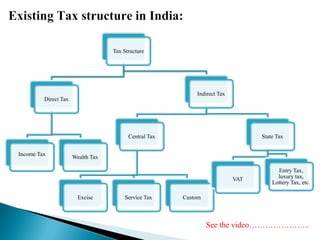
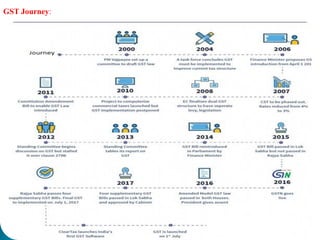
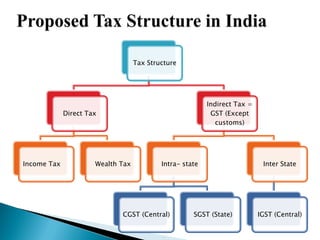
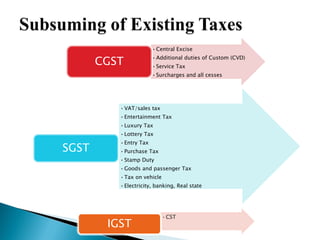
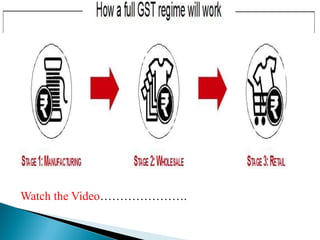
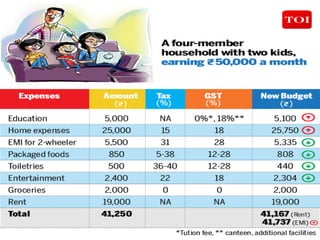
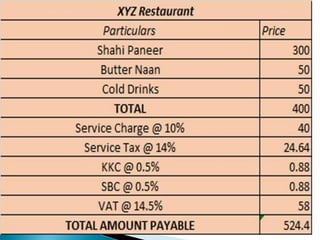
The document provides an overview of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system implemented in India in July 2017. It discusses how GST unifies several central and state taxes into a single tax system. GST is levied on the final consumption of goods and services, with credits provided for taxes paid at previous stages. A GST Council was established to make recommendations on tax rates and policies. The implementation involved passing legislation at both the central and state government levels.