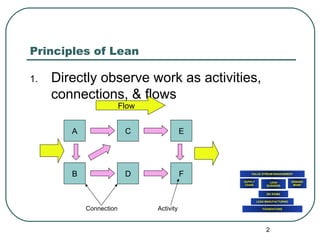
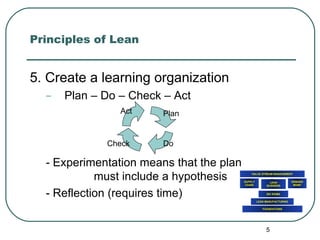
This document provides an overview of lean principles for leadership and personal practice. It discusses observing work flows, eliminating waste, establishing agreement on processes, using problem solving tools like the 5 Whys, creating a learning culture with Plan-Do-Check-Act cycles, and leadership techniques like building tension rather than stress and eliminating fear and comfort. For personal lean, it recommends always working for the customer, problem solving at a relationship level, managing commitments, using tools like 5 Whys, and directly observing processes.