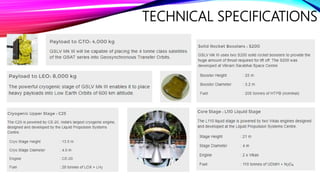
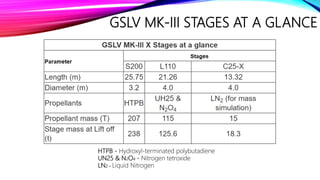
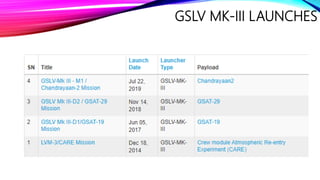
The document discusses the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III) developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). It has a higher payload capacity than the GSLV Mk II and can carry 4 ton class satellites to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit or 10 tons to Low Earth Orbit. The vehicle uses two solid strap-on boosters and a liquid core booster with a cryogenic upper stage. GSLV Mk III has successfully launched satellites like GSAT-19, GSAT-29 and the Chandrayaan-2 lunar mission.