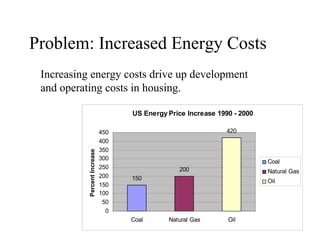
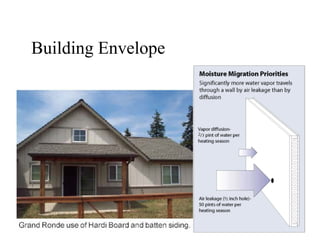
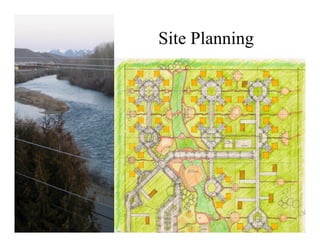
This document summarizes a green building workshop hosted by HUD's Office of Native American Programs. It discusses how green building practices can increase energy and water efficiency, reduce environmental impacts, and improve indoor air quality. Examples of green building strategies presented included energy-efficient appliances and building envelopes, renewable energy systems, sustainable building materials, water conservation, and construction waste management. Data showed that green building approaches can help control rising energy costs and address environmental hazards in existing housing. The workshop provided lessons on applying green development practices and next steps to promote these techniques in HUD programs.