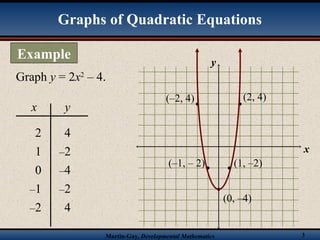
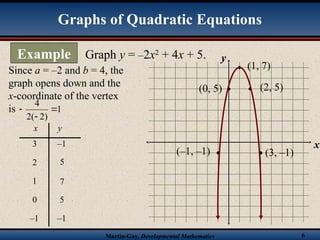
The document explains the process of graphing quadratic equations, focusing on key elements such as the vertex and axis of symmetry. It provides examples for finding x-intercepts and y-intercepts and discusses the characteristics of parabolas based on the coefficients of the standard form equation. The document emphasizes the significance of understanding these concepts in effectively graphing quadratic equations.