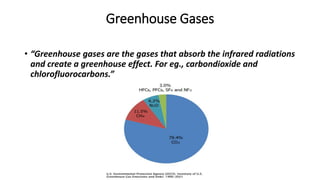
The document explains the greenhouse effect, the process by which greenhouse gases absorb solar radiation, preventing heat escape and warming the Earth's atmosphere, essential for sustaining life. It discusses the causes, including fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and industrial activities, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and lead to global warming and other environmental issues. The document concludes with a call for global collaboration and solutions to address the challenges posed by the greenhouse effect.