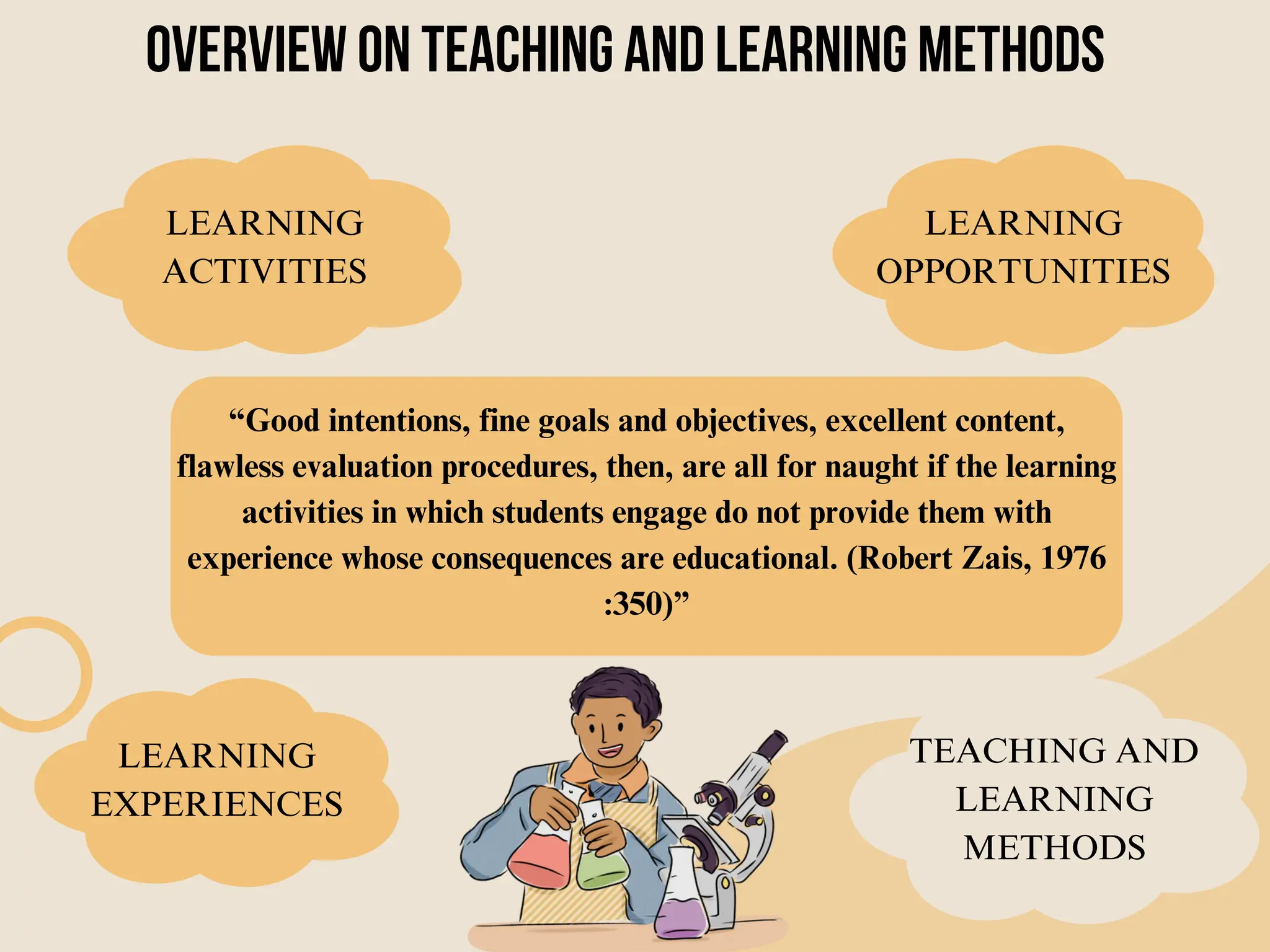
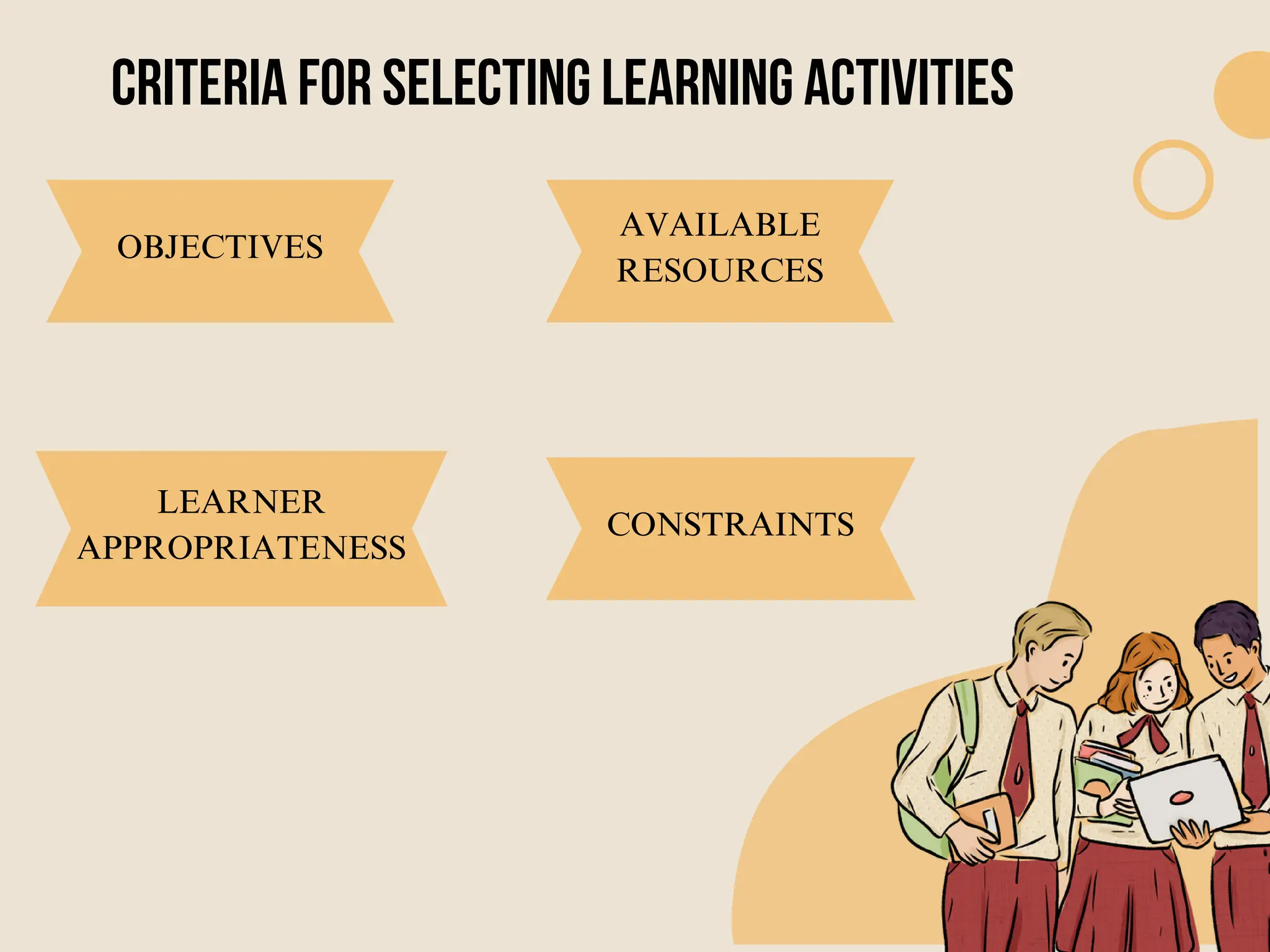
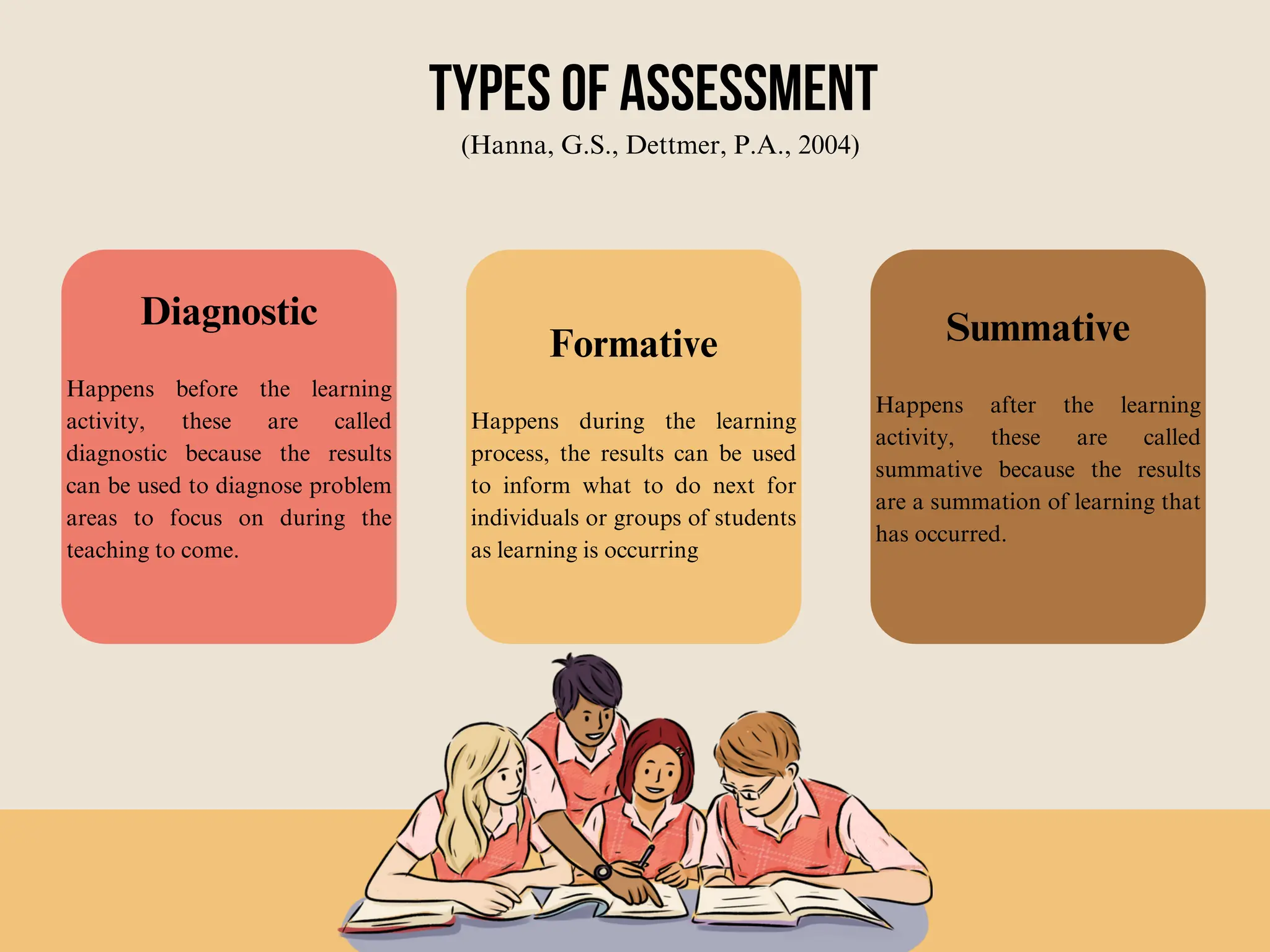
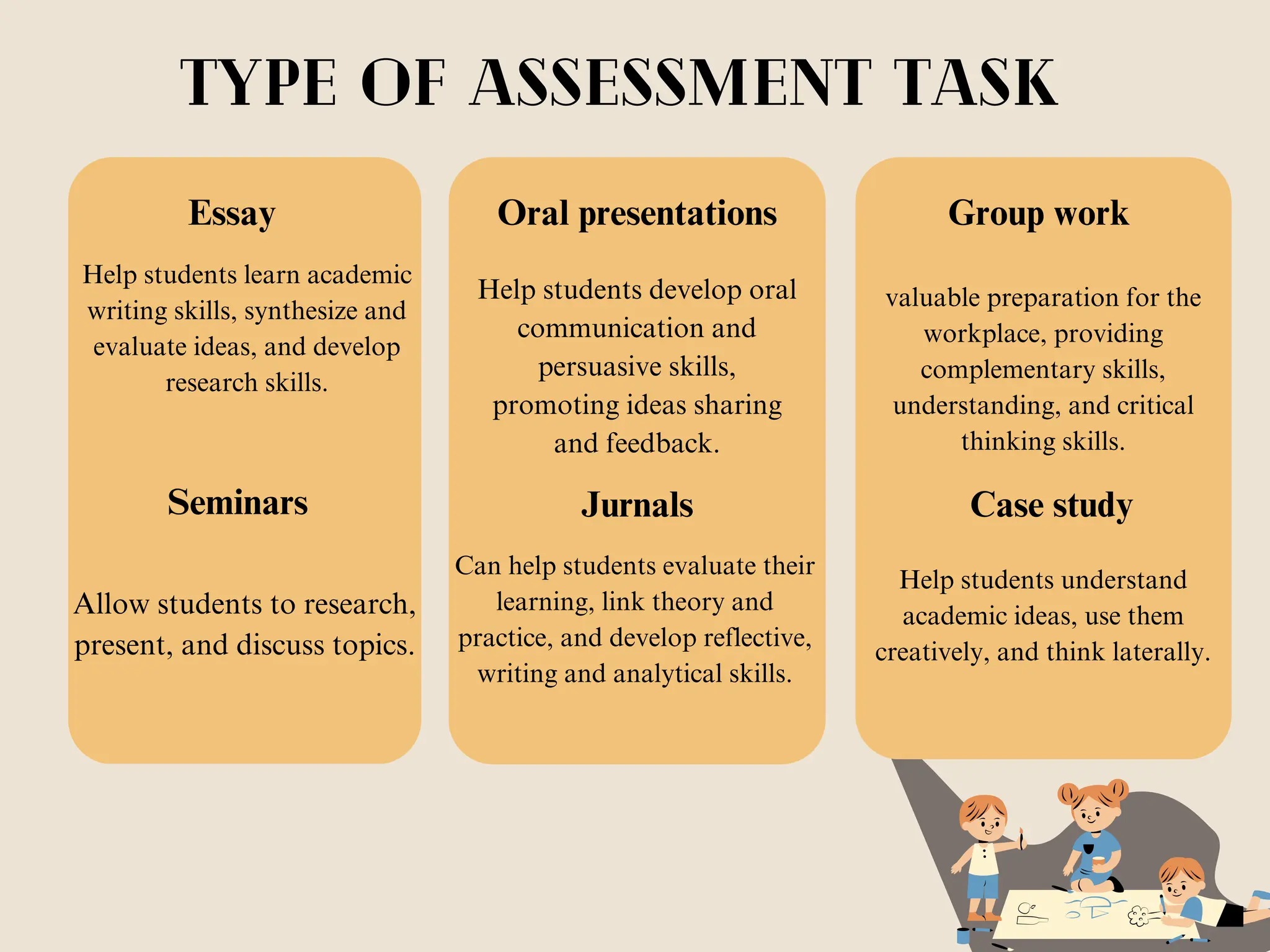
