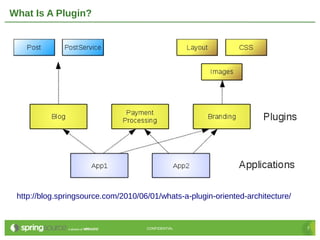
The document discusses plugins in Grails. It covers what a plugin is, the directory structure of plugins, common types of plugins, and implementation details like using the GrailsApplication object, configuring Spring, adding dynamic methods, and reloading on changes. The document is intended to teach plugin developers best practices for creating plugins in Grails.






















![Configuring Spring
class JcrGrailsPlugin {
def version = 0.1 Bean name is method name,
def dependsOn = [core:0.4] first argument is bean class
def doWithSpring = {
jcrRepository(RepositoryFactoryBean) {
configuration = "classpath:repository.xml"
homeDir = "/repo"
}
} Set properties on the bean
}
CONFIDENTIAL 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grailsplugginginburtbeckwith2011-110526034115-phpapp01/85/GR8Conf-2011-Grails-how-to-plug-in-24-320.jpg)






![Adding Elements to web.xml
def doWithWebDescriptor = { xml →
def contextParam = xml.'context-param'
contextParam[contextParam.size() - 1] + {
'filter' {
'filter-name'('springSecurityFilterChain')
'filter-class'(DelegatingFilterProxy.name)
}
}
def filterMapping = xml.'filter-mapping'
filterMapping[filterMapping.size() - 1] + {
'listener' {
'listener-class'(HttpSessionEventPublisher.name)
}
}
}
CONFIDENTIAL 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grailsplugginginburtbeckwith2011-110526034115-phpapp01/85/GR8Conf-2011-Grails-how-to-plug-in-31-320.jpg)
![Dependency Management
Jar files
• Prefer BuildConfig.groovy → Maven repos
• lib directory is ok if unavailable otherwise
Other plugins
• def dependsOn = [springSecurityCore: '1.1 > *']
• def loadAfter = ['controllers']
Grails
• def grailsVersion = '1.2.3 > *'
CONFIDENTIAL 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grailsplugginginburtbeckwith2011-110526034115-phpapp01/85/GR8Conf-2011-Grails-how-to-plug-in-32-320.jpg)








![Scripts
Typical Structure
includeTargets << new File(
"$cloudFoundryPluginDir/scripts/_CfCommon.groovy")
USAGE = '''
grails cf-list-files [path] [--appname] [--instance]
'''
target(cfListFiles: 'Display a directory listing') {
depends cfInit
// implementation of script
}
def someHelperMethod() { … }
setDefaultTarget cfListFiles
CONFIDENTIAL 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grailsplugginginburtbeckwith2011-110526034115-phpapp01/85/GR8Conf-2011-Grails-how-to-plug-in-41-320.jpg)

![Custom Artifacts
class MyGrailsPlugin {
def watchedResources = [
'file:./grails-app/controllerMixins/**/*ControllerMixin.groovy',
'file:./plugins/*/grails-app/controllerMixins/**/*ControllerMixin.groovy'
]
def artefacts = [ControllerMixinArtefactHandler]
def onChange = { event →
...
}
}
CONFIDENTIAL 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grailsplugginginburtbeckwith2011-110526034115-phpapp01/85/GR8Conf-2011-Grails-how-to-plug-in-43-320.jpg)








![Best Practices and Tips
Delete anything auto-generated that you don't use
• grails-app/views/error.gsp
• _Uninstall.groovy and other generated scripts
• Empty descriptor callbacks
Exclude files used in development or testing
• Use def pluginExcludes = [...]
• src/docs
• Test artifacts
Use Ivy + Maven repos in BuildConfig.groovy, not lib dir
CONFIDENTIAL 52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grailsplugginginburtbeckwith2011-110526034115-phpapp01/85/GR8Conf-2011-Grails-how-to-plug-in-52-320.jpg)



