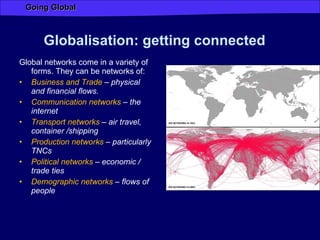
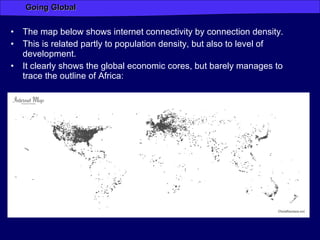
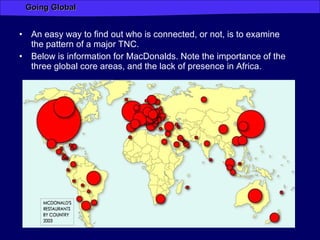
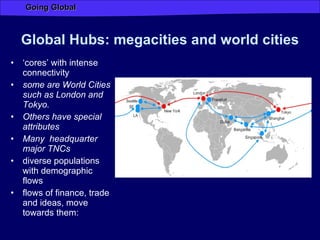
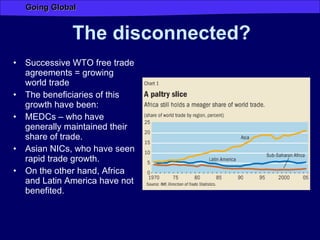
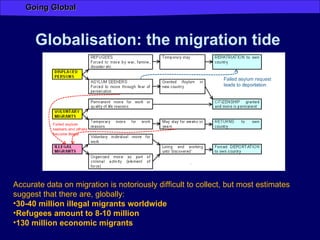
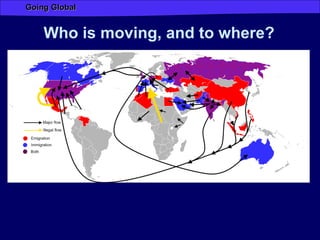
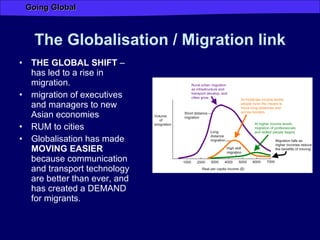
Globalization has increased connectivity worldwide through greater flows of goods, services, capital, technology and people. Key factors driving globalization include improved communication technologies like the internet and satellite networks, as well as reduced transportation costs. While globalization has connected many major cities and regions, some parts of the world like Africa remain less connected with limited participation in global trade and networks. Globalization both enables and results from increased human migration around the world, with many migrants moving to large cities and global hubs with high connectivity.