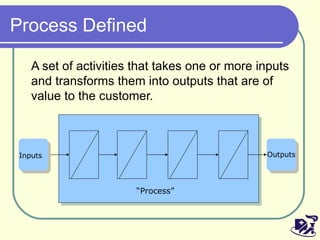
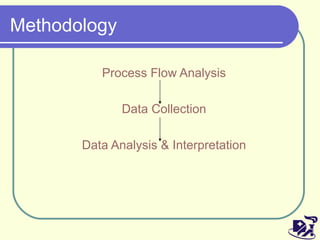
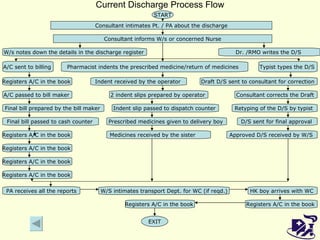
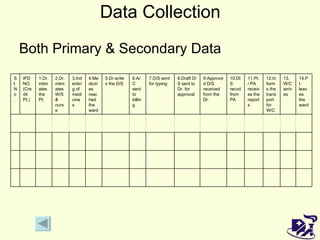
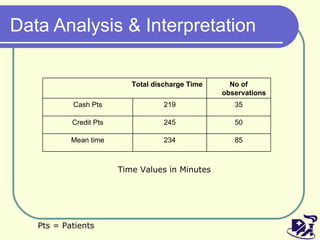
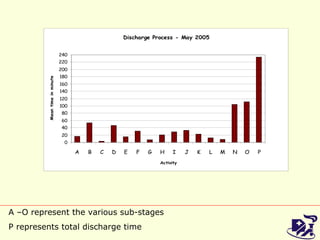
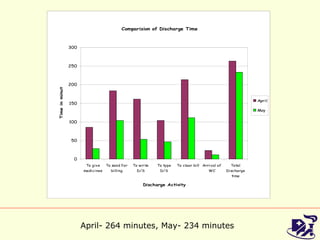
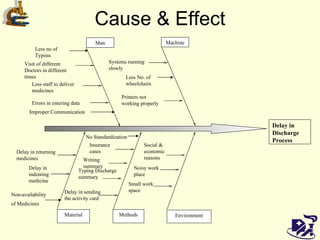
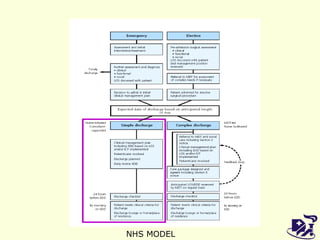
The document discusses analyzing and improving the inpatient discharge process at a hospital. It outlines the current discharge process flow, collects data on discharge times, and identifies inefficiencies and their causes. Suggestions are made to standardize the process, improve communication and reduce non-value adding steps to decrease discharge times. A proposed discharge checklist model is presented to help streamline the process.