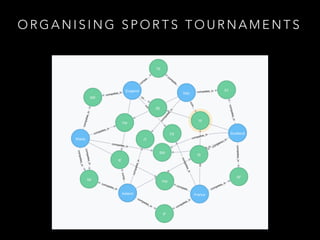
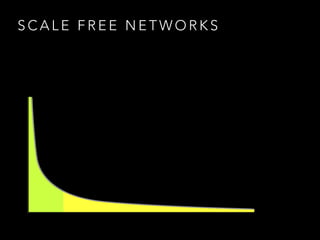
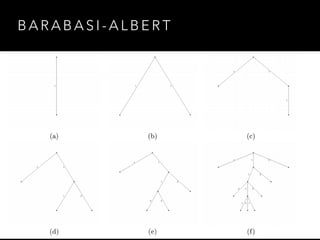
The document discusses the application of graph theory and its practical uses, particularly in data modeling and problem-solving. It highlights various concepts such as graphs, planar graphs, connectivity, spanning trees, and graph coloring, showcasing examples from real-world scenarios such as election data and sports tournament organization. The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding graph theory to leverage data efficiently and use it in various contexts, including the internet and social networks.





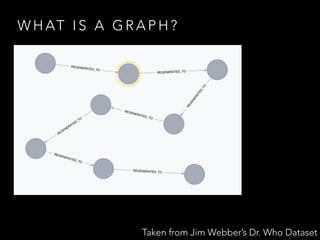
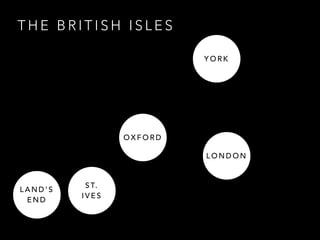
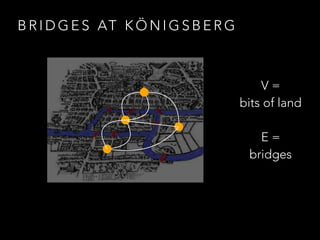
![W H AT I S A G R A P H ?
{ (V, E) : V = [n], E ⊆ V(2) }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryinpractise-150507114349-lva1-app6891/85/Graph-theory-in-Practise-9-320.jpg)
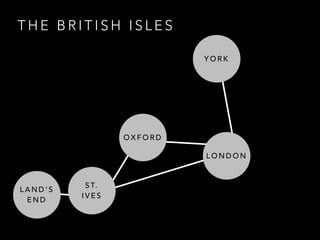
![W H AT I S A G R A P H ?
{ (V, E) : V = [n], E ⊆ V(2) }
Made up of two parts,
“V” and “E”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryinpractise-150507114349-lva1-app6891/85/Graph-theory-in-Practise-10-320.jpg)
![W H AT I S A G R A P H ?
{ (V, E) : V = [n], E ⊆ V(2) }
V is a set of n items](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryinpractise-150507114349-lva1-app6891/85/Graph-theory-in-Practise-11-320.jpg)
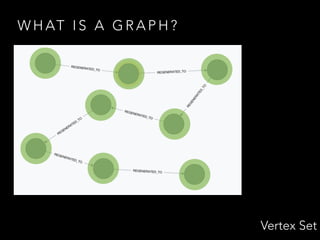
![W H AT I S A G R A P H ?
{ (V, E) : V = [n], E ⊆ V(2) }
E is made up of pairs
of elements of V
(Ordered and
not necessarily distinct)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryinpractise-150507114349-lva1-app6891/85/Graph-theory-in-Practise-13-320.jpg)



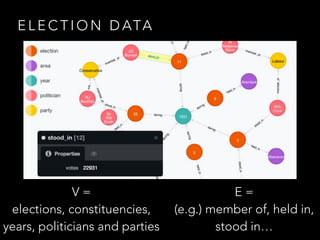




![W H AT I S A G R A P H ?
{ (V, E) : V = [n], E ⊆ V(2) }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphtheoryinpractise-150507114349-lva1-app6891/85/Graph-theory-in-Practise-25-320.jpg)