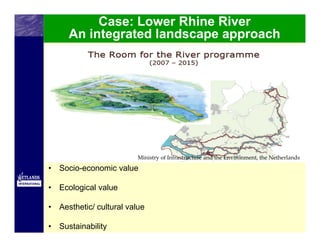
This document discusses opportunities and challenges for richer river environments through ecological restoration. It outlines that river restoration aims to restore natural river functioning and provides ecosystem services. Existing policies like the Water Framework Directive and Habitats Directive support some restoration but it is typically small in scale and focused on specific goals. The document calls for more innovative, landscape-scale restoration that provides multiple benefits and complements water management. It suggests leveraging agricultural policies and developing green infrastructure to advance restoration goals. Challenges include ensuring policy cross-compliance, implementation support through incentives and capacity building, and quantifying costs and benefits.