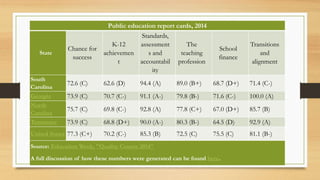
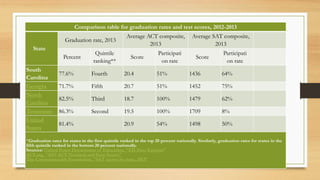
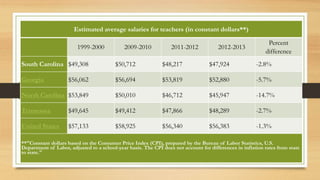
The document provides information about the educational system in South Carolina. It discusses that South Carolina has 751,660 students enrolled across 1,167 public schools within 79 districts. It also notes that South Carolina spends less on education as a percentage of its state budget than neighboring states and has lower scores than neighbors on standardized tests, with only 35% of 4th graders proficient in math. The document indicates that an area for improvement is student achievement, as South Carolina has room to boost test scores and the percentage of students performing at grade level.