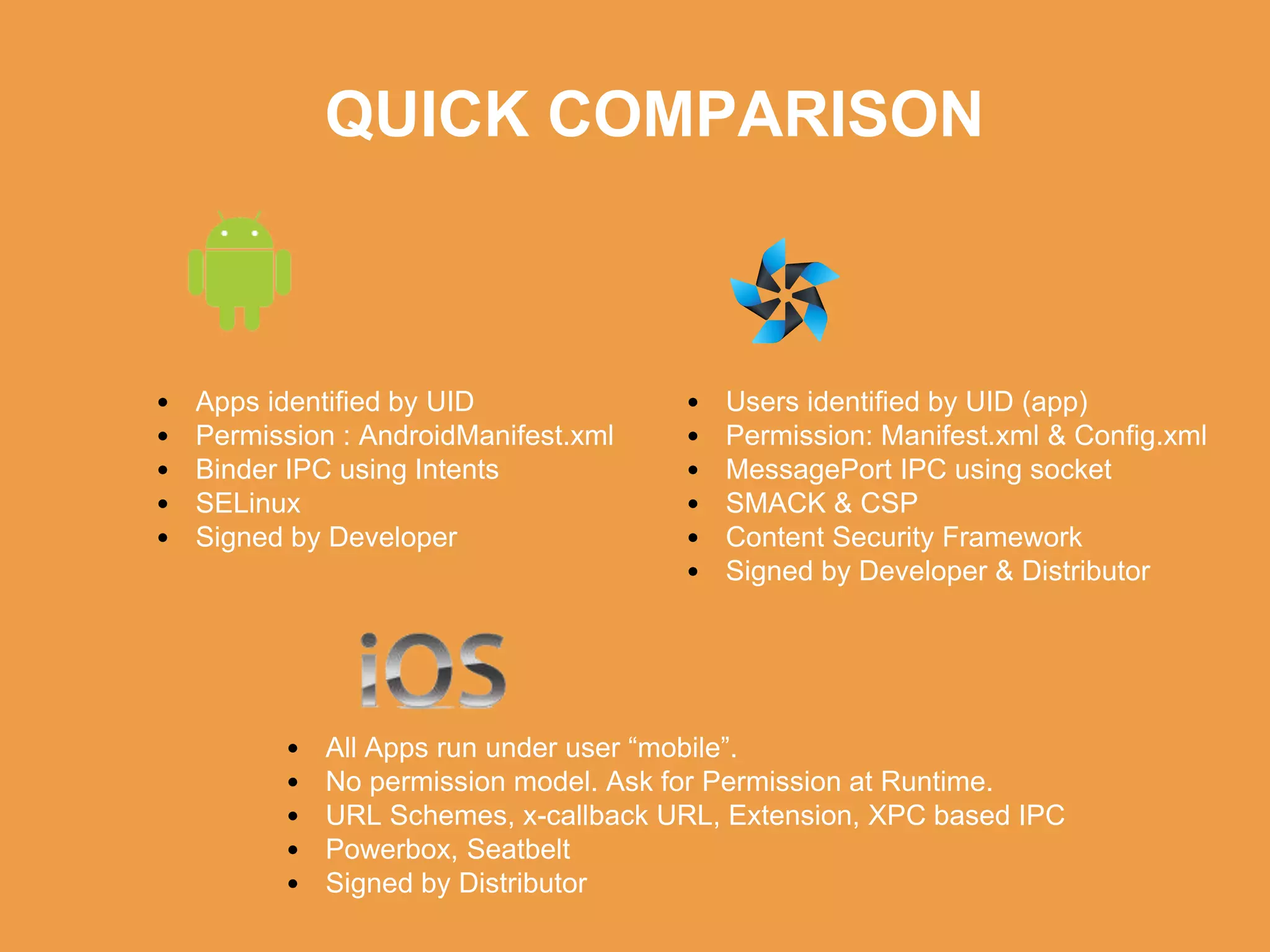
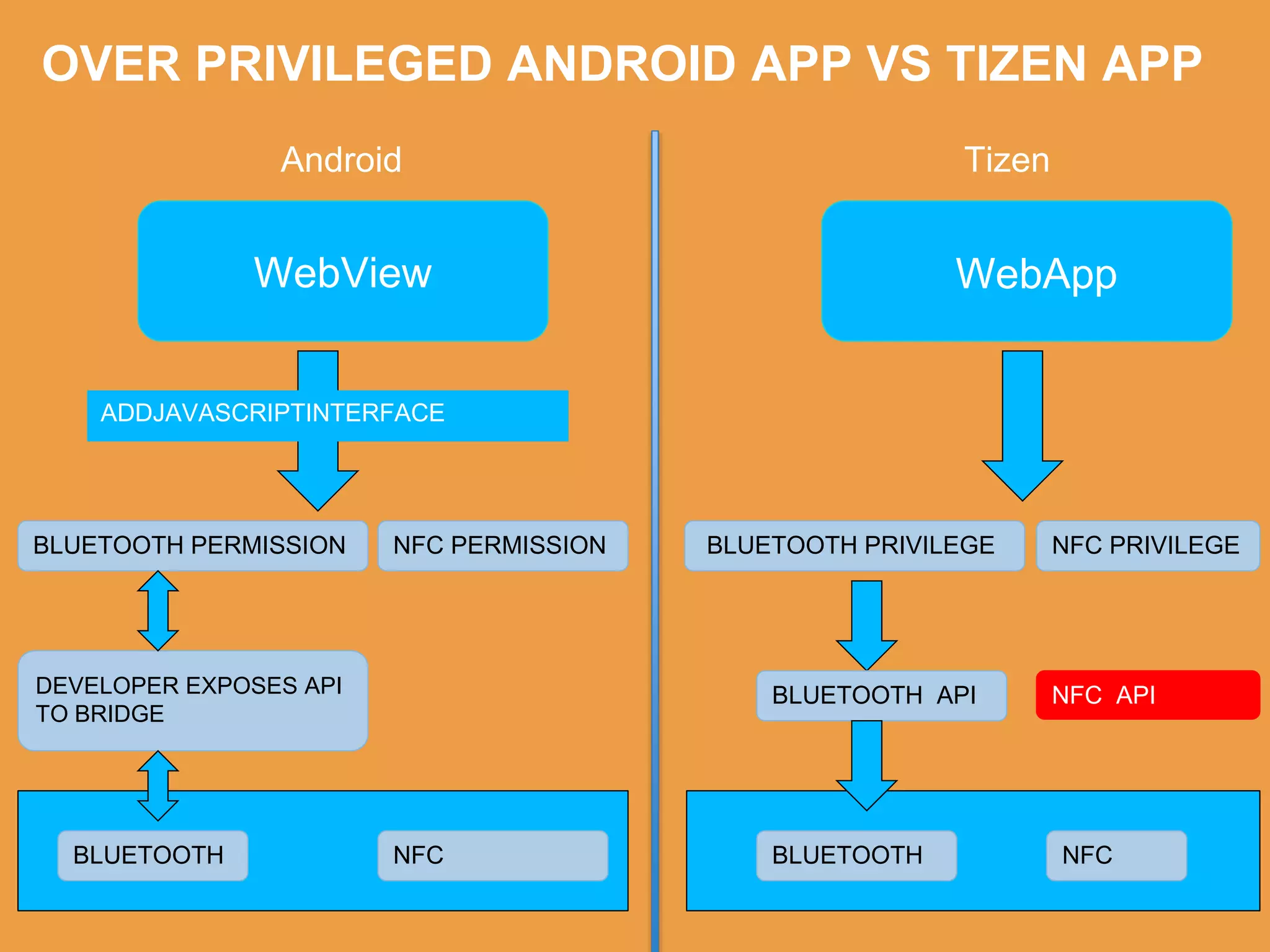
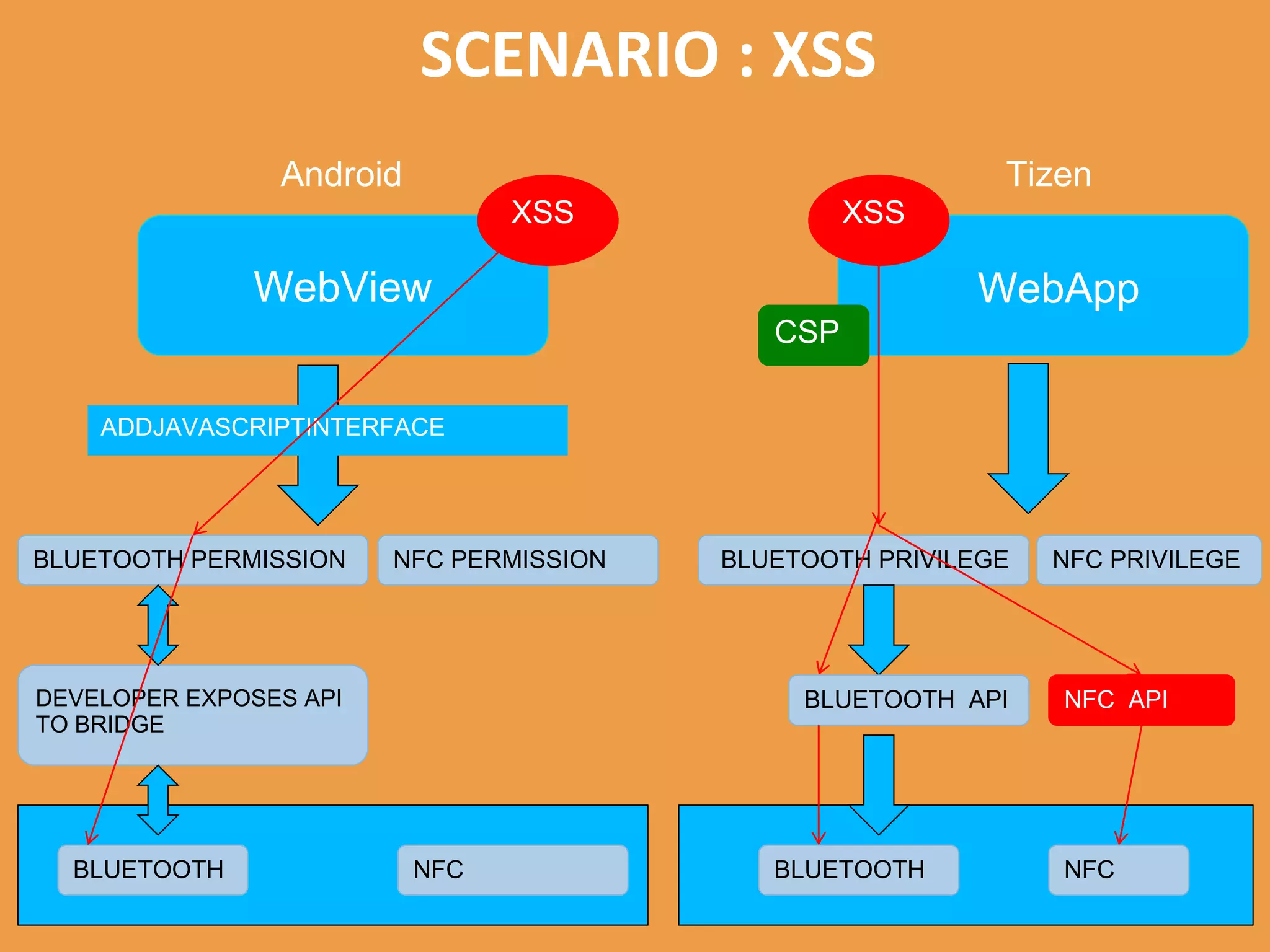
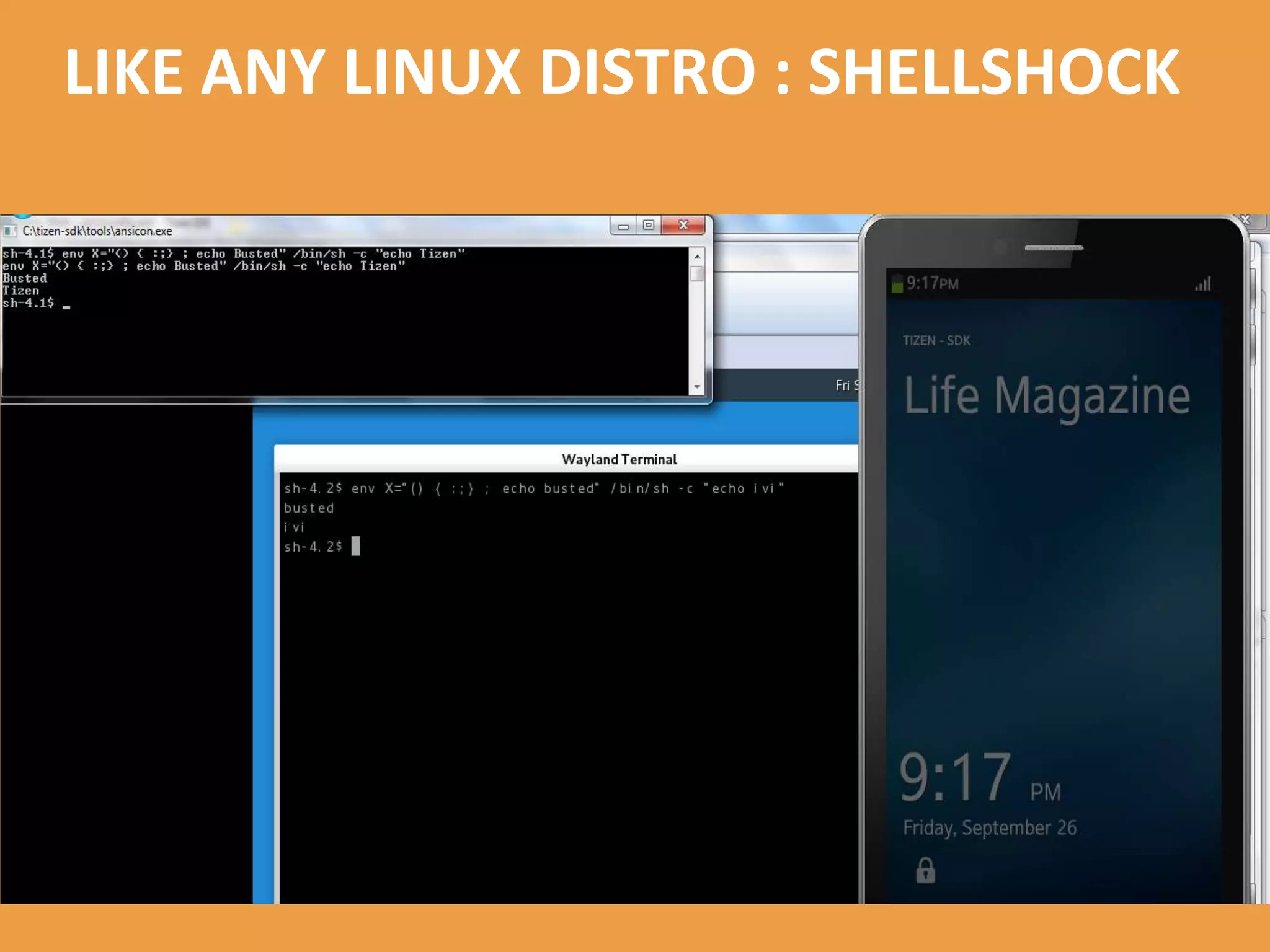
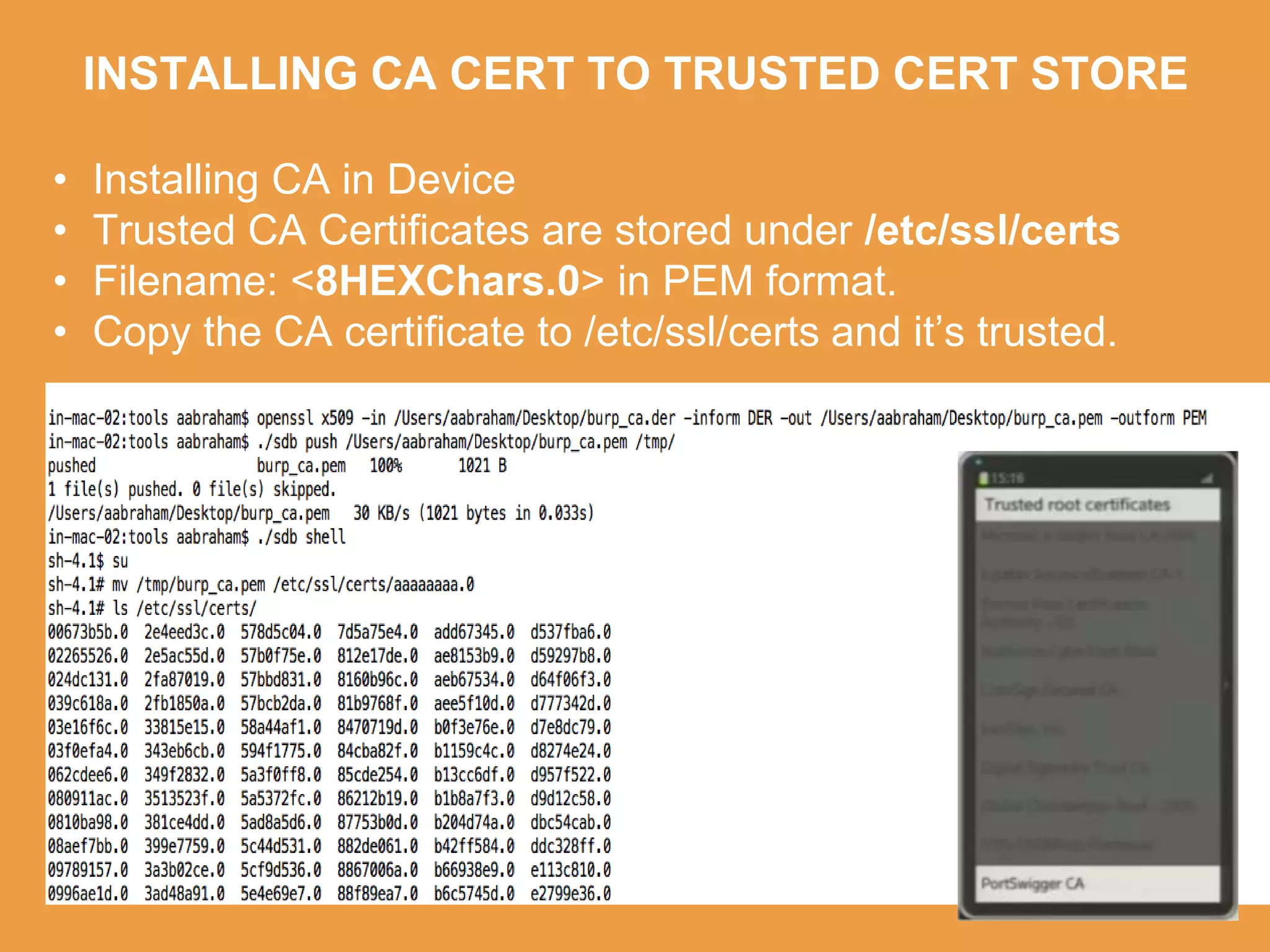
Tizen is an open source operating system that can run on various devices including smart TVs and IoT devices. It uses a security model that isolates applications using SMACK mandatory access control and enforces content security policies for web applications. The presentation discusses hacking techniques tested against Tizen like exploiting shellshock vulnerabilities, bypassing address space layout randomization protections, and circumventing content security policies. It also provides an overview of methodologies for analyzing Tizen application security like static analysis of manifest and configuration files, decompiling native applications, and network analysis using a proxy. Overall the presentation evaluates the security of Tizen and highlights some implementation issues found.