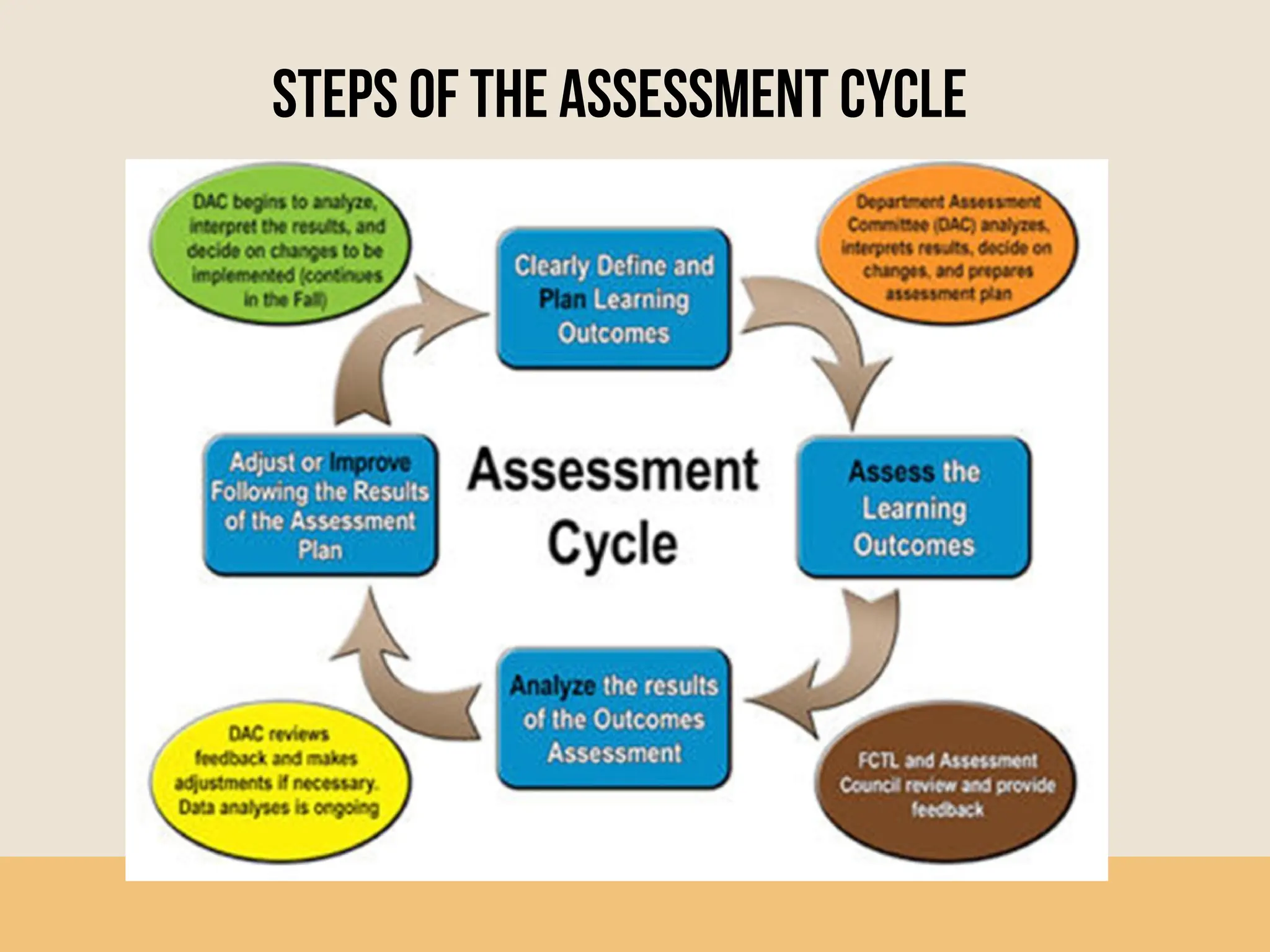
Group Six presented information on determining teaching-learning methods and assessment procedures. They discussed principles of learning, criteria for organizing learning activities, and selecting teaching methods. They also provided an overview of assessment, goals of assessment, types of assessment including diagnostic, formative and summative, and types of assessment tasks such as essays, oral presentations, group work, seminars, journals, and case studies. The group outlined the steps of the assessment cycle and concluded by asking if there were any questions.