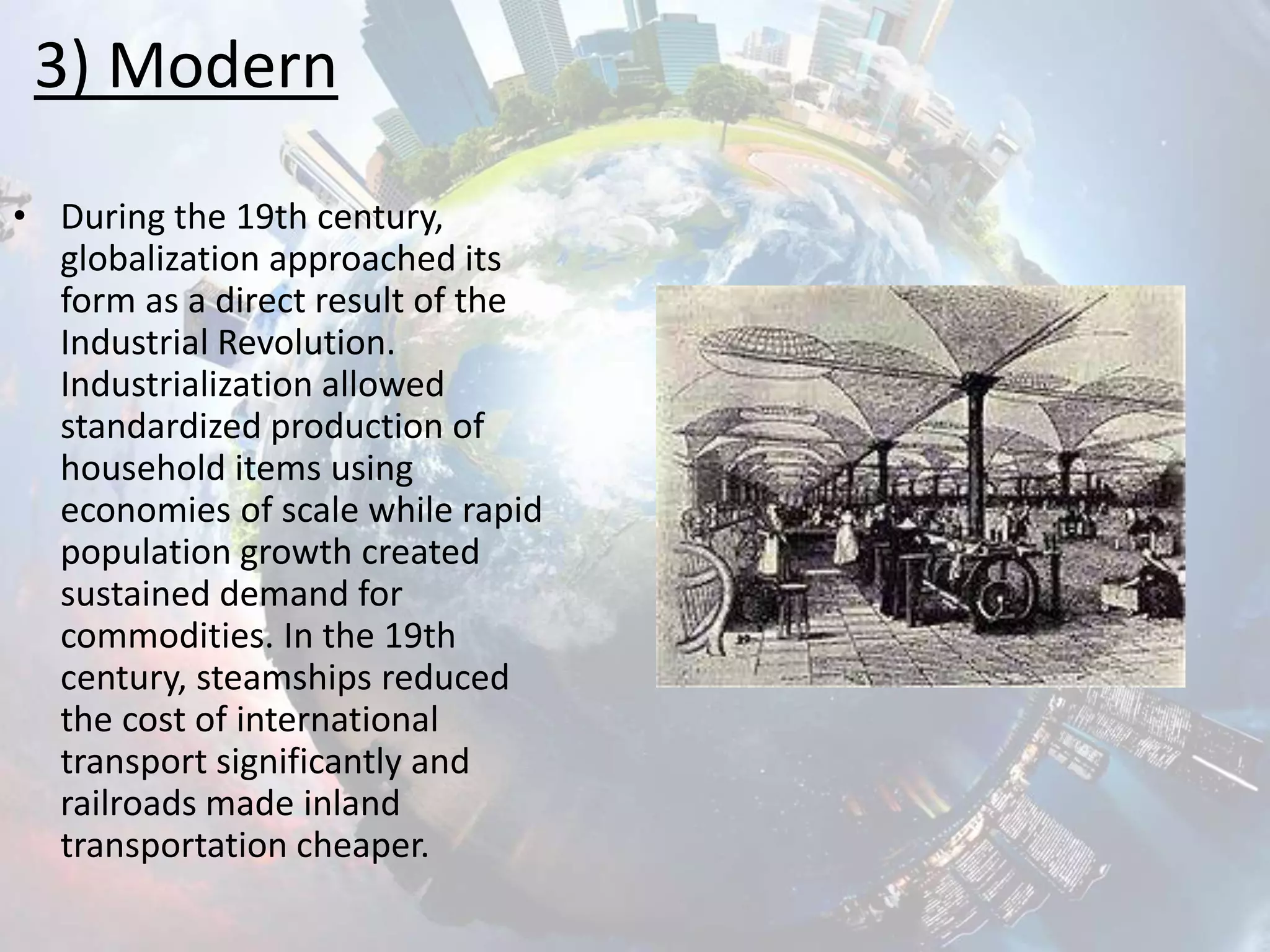
Globalization is the increasing integration and interaction between people, companies, and governments around the world. It began with early human migrations but accelerated in the 19th century due to advances in transportation and communication technology. Globalization can be divided into three historical phases - archaic, early modern, and modern. In the modern era beginning in the 19th century, industrialization, steamships, railroads, and later the internet further drove the increasing flow of goods, capital, and information worldwide and the rise of today's globalized economy.