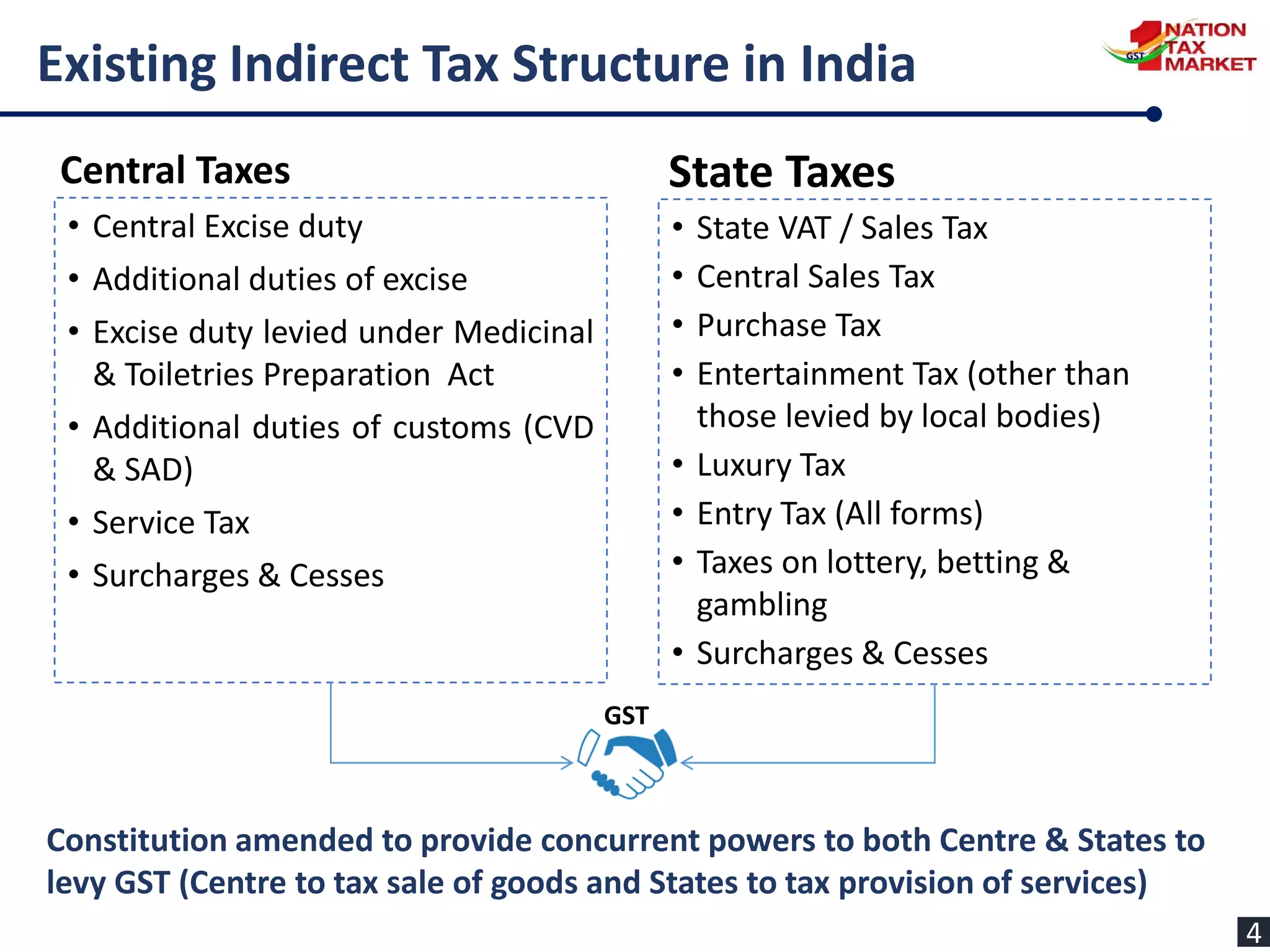
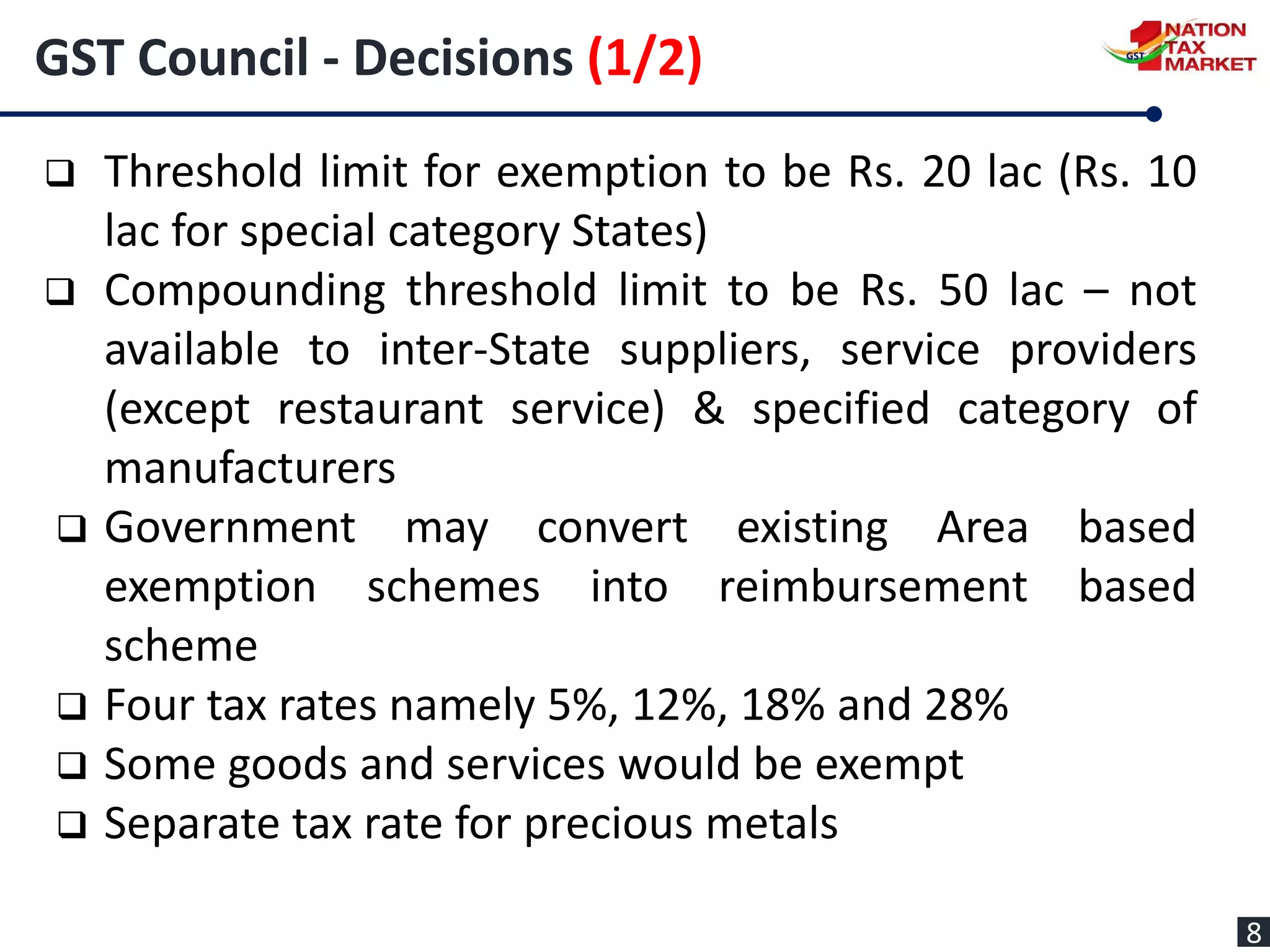
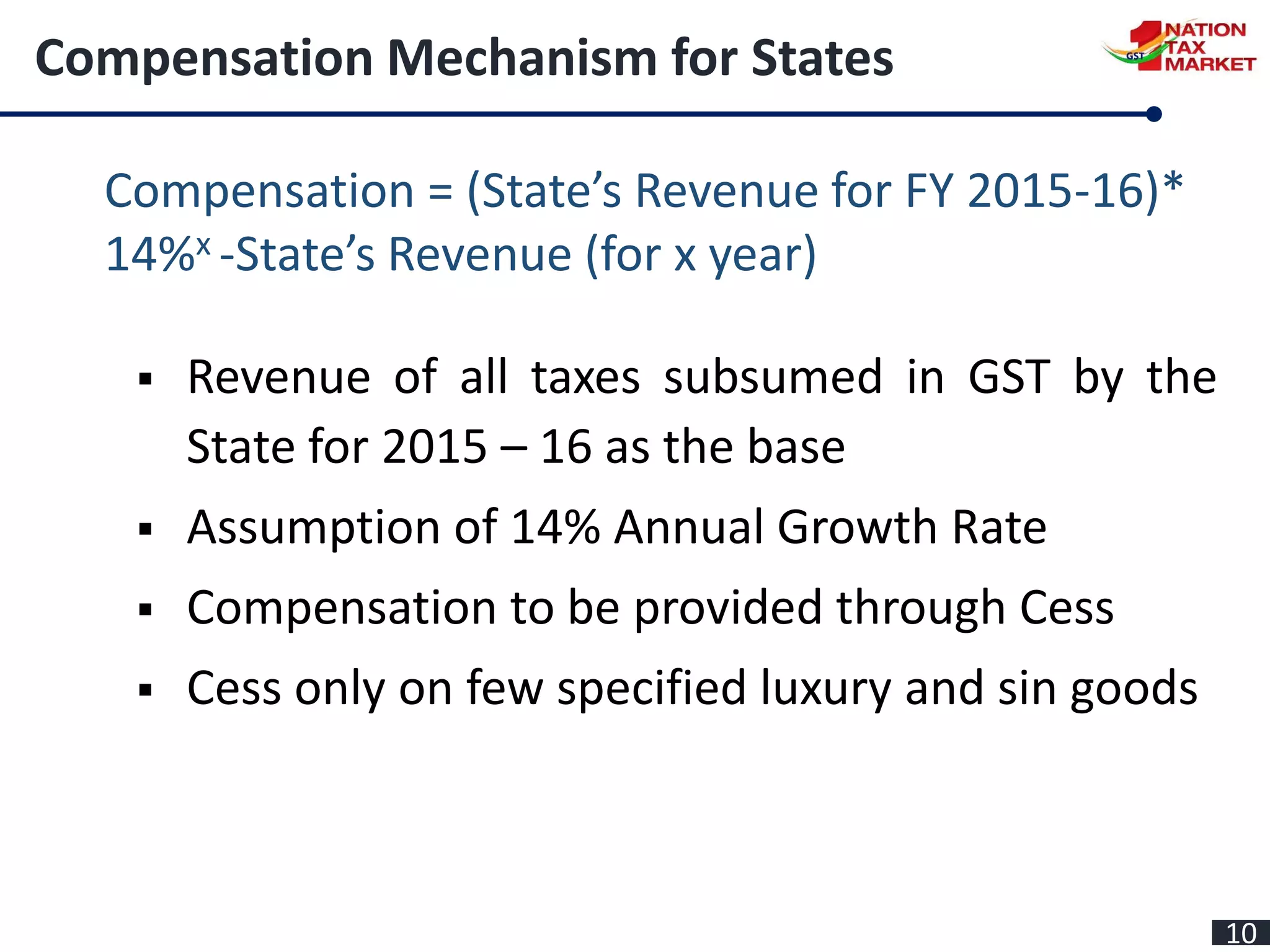
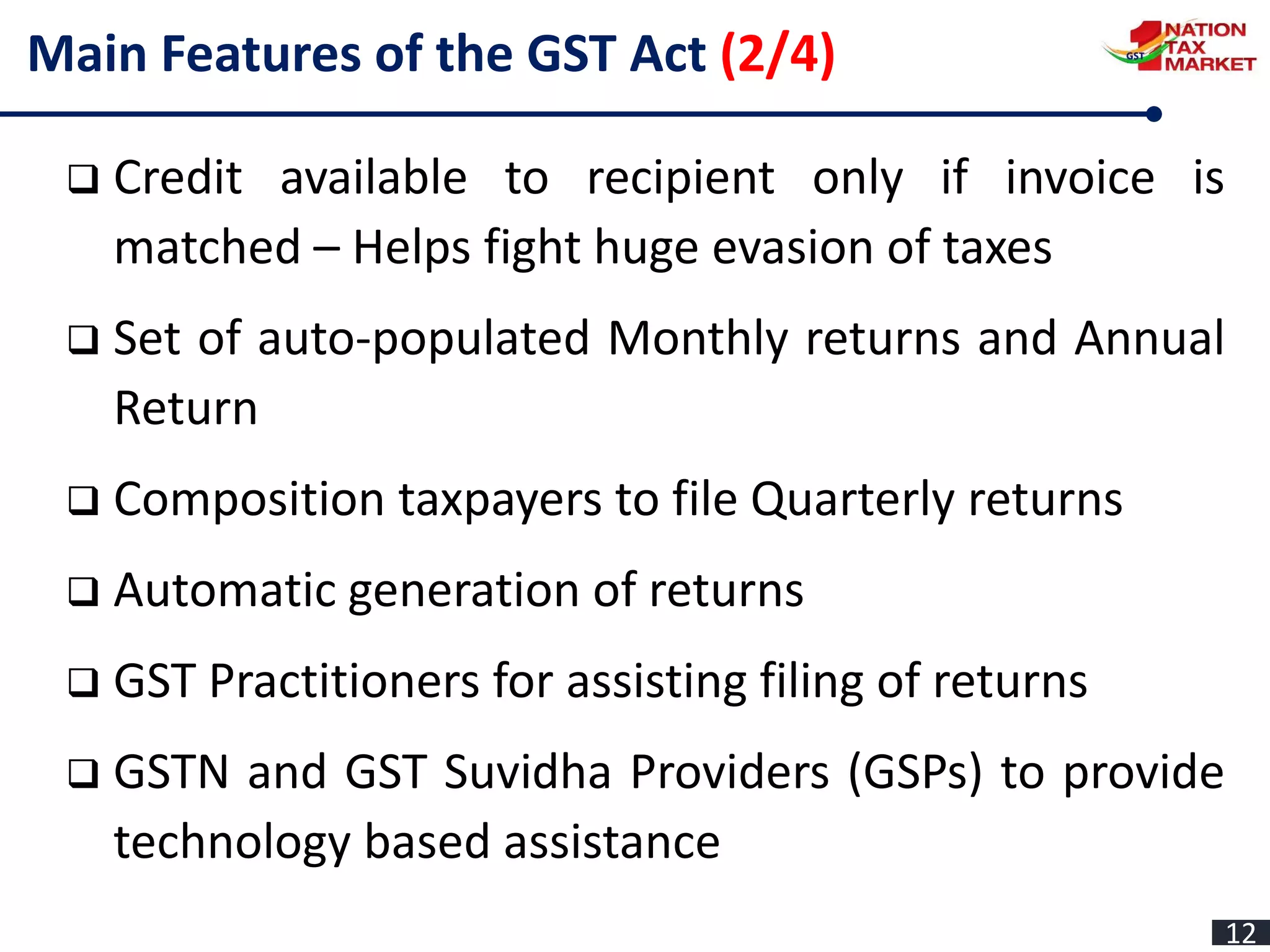
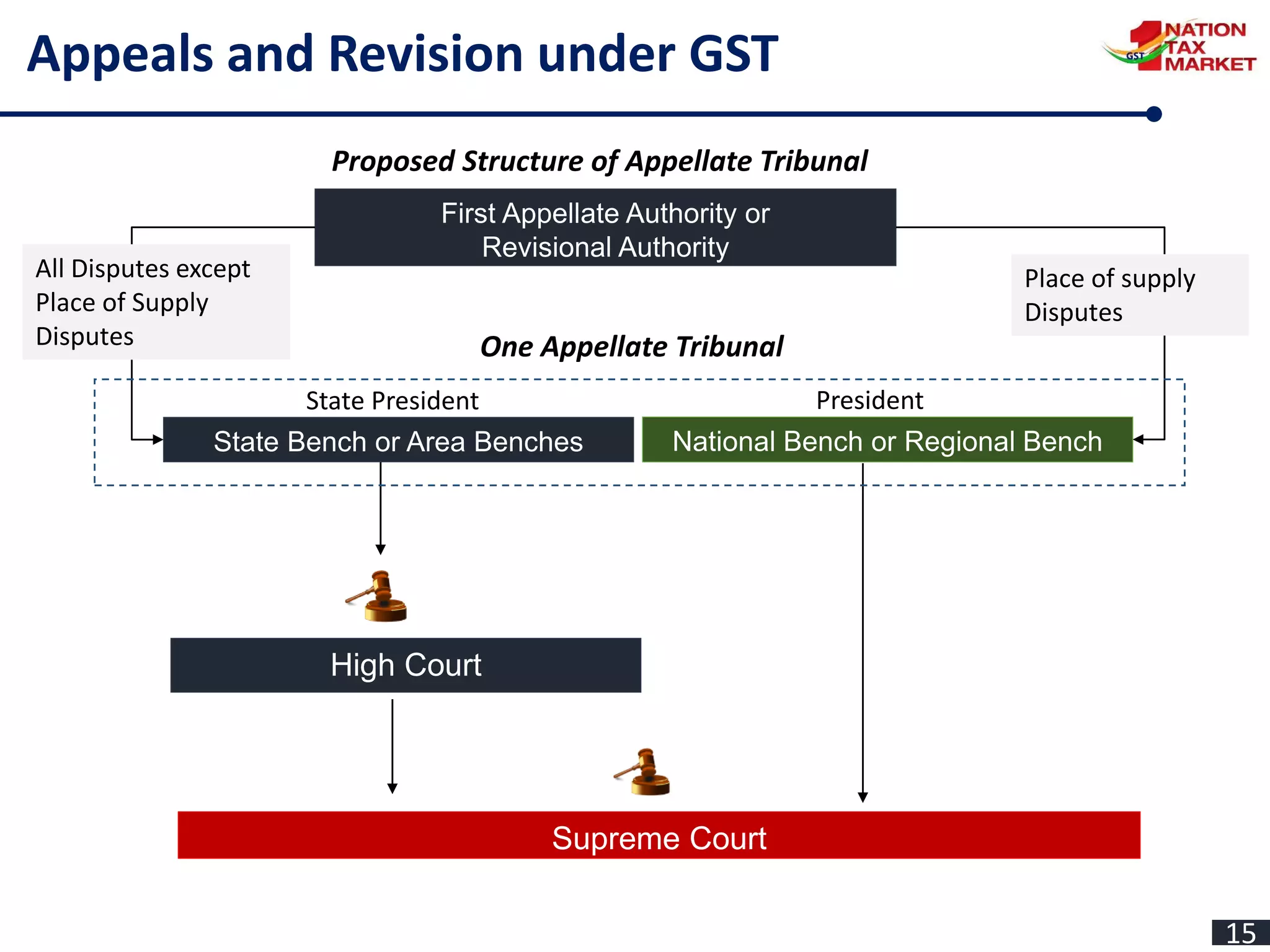
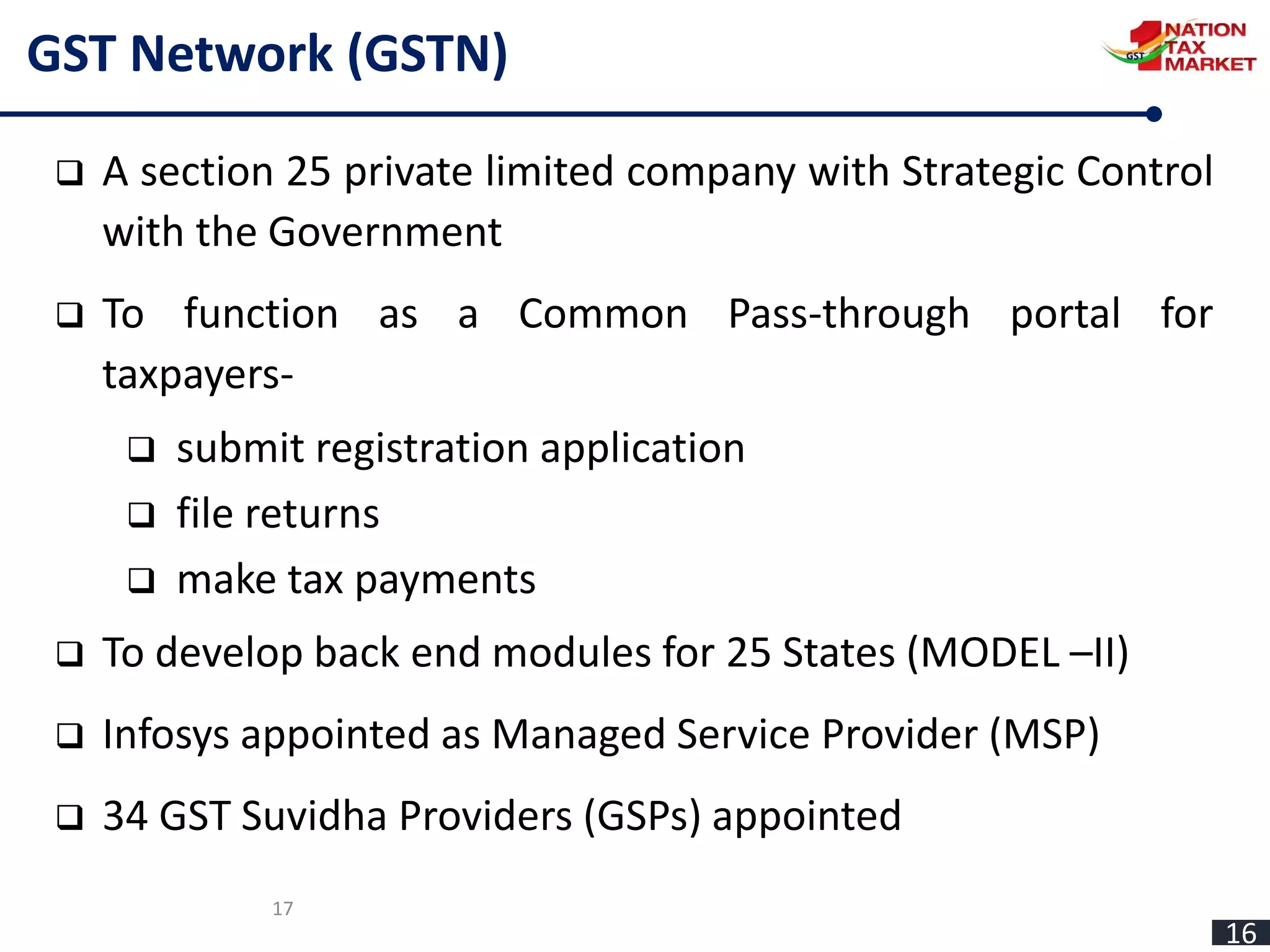
The document outlines the journey and implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, detailing its design, features, benefits, and administrative framework. Key aspects include the constitutional amendments that enable concurrent taxation by the center and states, the role of the GST council, and various tax rates introduced. The GST aims to streamline taxation, reduce cascading taxes, and enhance compliance through an electronic system.